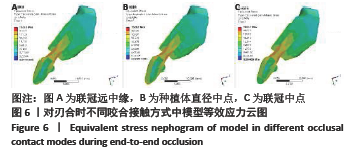
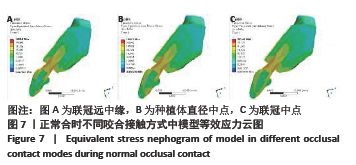
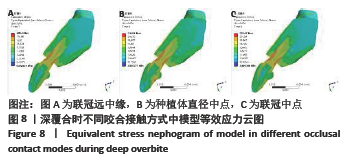
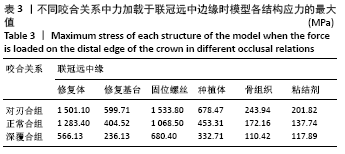
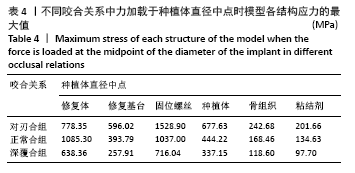
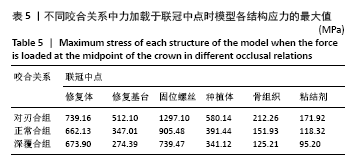
[1] PRADO FB, ROSSI AC, FREIRE AR, et al. The application of finite element analysis in the skull biomechanics and dentistry Indian. J Dent Res. 2014; 253(3): 390-397.
[2] VAN STADEN RC, GUAN H, LOO YC. Application of the finite element method in dental implant research. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2006;9(4): 257-270.
[3] TRIVEDI S. Finite element analysis: A boon to dentistry. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2014;4(3):200-203.
[4] 韩丽会,邱晓霞,邢旭娜,等.上颌前牙区种植方案中角度设计的三维有限元分析[J].上海口腔医学,2015,24(2):157-163.
[5] 王淑英,江青松,蒋向华,等.钛基台支持的CAD/CAM全瓷单冠不同载荷位置的三维有限元应力分析[J].北京口腔医学,2019,27(2):72-75.
[6] 魏玮,张寒,陈梦琦,等.钛材料仿生天然磨牙的三维有限元分析[J].南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2019,39(7):1057-1061.
[7] SHURBAJI MOZAYEK R, ALLAF M, ABUHARB MB. Efficacy of adding a supporting implant in stress distribution of long-span fixed partial dentures: a 3D finite element analysis. J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects. 2016;10(2):81-86.
[8] 雍苓,黄仕禄,刘洪,等.不同骨缺损类型牙种植体的三维有限元分析[J].医用生物力学,2016,31(2):148-153.
[9] HUSSEIN FA, SALLOOMI KN, ABDULRAHMAN BY, et al. Effect of thread depth and implant shape on stress distribution in anterior and posterior regions of mandible bone: A finite element analysis. Dent Res J. 2019;16(3):200-207.
[10] OZAN O, KURTULMUS-YILMAZ S. Biomechanical comparison of different implant inclinations and cantilever lengths in all-on-4 treatment concept by three-dimensional finite element analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2018;33(1):64-71.
[11] DU L, LI Z, CHANG X, et al. Effects of the screw-access hole diameter on the biomechanical behaviors of 4 types of cement-retained implant prosthodontic systems and their surrounding cortical bones: A 3D finite element analysis. Implant Dent. 2018;27(5):555-563.
[12] SHERIDAN RA, DECKER AM, PLONKA AB, et al. The role of occlusion in implant therapy: A comprehensive updated review. Implant Dent. 2016;25(6):829-838.
[13] NIROOMAND MR, ARABBEIKI M. Effect of the dimensions of implant body and thread on bone resorption and stability in trapezoidal threaded dental implants: a sensitivity analysis and optimization. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Eng. 2020;(5):1-9.
[14] JIANG X, YAO Y, TANG W, et al. Design of dental implants at materials level: An overview. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2020;108(8):1634-1661.
[15] ROBERTS SD, KAPADIA H, GREENLEE G, et al. Midfacial and dental changes associated with nasal positive airway pressure in children with obstructive sleep apnea and craniofacial conditions. J Clin Sleep Med. 2016;12(4):469-475.
[16] 罗强,丁茜,张磊,等.后牙种植冠桥修复后局部咬合变化的定量分析[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2019,51(6):1119-1123.
[17] LEE DJ, LEE JM, KIM EJ, et al. Bio-implant as a novel restoration for tooth loss. Sci Rep. 2017; 7(1): 7414.
[18] 甘雪琦,肖宇,马瑞阳,等.种植体的生物力学研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志, 2019,37(2):115-123.
[19] 张永丽.四种不同形状种植体应力分布比较的三维有限元分析[D].济南:山东大学,2003.
[20] 赵宝红,张娇, 蔺增,等.种植体长度与直径对骨界面应力分布影响的三维有限元分析[J].口腔医学,2014,34(1):22-27.
[21] LIU ZY, ZHAO L, YANG LY, et al. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of different endodontic access methods and full crown restoration in the maxillary central incisor. West China Stomatol. 2019;37(6):642-647.
[22] BAYRAK A, YARAMANOLU P, KLARSLAN MA, et al. Biomechanical comparison of a new triple cylindrical implant design and a conventional cylindrical implant design on the mandible by three-dimensional finite element analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2020;35(2):257-264.
[23] KANG X, LI Y, WANG Y, et al. Relationships of stresses on alveolar bone and abutment of dental implant from various bite forces by three-dimensional finite element analysis. BioMed Res Int. 2020;2020(2):1-9.
[24] MORITA J, WADA M, MAMENO T, et al. Ideal placement of an implant considering the positional relationship to an opposing tooth in the first molar region: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. Int J Implant Dent. 2020;6(1):31.
[25] TRIBST JPM, DAL PIVA AMO, BORGES APLS, et al. Does the prosthesis weight matter? 3D finite element analysis of a fixed implant-supported prosthesis at different weights and implant numbers. J Adv Prosthodont. 2020;12(2):67-74.
[26] 连颂峰,林敬凯,蔡坤灿,等.CAD/CAM纯钛烤瓷冠的抗疲劳性与抗折性分析[J].上海口腔医学,2019,28(2):118-122.
[27] AZCARATE-VELÁZQUEZ F, CASTILLO-OYAGÜE R, OLIVEROS-LÓPEZ LG, et al. Influence of bone quality on the mechanical interaction between implant and bone: A finite element analysis. J Dent. 2019;88:103161.
[28] TOIA M, STOCCHERO M, JINNO Y, et al. Effect of misfit at implant-level framework and supporting bone on internal connection implants: Mechanical and finite element analysis[J]. International J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2019; 34(2): 320-328.
[29] 邹英楠,王屹博,丁超,等.动态载荷下双种植体单冠修复下颌磨牙的三维有限元分析[J].口腔医学,2019,39(12):1078-1081+1094.
[30] DELGADO-RUIZ RA, CALVO-GUIRADO JL, ROMANOS GE. Effects of occlusal forces on the peri‐implant‐bone interface stability. Periodontology. 2019;81(1):179-193.
[31] RODRIGUES EDS, BENETTI P, CARLI JP, et al. A Comparison of torque stress on abutment screw of external hexagon and morse taper implant. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2018;19(11):1306-1311.
[32] MANEA A, BACIUT G, BACIUT M, et al. New dental implant with 3D shock absorbers and tooth-like mobility—prototype development, finite element analysis (FEA), and mechanical testing. Materials. 2019;12(20):3444. |