[1] 赵献芝, 白小青, 左福元. 多指(趾)基因研究进展[J]. 上海畜牧兽医通讯,2007,52(1):5-6.
[2] VERMA PK, EL-HAROUNI AA. Review of literature: genes related to postaxial polydactyly. Front Pediatr. 2015;3:8.
[3] ZAIB T, JI W, SALEEM K, et al. A heterozygous duplication variant of the HOXD13 gene caused synpolydactyly type 1 with variable expressivity in a Chinese family. BMC Med Genet. 2019;20(1):203.
[4] PHADKE SR, SANKAR VH. Polydactyly and genes. Indian J Pediatr. 2010; 77(3):277-281.
[5] LETTICE LA, WILLIAMSON I, WILTSHIRE JH, et al. Opposing functions of the ETS factor family Ddefine SHH spatial expression in limb buds and underlie polydactyly. Development Cell. 2012;22(2):459-467.
[6] WANG T, XUAN ZP, DOU YC, et al. Identification of novel mutations in preaxial polydactyly patients through whole-exome sequencing.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019;7(6):e690.
[7] BURGER EB, BAAS M, HOVIUS SER. A Jeannette M Hoogeboom, Christianne A van Nieuwenhoven. Preaxial polydactyly of the foot. Acta Orthop. 2018;89(1):113-118.
[8] RADHAKRISHNA U, BLOUIN JL, MEHENNI H, et al. Mapping one form of autosomal dominant postaxial polydactyly type A to chromosome 7p15-q11.23 by linkage analysis. Am J Hum Genet. 1997;60:597-604.
[9] FURNISS D, CRITCHLEY P, GIELE H, et al. Nonsense-mediated decay and the molecular pathogenesis of mutations in SALL1 and GLI3. Am J Med Genet A. 2007;143(24):3150-3160.
[10] AL-QATTAN MM. A novel frameshift mutation of the GLI3 gene in a family with broad thumbs with/without big toes, postaxial polydactyly and variable syndactyly of the hands/feet. Clin Genet. 2012;82(5):502-504.
[11] CHANDRA SR, DARYAPPA MM , MUDABBIR MAM, et al. Pallister-Hall Syndrome. J Pediatr Neurosci. 2017;12(3):276-279.
[12] WOISCHNIK M, MORAES CT. Pattern of organization of human mitochondrial pseudogenes in the nuclear genome. Genome Res. 2002;12:885-893.
[13] BIESECKER LG, JOHNSTON JJ, ADAM MP, et al. Greig Cephalopolysyndactyly Syndrome. University of Washington. 2020.
[14] PETTIGRE AL, GREENBERG F, CASKEY CT, et al. Greig syndrome associated with an interstitial deletion of 7p: confirmation of the localization of Greig syndrome to 7p13. Hum Genet. 1991;87:452-456.
[15] SUSKE MK, WILD A, TOPP J, et al. Point mutations throughout the GLI3 gene cause Greig cephalopolysyndactyly syndrome. Hum Molec Genet. 1999;8:1769-1777.
[16] UNNI JV, DARYANI D, SREEJAN KC, et al. Greig Cephalopolysyndactyly Syndrome with Oral Manifestations: A Rare Case Report. Int J Appl Basic Med Res. 2020;10(2):140-142.
[17] WANG B, DIAO YT, LIU QJ, et al. An increased duplication of ZRS region that caused more than one supernumerary digits preaxial polydactyly in a large Chinese family. Sci Rep. 2016;6:38500.
[18] ITO S, KITAZAWA R, HARAGUCHI R, et al. Novel GLI3 variant causing overlapped Greig cephalopolysyndactyly syndrome (GCPS) and Pallister-Hall syndrome (PHS) phenotype with agenesis of gallbladder and pancreas. Diagn Pathol. 2018;13(1):1.
[19] AL-QATTAN MM. Zone of polarizing activity regulatory sequence mutations/duplications with preaxial polydactyly and longitudinal preaxial ray deficiency in the phenotype: a review of human cases, animal models, and insights regarding the pathogenesis. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:1573871.
[20] PETIT F, JOURDAIN AS, HOLDER-ESPINASSE M, et al. The disruption of a novel limb cis-regulatory element of SHH is associated with autosomal dominant preaxial polydactyly hypertrichosis. Eur J Hum Genet. 2016; 24(1):37-43.
[21] ROELINK H, AUGSBURGER A, HEEMSKERK J, et al. Floorplate and moyor neuron induction by VHH-1, a vertebrate homolog of hedgehog expressed by the notochord. Cell. 1994;76(4):761-775.
[22] NACU E, GROMBERG E, OLIVEIRA CR, et al. FGF8 and SHH substitute for anterior-posterior tissue interactions to induce limb regeneration. Nature. 2016;533(7603):407-410.
[23] Zúñiga A, Haramis AP, McMahon AP, et al. Signal relay by BMP antagonism controls the SHH/FGF4 feedback loop in vertebrate limb buds. Nature. 1999;401(6753):598-602.
[24] JACQUELINE L, NORRIEA, LEWANDOWSKI JP, et al. Dynamics of BMP signaling in limb bud mesenchyme and polydactyly. Dev Biol. 2014; 393(2):270-281.
[25] LIU ZH, YIN N, GONG LH, et al. Microduplication of 7q36.3 encompassing the SHH long-range regulator(ZRS) in a patient with triphalangeal thumb-polysyndactyly syndrome and congenital heart disease. Mol Med Rep. 2017;15:793-797.
[26] HULLEMAN JD, NGUYEN A, RAMPRASAD VL, et al. A novel H395R mutation in MKKS/BBS6 causes retinitis pigmentosa and polydactyly without other findings of Bardet-Biedl or McKusick-Kaufman ayndrome. Mol Vis. 2016;22:73-81.
[27] OMAIR A, KHAN, MAJEED R, et al. Rarity of laurence moon bardet biedl syndrome and its poor management in the pakistani population. Cureus. 2019;11(2):e4114.
[28] KLEIN S D, NGUYEN D C, BHAKTA V, et al. Mutations in the sonic hedgehog pathway cause macrocephaly-associated conditions due to crosstalk to the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Am J Med Genet A. 2019;179(12):2517-2531.
[29] ZHANG QH, SEO S, BUGGE K, et al. BBS proteins interact genetically with the IFT pathway to influence SHH-related phenotypes. Hum Mol Genet. 2012;21(9):1945-1953.
[30] LOEBEL DA, HOR AC, BILDSOE H, et al. Regionalized TWIST1 activity in the forelimb bud drives the morphogenesis of theproximal and preaxial skeleton. Dev Biol. 2012;362(2):132-140.
[31] Firulli BA, KRAWCHUK D, CENTONZE VE, et al. Altered TWIST1 and HAND2 dimerization is associated with Saethre-Chotzen syndrome and limb abnormalities. Nat Genet. 2005;37(4):373-381.
[32] HIRSCH N, ESHEL R, YAACOV RB, et al. Unraveling the transcriptional regulation of TWIST1 in limb development. PLoS Genet. 2018;14(10): e1007738.
[33] CHEN RZ, CHENG XB, TAN YX, et al. An ENU-induced mutation in TWIST1 transactivation domain causes hindlimb polydactyly with complete penetrance and dominant-negatively impairs E2A-dependent transcription. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):2501.
[34] PELC A, MIKULEWICZ M. Saethre-Chotzen Syndrome: Case report and literature review. Dent Med Probl. 2018;55(2):217-225.
[35] ZHANG Z, SUI PF, DONG AW, et al. Preaxial polydactyly: interactions among ETV, TWIST1 and HAND2 control anterior-posterior patterning of the limb. Development. 2010;137(20):3417-3426.
[36] CARONIA G, GOODMAN FR, MCKEOWN CM, et al. An I47L substitution in the HOXD13 homeodomain causes a novel human limb malformation by producing a selective loss of function. Development. 2003;130(8):1701-1712.
[37] SHETH R, MARCON L, BASTIDA MF, et al. HOX genes regulate digit patterning by controlling the wavelength of a Turing-type mechanism. Science. 2012; 338(6113):1476-1480.
[38] KHERDJEMIL Y, LALONDE RL, SHETH R, et al. Evolution of HOXA11 regulation in vertebrates is linked to the pentadactyl state. Nature. 2016;539(7627): 89-92.
[39] MALIK S, GRZESCHIK KH. Synpolydactyly: clinical and molecular advance. Clin Genet. 2008;73(2):113-120.
[40] ROGERS BH, SCHMIEG SL, PEHNKE ME, et al. Evaluation and management of preaxial polydactyly. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2020;13(4):545-551.
[41] LEX RK, JI ZC, FALKENSTEIN KN, et al. GLI transcriptional repression regulates tissue-specific enhancer activity in response to Hedgehog signaling. Elife. 2020;9:e50670.
[42] RUBINO S, QIAN J, PINHEIRO-NETO CD, et al. A familial syndrome of hypothalamic hamartomas, polydactyly, and SMO mutations: a clinical report of 2 cases. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2018;23(1)98-103.
[43] HARAGUCHI R, KITAZAWA R, KOHARA Y. Recent Insights into Long Bone Development: Central Role of Hedgehog Signaling Pathway in Regulating Growth Plate. INT J Mol Sci. 2019;20(23):5840.
[44] CHEN W, REN XR, NELSON CD, et al. Activity-dependent internalization of smoothened mediated by beta-arrestin 2 and GRK2. Science. 2004; 306:2257-2260.
[45] Verma PK, EL-HAROUNI AA. Review of literature: genes related to postaxial polydactyly. Front Pediatr. 2015;3:8.
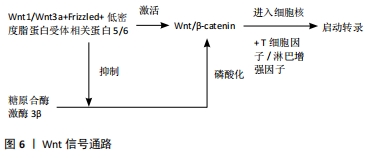
[46] PARRA-TORRES AY, ENRÍQUEZ J, JIMÉNEZ-ORTEGA RF. Expression profiles of the Wnt/β catenin signaling related extracellular antagonists during proliferation and differentiation in human osteoblast like cells. Exp Ther Med. 2020;20(6):254.
[47] TAMAMURA Y, OTANI T, KANATAIN N, et al. Developmental regulation of Wnt/β-catenin signals is required for growth plate assembly, cartilage integrity, and endochondral ossification. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280: 19185-19195.
[48] LOGAN CY, NUSSE R. The Wnt signaling pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2004;20:781-810.
[49] GORDON MD, NUSSE R. Wnt signaling: multiple pathways, multiple receptors, and multiple transcription factors. J Biol Chem. 2006;281: 22429-22433.
[50] MOSIMANN C, HAUSMANN G, BASLER K. β-catenin hits chromatin: regulation of Wnt target gene activation. Nat Rev Mol. Cell Biol. 2009; 10:276-286.
[51] LI X, ZHANG Y , KANG H, et al. Sclerostin binds to LRP5/6 and antagonizes canonical Wnt signaling. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:19883-19887.
[52] LI XH, YANG ST, HAN L, et al. Ciliary IFT80 is essential for intervertebral disc development and maintenance. FASEB. 2020;34(5):6741-6756.
[53] LIU M, ALHARBI M, GRAVES D, et al. IFT80 is required for fracture healing through controlling the regulation of TGFβ signaling in chondrocyte differentiation and function. J Bone Miner Res. 2020;35(3):571-582.
[54] ZHANG CY, ZHANG S, SUN Y. Expression of IFT140 During Bone Development. J Histochem. 2019;67(10):723-734.
[55] LIM J, LI X H, YUAN X, et al. Primary cilia control cell alignment and patterning in bone development via ceramide-PKCζ-β-catenin signaling. Commun Biol. 2020;3(1):45.
[56] HE X. Cilia put a brake on Wnt signalling. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10:11-13.
[57] CHANG CF, SERRA R. Ift88 regulates hedgehog signaling, Sfrp5 expression, and beta-catenin activity in post-natal growth plate. J Orthop Res. 2013; 31(3):350-356.
[58] BIZAOUI V, HUBER C, KOHAUT E, et al. Mutations in IFT80 cause SRPS Type IV. Report of two families and review. Am J Med Genet A. 2019;179(4):639-644.
[59] DENG Q, LI P, CHE MJ, et al. Activation of hedgehog signaling in mesenchymal stem cells induces cartilageand bone tumor formation via Wnt/b-Catenin. Elife. 2019;8:e50208.
[60] WANG Y, ZENG HQ, LIU AM. Distinct Activities of Gli1 and Gli2 in the Absence of Ift88 and the Primary Cilia. J Dev Biol. 2019;7(1):5.
[61] EGGENSCHWILER JT, ANDERSON KV. Cilia and developmental signaling. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2007;23:345-373.
|