[1] GONG C, ZHANG X, SHI M, et al. Tumor exosomes reprogrammed by low pH are efficient targeting vehicles for smart drug deliveryand personalized therapy against their homologous tumor. Adv Sci. 2021. doi:10.1002/advs.202002787.
[2] 杨紫恩,赵继凯,于卉影.间充质干细胞来源外泌体生物学功能及对肿瘤调控作用研究现状[J].临床军医杂志,2020,48(11):1386-1388.
[3] WHITESIDE TL. Exosome and mesenchymal stem cell cross-talk in the tumor microenvironment. Semin Immunol. 2018;35:69-79.
[4] LAZENNEC G, LAM PY. Recent discoveries concerning the tumor-mesenchymal stem cell interactions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016; 1866(2):290-299.
[5] 纪成,费书琴,陈鸣,等.间充质干细胞来源外泌体在肾脏疾病中的研究进展[J].第二军医大学报,2018,39(7):722-725.
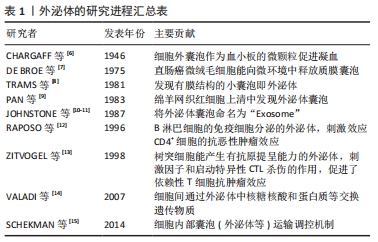
[6] CHARGAFF E, WEST R. The biological signifi cance of the thromboplastic protein of blood. J Biol Chem. 1946;166(1):189-197.
[7] DE BROE M, WIEME R, ROELS F. Leteer: Mem brane fragments with koinozymic properties released from villous adenoma of the rectum. Lancet. 1975;2(7946):1214-1215.
[8] TRAMS EG, LAUTER CJ, SALEM N JR, et al. Exfoliation of membrane ecto-enzymes in the form of micro-vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981;645:63-70.
[9] PAN BT, JOHNSTONE RM. Fate ofthe transferrin receptor during maturation of sheep reticuIocytes in vitro:selective externalization of the receptor. Cell. 1983;33(31):967-978.
[10] JOHNSTONE RM, ADAM M, HAMMONDJ R, et al. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J Biol Chem. 1987;262: 9412-9420.
[11] MATHIVANAN S, FAHNER CJ, REIDG E, et al. ExoCarta 2012:database of exosomal proteins, RNA and lipids. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40(Database issue):D1241-1244.
[12] RAPOSO G, NIJMAN HW, STOORVOGEL W, et al. B lymphocytes secrete anti-gen-presenting vesicles. J Exp Med. 1996;183(3):1161.
[13] ZITVOGEL L, REGNAULT A, LOZIER A, et al. Eradication of estab lished murine tumors using a novel cell-free vaccine: dendritic cell-derived exosomes. Nat Med. 1998;4(5):594-600.
[14] VALADI H, EKSTRÖM K, BOSSIOS A, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(6):654-659.
[15] SCHEKMAN R, SÜDHOF T. An interview with Randy Schekman and Thomas Südhof. Trends Cell Biol. 2014;24(1):6-8.
[16] AlENQUER M, AMORIM MJ. Exosome biogenesis, regulation, and function in viral infection. Viruses. 2015;7(9):5066-5083.
[17] VANNIEL G, D’ANGELO G, RAPOSO G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19(4):213-228.
[18] SADRI NAHAND J, BOKHARAEI-SALIM F, KARIMZADEH M, et al. MicroRNAs and exosomes: key players in HIV pathogenesis. HIV Med. 2020;21(4):246-278.
[19] LI X, LI Z. Effects of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on co-cultured ovarian carcinoma cells. Microsc Res Tech. 2019;82(6):898-902.
[20] EL ANDALOUSSI S, LAKHAL S, MÄGER I, et al. Exosomes for targeted siRNA delivery across biological barriers. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013;65(3):391-397.
[21] COOPER JM, WIKLANDER PO, NORDIN JZ, et al. Systemic exosomalsiRNA delivery reducedalpha-synuclein aggregates in brains of transgenic mice. Mov Disord. 2014;29(12):1476-1485.
[22] 严冰浩.人间充质干细胞的增殖调控机制及体外扩增技术的优化策略研究[D].上海:第二军医大学,2016:1-71.
[23] KANG L, WONG DK, HONG KY, et al. Cushioned–density gradient ultracentrifugation (c-dguc): a refined and high performance method for the isolation, characterization, and use of exosomes. Methods MolBiol. 2018;1740:69-83.
[24] MORRISON SJ, SCADDEN DT. The bone marrow niche for haematopoietic stem cells. Nature. 2014;505:327-334.
[25] DORON B, HANDU M, KURRE P. Concise review: adaptation of the bone marrow stroma in hematopoietic malignancies: current concepts and models. Stem Cells. 2018;36(3):304-312.
[26] WHITES TL. Exosome and mesenchymal stem cell cross-talk in the tumor microenvironment. Semin Immunol. 2018;35:69-79.
[27] CORRADO C, RAIMONDO S, SAIEVA L, et al. Exosome-mediated crosstalk between chronic myelogenous leukemia cells and human bone marrow stromal cells triggers an Interleukin 8-dependent survival of leukemia cells. Cancer Lett. 2014;348(1):71-76.
[28] SHOJAEI S, HASHEMI SM, GHANBARIAN H, et al. Effect of mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes on tumor microenvironment: tumor progression versus tumor suppression. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(4):3394-3409.
[29] KONOPLEVA M, KONOPLEV S, HU W, et al. Stromal cells prevent apoptosis of AML cells by upregulation of anti-apoptotic proteins. Leukemia. 2002;16(9):1713-1724.
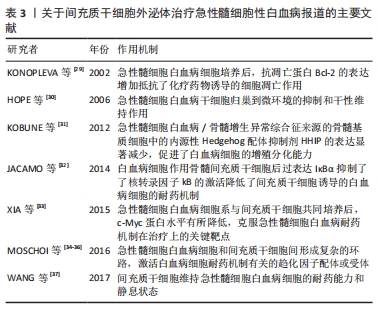
[30] HOPE KJ, JIN L, SMADJA-JOFFE F, et al. Targeting of CD44 eradicates human acute myeloid leukemic stem cells. Nat Med. 2006;12(10):1167-1174.
[31] KOBUNE M, IYAMA S, KIKUCHI S, et al. Stromal cells expressing hedgehog-interacting protein regulate the proliferation of myeloidneoplasms. Blood Cancer J. 2012;2(9):e87.
[32] JACAMO R, CHEN Y, WANG Z, et al. Reciprocal leukemia-stroma VCAM-1/VLA-4-dependent activation of NF-kappaB mediates chemoresistance. Blood. 2014;123(17):2691-2702.
[33] XIA B, TIAN C, GUO S, et al. c-Myc plays part in drug resistance mediated by bone marrow stromal cells in acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk Res. 2015;39(1):92-99.
[34] MOSCHOI R, IMBERT V, NEBOUT M, et al. Protective mitochondrial transfer from bone marrow stromal cells to acute myeloid leukemic cells during chemotherapy. Blood. 2016;128(2):253-264.
[35] CARTER BZ, MAKP Y, CHEN Y, et al. Anti-apoptotic ARC protein confers chemoresistance by controllingleukemia-microenvironment interactions through a NFkappaB/IL1beta signaling network. Oncotarget. 2016;7(15):20054-20067.
[36] LEE M W, RYU S, KIM DS, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells in suppression or progression of hema-tologic malignancy: current status and challenges. Leukemia. 2019;33(3):597-611.
[37] WANG W, BOCHTLER T, WUCHTER P, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells contribute to quiescence of therapy‐resistant leukemic cells in acute myeloid leukemia. Eur J Haematol. 2017;99(5):392-398.
[38] CAIVANO A, DEL VECCHIO L, MUSTO P. Do we need to distinguish exosomes from microvesicles in hematological malignancies? Leukemia. 2017;31(9):2009-2010.
[39] THOMPSON PA, KANTARJIAN HM, CORTES JE. Diagnosis and treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia in 2015. Mayo Clin Proc. 2015;90:1440-1454.
[40] WOHRER S, RABITSCH W, SHEHATA M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells in patients with chronic myelogenousleukaemia or bi-phenotypic Ph+ acute leukaemia are not related to the leukaemic clone. Anticancer Res. 2007;27:3837-3841.
[41] JOOTAR S, PORNPRASERTSUD N, PETVISES S, et al. Bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells from chronic myeloid leukemia t(9;22) patients are devoid of Philadelphia chromosome and support cord blood stem cell expansion. Leuk Res. 2006;30:1493-1498.
[42] ZHAO Z, TANG X, YOU Y, et al. Assessment of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell biological characteristics and support hemotopoiesis function in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia. Leuk Res. 2006;30:993-1003.
[43] 陈莹.抑制RAB27B重启急性髓系白血病干细胞衰老并阻止其诱导骨髓间充质细胞衰老的研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2019.
[44] PARAGUASSFI-BRAGA FH, BOROJEVIC R, BOUZAS LF, et a1. Bone marrow stroma inhibits proliferation and apoptosis in leukemic cells through gap junction-mediated cell communication. Cell Death Differ. 2003;10(9):
1101-1108.
[45] 付相建,陈幸华.急性白血病骨髓基质细胞体外培养的生长特性及细胞外基质的检测[J].西南军医,2006,8(1):28-30.
[46] WANG L, FORTNEY JE, GIBSON LE. Stromal cell protection of B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemic cells during chemotherapy requires active Akt. Leuk Res. 2004;28(7):733-742.
[47] JIN L, TABE Y, KONOPLEV S, et a1. CXCR4 up-regulation by imatinib induces chronic myelogenous leukemia(CML)cell migration to bone marrow stroma and promotes survival ofquiescent CML cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008;7(1):
48-58.
[48] PAGGETTI J, HADERK F, SEIFFERT M, et al. Exosomes released bychronic lymphocytic leukemia cells induce the transition ofstromal cells into cancer-associated fibroblasts. Blood. 2015;126(9):1106-1117.
[49] CROMPOT E, VAN DAMME M, PIETERS K, et al. Extracellular vesicles of bone marrow stromal cells rescue chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells from apoptosis, enhance their migration and induce gene expression modifications. Haematologica. 2017;102(9):1594-1604.
[50] MA F. Exosomes from mesenchymal stromal cells enhance imatinib-induced apoptosis in human leukemia cells via activation of caspase signaling pathway. Cytotherapy. 2018;20(2):181-188.
[51] ROCCARO AM , SACCO A, MAISO P, et al. BM mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes facilitate multiple myeloma progression. J Clin Invest. 2013;123(4):1542-1555.
[52] UMEZUT, IMANISHI S, AZUMA K, et al. Replenishing exosomesfrom older bone marrow stromal cells with miR-340 inhibits myeloma-related angiogenesis. Blood Adv. 2017;1(13):812-823.
[53] BATTH IS, MITRA A, MANIER S, et al. Circulating tumor markers: harmonizing the yin and yang of CTCs and ctDNA for precision medicine. Ann Oncol. 2017;1;28(3):468-477.
[54] 程琳,许天敏.间充质干细胞源性外泌体及其在肿瘤治疗中的研究进展[J].现代肿瘤医学,2016,24(15):2470-2473.
[55] 李嘉,王智慧,吴迪,等.间充质干细胞源性外泌体在骨科疾病治疗中的作用与应用前景[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(25):4068-4072.
[56] EDWIN J, BUNGGULAWA, WANG W, et al. Recent advancements in the use of exosomes as drug deIivery systems. J Nanobiotechnol. 2018;16(1):81.
[57] 缪着,卢福琼,马波,等.人间充质干细胞外泌体研究进展[J].中国医药生物技术,2019,14(4):361-365.
[58] BELUN G, GARDlN C, FERRONl L, et al. Exosome in cardiovascular diseases: a complex world full of hope. Cells. 2019;8(2):166.
[59] MA CH, WU CH, JOU IM, et al. PKR promotes oxidative stress and apoptosis of human articular chondrocytes by causing mitochondrial dysfunction through p38, ARK activation-PLR activation causes apoptosis in human chondrocytes. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019;8(9):2201-2209.
|