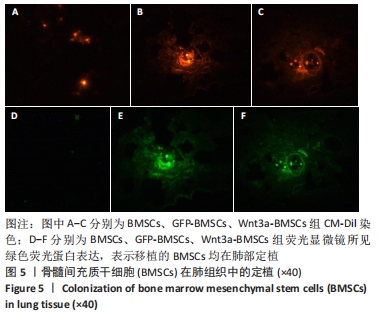
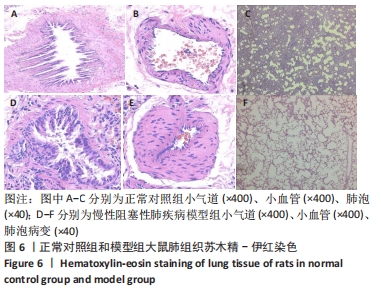
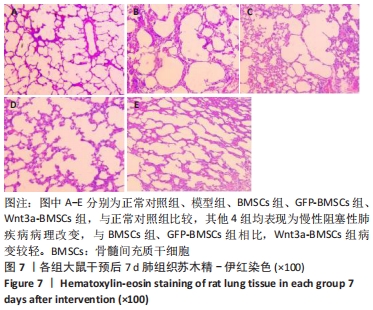
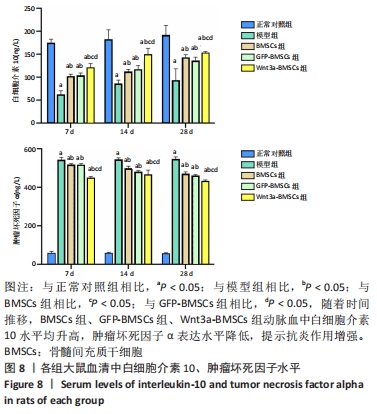
[1] REGAN EA, LYNCH DA, CURRAN-EVERETT D, et al. Clinical and Radiologic Disease in Smokers With Normal Spirometry. JAMA Intern Med. 2015;175(9):1539-1549.
[2] PIERÓG J, FYTIANOS K, TAMÒ L, et al. Stem cell secretome attenuates acute rejection in rat lung allotransplant. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2019;28(5):812-818.
[3] CAHILL EF, TOBIN LM, CARTY F, et al. Jagged-1 is required for the expansion of CD4+ CD25+ FoxP3+ regulatory T cells and tolerogenic dendritic cells by murine mesenchymal stromal cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6(1):19.
[4] WANG K, LI Y, ZHU T, et al. Overexpression of c-Met in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improves their effectiveness in homing and repair of acute liver failure. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):162.
[5] CHEN X, ZHANG Y, WANG W, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Modified with Heme Oxygenase-1 Have Enhanced Paracrine Function and Attenuate Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory and Oxidative Damage in Pulmonary Microvascular Endothelial Cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;49(1):101-122.
[6] PIERÓG J, TAMO L, FAKIN R, et al. Bone marrow stem cells modified with human interleukin 10 attenuate acute rejection in rat lung allotransplantation. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2018;53(1):194-200.
[7] KENNELLY H, MAHON BP, ENGLISH K. Human mesenchymal stromal cells exert HGF dependent cytoprotective effects in a human relevant pre-clinical model of COPD. Sci Rep. 2016;6:38207.
[8] CURLEY GF, HAYES M, ANSARI B, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells enhance recovery and repair following ventilator-induced lung injury in the rat. Thorax. 2012;67(6): 496-501.
[9] SHI Y, HU G, SU J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells: a new strategy for immunosuppression and tissue repair. Cell Res. 2010;20(5):510-518.
[10] YANG J, JIA Z. Cell-based therapy in lung regenerative medicine. Regen Med Res. 2014;2(1):7.
[11] LIU AR, LIU L, CHEN S, et al. Activation of canonical wnt pathway promotes differentiation of mouse bone marrow-derived MSCs into type II alveolar epithelial cells, confers resistance to oxidative stress, and promotes their migration to injured lung tissue in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 2013;228(6):1270-1283.
[12] HOLLAND JD, KLAUS A, GARRATT AN, et al. Wnt signaling in stem and cancer stem cells. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2013;25(2):254-264.
[13] FALCONI G, FABIANI E, FIANCHI L, et al. Impairment of PI3K/AKT and WNT/β-catenin pathways in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells isolated from patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Exp Hematol. 2016;44(1):75-83.e1-4.
[14] 吴华拉,周湘乡,钟玉兰,等. 碱性成纤维细胞生长因子转染骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗慢性阻塞性肺疾病的作用及机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2019, 23(21):3378-3385.
[15] CHANG C, GUO Z, SHEN N, et al. Dynamics of inflammation resolution and symptom recovery during AECOPD treatment. Sci Rep. 2014;4:5516.
[16] RABE KF, WATZ H. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lancet. 2017;389 (10082):1931-1940.
[17] CHEN M, HUANG Z, BI H, et al. Effects of bone marrow‑derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease/obstructive sleep apnea overlap syndrome in rats. Mol Med Rep. 2019;20(5):4665-4673.
[18] LI X, XU J, LI P. Rat bone mesenchymal stem cells exert antiproliferative effects on nicotine‑exposed T cells via iNOS production. Mol Med Rep. 2020;21(5):2267-2275.
[19] NAJAR M, BOUHTIT F, MELKI R, et al. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Based Therapy: New Perspectives and Challenges. J Clin Med. 2019;8(5):626.
[20] BLÁZQUEZ R, SÁNCHEZ-MARGALLO FM, ÁLVAREZ V, et al. Surgical meshes coated with mesenchymal stem cells provide an anti-inflammatory environment by a M2 macrophage polarization. Acta Biomater. 2016;31:221-230.
[21] LI Q, CHEN X, LI J. Marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells regulate the inflammatory response and repair alveolar type II epithelial cells in acute lung injury of rats. J Int Med Res. 2020;48(4):300060520909027.
[22] LI X, AN G, WANG Y, et al. Targeted migration of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells inhibits silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):335.
[23] TANG Y, CAI QH, WANG YJ, et al. Protective effect of autophagy on endoplasmic reticulum stress induced apoptosis of alveolar epithelial cells in rat models of COPD. Biosci Rep. 2017;37(6):BSR20170803.
[24] GENG L, CHEN Z, REN H, et al. Effects of an early intervention using human amniotic epithelial cells in a COPD rat model. Pathol Res Pract. 2016;212(11): 1027-1033.
[25] STEINHART Z, ANGERS S. Wnt signaling in development and tissue homeostasis. Development. 2018;145(11):dev146589.
[26] CAI SX, LIU AR, HE HL, et al. Stable genetic alterations of β-catenin and ROR2 regulate the Wnt pathway, affect the fate of MSCs. J Cell Physiol. 2014;229(6): 791-800.
[27] CAI SX, LIU AR, CHEN S, et al. Activation of Wnt/β-catenin signalling promotes mesenchymal stem cells to repair injured alveolar epithelium induced by lipopolysaccharide in mice. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6(1):65.
[28] PHINNEY DG, PITTENGER MF. Concise Review: MSC-Derived Exosomes for Cell-Free Therapy. Stem Cells. 2017;35(4):851-858.
[29] 钟玉兰,淦鑫.间充质干细胞源外泌体在肺部疾病中的应用与作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(13):2121-2126.
[30] ALIOTTA JM, PEREIRA M, WEN S, et al. Exosomes induce and reverse monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in mice. Cardiovasc Res. 2016; 110(3):319-330.
[31] MACHIN M, AMARAL AF, WIELSCHER M, et al. Systematic review of lung function and COPD with peripheral blood DNA methylation in population based studies. BMC Pulm Med. 2017;17(1):54.
[32] MALAVIYA R, LASKIN JD, LASKIN DL. Anti-TNFalpha therapy in inflammatory lung diseases. Pharmacol Ther. 2017;180:90-98.
[33] YAO Y, ZHOU J, DIAO X, et al. Association between tumor necrosis factor-alpha and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2019;13:1753466619866096.
[34] DOLGACHEV VA, YU B, SUN L, et al. Interleukin 10 overexpression alters survival in the setting of gram-negative pneumonia following lung contusion. Shock. 2014; 41(4):301-310.
[35] YAGI H, SOTO-GUTIERREZ A, PAREKKADAN B, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells: Mechanisms of immunomodulation and homing. Cell Transplant. 2010;19(6): 667-679.
[36] PEDROSA M, GOMES J, LARANJEIRA P, et al. Immunomodulatory effect of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal/stem cells on peripheral blood T cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2020;14(1):16-28.
[37] HE QQ, HE X, WANG YP, et al. Transplantation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) improves brain ischemia-induced pulmonary injury in rats associated to TNF-α expression. Behav Brain Funct. 2016;12(1):9.
[38] ZHU H, XIONG Y, XIA Y, et al. Therapeutic Effects of Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Acute Lung Injury Mice. Sci Rep. 2017;7:39889.
|