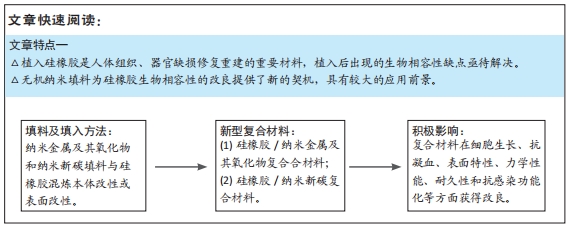
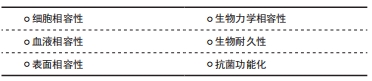
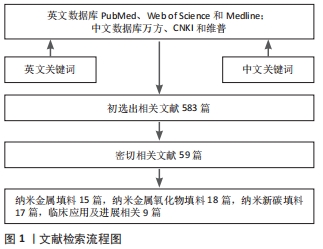
[1] PAINTINDIA GROUP.Silicone market worth 20.3 billion USD by 2020. Paintindia. 2015;65(10):1.
[2] CIFTER ED, OZDEMIR-KARATAS M, CINARLI A, et al. In vitro study of effects of aging and processing conditions on colour change in maxillofacial silicone elastomers. BMC Oral Health. 2019;19(1):122-126.
[3] FLEMING D, STONE J, TANSLEY P. Spontaneous Regression and Resolution of Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma: Implications for Research, Diagnosis and Clinical Management. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2018;42(3):672-678.
[4] ZARE Y, SHABANI I. Polymer/metal nanocomposites for biomedical applications. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;60(2):195-203.
[5] SHAFEY AME. Green synthesis of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles from plant leaf extracts and their applications: A review. Green Process Synth. 2020;9(1):304-339.
[6] MOHAMMADINEJAD R, MOOSAVI MA, TAVAKOL S, et al. Necrotic, apoptotic and autophagic cell fates triggered by nanoparticles. Autophagy. 2019;15(1):4-33.
[7] NIKOLOVA MP, CHAVALI MS. Metal Oxide Nanoparticles as Biomedical Materials. Biomimetics (Basel). 2020;5(2):27-48.
[8] KRÓL A, POMASTOWSKI P, RAFIŃSKA K, et al. Zinc oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, antiseptic activity and toxicity mechanism. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2017;249(1):37-52.
[9] CABAL B, SEVILLANO D, FERNÁNDEZ-GARCÍA E, et al. Bactericidal ZnO glass-filled thermoplastic polyurethane and polydimethyl siloxane composites to inhibit biofilm-associated infections. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):2762.
[10] Sankar GG, Murthy PS, Das A, et al. Polydimethyl siloxane based nanocomposites with antibiofilm properties for biomedical applications. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2017;105(5):1075-1082.
[11] 李翔,陈瑶,周鑫.碳,银和氮离子注入硅橡胶对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞生物学行为的影响[J].第三军医大学学报,2018,40(23): 2162-2167,2189.
[12] BOUDOT C, KÜHN M, KÜHN-KAUFFELDT M, et al. Vacuum arc plasma deposition of thin titanium dioxide films on silicone elastomer as a functional coating for medical applications. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;74(3):508-514.
[13] AGARWAL H, NAKARA A, SHANMUGAM VK. Anti-inflammatory mechanism of various metal and metal oxide nanoparticles synthesized using plant extracts: A review. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;109(10):2561-2572.
[14] KOVACH KM, CAPADONA JR, GUPTA AS, et al. The effects of PEG-based surface modification of PDMS microchannels on long-term hemocompatibility. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014;102(12):4195-4205.
[15] 阎国钢,吴幸,林尤仕,等. 硅橡胶纳米铁显影复合材料体外血液相容性研究[J].海南医学院学报,2014,20(3):324-327.
[16] KHAN I, VISHWAKARMA SK, KHAN AA, et al. In vitro hemocompatability evaluation of gold nanoparticles capped with Lactobacillus plantarum derived lipase1. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2018;69(1-2):197-205.
[17] CHENG C, LIU C, HAN B, et al. Silver Nanoparticles Modified with Sodium Triphosphate: Antibacterial Activity, Hemocompatibility and Cytotoxicity. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2018;18(6):3816-3824.
[18] MENDONÇA MUNHOZ A, SANTANELLI DI POMPEO F, DE MEZERVILLE R. Nanotechnology, nanosurfaces and silicone gel breast implants: current aspects. Case Reports Plast Surg Hand Surg. 2017;4(1):99-113.
[19] MONIKA B, MACIEJ K. Aging resistant TiO2/silicone rubber composites. Compos Sci Technol. 2018;164(18):74-81.
[20] ZHANG K, HAN QY, LIU C, et al. Superhydrophobic and Superparamagnetic Composite Coatings: A Comparative Study on Dual-Sized Functional Magnetite Nanoparticles/Silicone Rubber. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater. 2017;27(6):1816-1825.
[21] ZHANG Y, FEYERABEND F, TANG S, et al. A study of degradation resistance and cytocompatibility of super-hydrophobic coating on magnesium. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;78(3):405-412.
[22] ze w, wen-sheng t, ye x, et al. Preparation of anticoagulant PyC biomaterials with super-hydrophobic surface. J Appl Biomater Funct Mater. 2018;16(1_suppl):125-131.
[23] KIM CY, XU LX, LEE EH, et al. Magnetic Silicone Composites with Uniform Nanoparticle Dispersion as a Biomedical Stent Coating for Hyperthermia. Adv Polym Tech. 2013;32(S1):714-723.
[24] SCHULTE C, PODESTÀ A, LENARDI C, et al. Quantitative Control of Protein and Cell Interaction with Nanostructured Surfaces by Cluster Assembling. Acc Chem Res. 2017;21;50(2):231-239.
[25] BENDO DEMÉTRIO K, GIOTTI CIOATO MJ, MORESCHI A, et al. Polydimethylsiloxane/nano calcium phosphate composite tracheal stents: Mechanical and physiological properties. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2019;107(3):545-553.
[26] SONNAHALLI NK, CHOWDHARY R. Effect of adding silver nanoparticle on physical and mechanical properties of maxillofacial silicone elastomer material-an in-vitro study. J Prosthodont Res. 2020;64(4): 431-435.
[27] BARMAN A, RASHID F, FAROOK TH, et al. The Influence of Filler Particles on the Mechanical Properties of Maxillofacial Prosthetic Silicone Elastomers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Polymers (Basel). 2020;12(7):E1536.
[28] OU G, THAKAR D, TUNG JC, et al. Visualizing mechanical modulation of nanoscale organization of cell-matrix adhesions. Integr Biol (Camb). 2016;8(7):795-804.
[29] CHEN TA, MERCADO CL, TOPPING KL, et al. Disseminated silicone granulomatosis in the face and orbit. Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep. 2018; 10(1):32-34.
[30] FUSCONI M, TADDEI AR, GALLO A, et al. Degradation of silicone rubber causes Provox 2 voice prosthesis malfunctioning. J Voice. 2014;28(2): 250-254.
[31] WANG L, LIU Q, JING D, et al. Biomechanical properties of nano-TiO(2) addition to a medical silicone elastomer: the effect of artificial ageing. J Dent. 2014;42(4):475-483.
[32] PLATT SM, IEZZI R, MAHR MA, et al. Surgical removal of dystrophic calcification on a silicone intraocular lens in association with asteroid hyalosis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2017;43(12):1608-1610.
[33] Washer LL, Gutowski K. Breast implant infections. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2012;26(1):111-125.
[34] LIAO C, LI Y, TJONG SC. Bactericidal and Cytotoxic Properties of Silver Nanoparticles. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(2):449-459.
[35] Morris D, Ansar M, Speshock J, et al. Antiviral and Immunomodulatory Activity of Silver Nanoparticles in Experimental RSV Infection. Viruses. 2019;11(8):732.
[36] LARA HH, IXTEPAN-TURRENT L, JOSE YACAMAN M, et al. Inhibition of Candida auris Biofilm Formation on Medical and Environmental Surfaces by Silver Nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020; 12(19):21183-21191.
[37] MOUSTAFA MA, MOSSALEM HS, SARHAN RM, et al. The potential effects of silver and gold nanoparticles as molluscicides and cercaricides on Schistosoma mansoni. Parasitol Res. 2018;117(12):3867-3880.
[38] BHARGAVA A, PAREEK V, ROY CHOUDHURY S, et al. Superior Bactericidal Efficacy of Fucose-Functionalized Silver Nanoparticles against Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 and Prevention of Its Colonization on Urinary Catheters. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018; 10(35):29325-29337.
[39] Vlsan MN, Snmez M, Georgescu M. Antibacterial Nanocompound Based on Silicone Rubber. Part I – Obtaining and Characterisation . Leather & Footwear J. 2017;17(1):39-44.
[40] KHEIRI S, MOHAMED MGA, AMEREH M, et al. Antibacterial efficiency assessment of polymer-nanoparticle composites using a high-throughput microfluidic platform. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;111(6):110754.
[41] WANG D, LIN Z, WANG T, et al. Where does the toxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles come from: The nanoparticles, the ions, or a combination of both?. J Hazard Mater. 2016,308(2):328-334.
[42] KIM KK, KIM SM, LEE YH. Chemically Conjugated Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene for Carrier Modulation. Acc Chem Res. 2016;49(3):390-399.
[43] BHATTACHARYA K, MUKHERJEE SP, GALLUD A, et al. Biological interactions of carbon-based nanomaterials: From coronation to degradation. Nanomedicine. 2016;12(2):333-351.
[44] ONISHI M, OKONOGI N, OIKE T, et al. High linear energy transfer carbon-ion irradiation increases the release of the immune mediator high mobility group box 1 from human cancer cells. J Radiat Res. 2018; 59(5):541-546.
[45] WANG SL, SHI XH, YANG Z, et al. Osteopontin (OPN) is an important protein to mediate improvements in the biocompatibility of C ion-implanted silicone rubber. PLoS One. 2014;9(6):e98320.
[46] LI X, ZHOU X, CHEN Y, et al. Surface changes of nanotopography by carbon ion implantation to enhance the biocompatibility of silicone rubber: an in vitro study of the optimum ion fluence and adsorbed protein. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2017;28(10):167.
[47] ZHOU X, CHEN X, MAO TC, et al. Carbon Ion Implantation: A Good Method to Enhance the Biocompatibility of Silicone Rubber. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016;137(4):690e-699e.
[48] ZHOU X, ZHOU X, YAN R, et al. Co-effects of C/Ag dual ion implantation on enhancing antibacterial ability and biocompatibility of silicone rubber. Biomed Mater. 2020;15(6):65003.
[49] Raphey VR, Henna TK, Nivitha KP,et al. Advanced biomedical applications of carbon nanotube. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;100(3):616-630.
[50] MATSUOKA M, AKASAKA T, HASHIMOTO T, et al. Improvement in cell proliferation on silicone rubber by carbon nanotube coating. Biomed Mater Eng. 2009;19(2-3):155-162.
[51] LUO B, WEI Y, CHEN H, et al. Printing Carbon Nanotube-Embedded Silicone Elastomers via Direct Writing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(51):44796-44802.
[52] KAVAND H, RAHAIE M, KOOHSORKHI J, et al. A conductive cell-imprinted substrate based on CNT-PDMS composite. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2019;66(3):445-453.
[53] BANNYCH A, KATZ S, BARKAY Z, et al. Preserving Softness and Elastic Recovery in Silicone-Based Stretchable Electrodes Using Carbon Nanotubes. Polymers (Basel). 2020;12(6):1345.
[54] WANG C, OH S, LEE HA, et al. In vivo feasibility test using transparent carbon nanotube-coated polydimethylsiloxane sheet at brain tissue and sciatic nerve. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017;105(6):1736-1745.
[55] GURUNATHAN S, KIM JH. Synthesis, toxicity, biocompatibility, and biomedical applications of graphene and graphene-related materials. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016;11(5):1927-1945.
[56] LORDEUS M, ESTRADA A, STEWART D, et al. Graphene nanoplatelet-reinforced silicone for the valvular prosthesis application. J Long Term Eff Med Implants. 2015;25(1-2):95-103.
[57] WAIWIJIT U, MATUROS T, PAKAPONGPAN S, et al. Highly cytocompatible and flexible three-dimensional graphene/polydimethylsiloxane composite for culture and electrochemical detection of L929 fibroblast cells. J Biomater Appl. 2016;31(2):230-240.
[58] LI J, LIU X, CROOK JM, et al. Development of a porous 3D graphene-PDMS scaffold for improved osseointegration. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017;159(1):386-393.
[59] COHRS NH, SCHULZ-SCHÖNHAGEN K, MOHN D, et al. Modification of silicone elastomers with Bioglass 45S5® increases in ovo tissue biointegration. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2019;107(4): 1180-1188.
|