[1] PAULA ACC, CARVALHO PH, MARTINS TMM, et al. Improved vascularisation but inefficient in vivo bone regeneration of adipose stem cells and poly-3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate scaffolds in xeno-free conditions. Mater Sci Eng C. 2020;107:110301.
[2] GARCIA JR, GARCIA AJ. Biomaterial-mediated strategies targeting vascularization for bone repair. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2016;6(2):77-95.
[3] PARK H, LIM DJ, SUNG M, et al. Microengineered platforms for co-cultured mesenchymal stem cells towards vascularized bone tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2016;13(5):465-474.
[4] MA MX, LIU Q, YE C, et al. Preparation of P3HB4HB/(Gelatin+PVA) composite scaffolds by coaxial electrospinning and its biocompatibility evaluation. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:9251806.
[5] KELLY ER, PLAT J, HAENEN GRMM, et al. The effect of modified eggs and an egg-yolk based beverage on serum lutein and zeaxanthin concentrations and macular pigment optical density:Results from a randomized trial. PLoS One. 2014;9(3): e92659.
[6] JALILI-FIROOZINEZHAD S, RAJABI-ZELETI S, MOHAMMADI P, et al. Facile fabrication of egg white macroporous sponges for tissue regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2015;4:2281-2290.
[7] YOU R, ZHANG J, GU S, et al. Regenerated egg white/silk fibroin composite films for biomedical applications. Mater Sci Eng C. 2017;79:430-435.
[8] JUN I, HAN HS, EDWARDS JR, et al. Electrospun fibrous scaffolds for tissue engineering: Viewpoints on architecture and fabrication. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(3):745.
[9] GOZUTOK M, SADHU V, SASMAZEL HT. Development of poly(vinyl alcohol) (pva)/reduced grapheneoxide (rgo) electrospun mats. J Nanosci Nanotechno. 2019;19: 4292-4298.
[10] LEE SY, JANG DH, KANG YO, et al. Cellular response to poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibers coated with biocompatible proteins and polysaccharides. Appl Surf Sci. 2012;258(18):6914-6922.
[11] SHIN SR, LI YC, JANG HL, et al. Graphene-based materials for tissue engineering. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016;S0169409X1630093X.
[12] ZHOU T, LI G, LIN S, et al. Electrospun poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate)/ graphene oxide scaffold:Enhanced properties and promoted in vivo bone repair in rats. Acs Appl Mater Inter. 2017;9:42589-42600.
[13] GIL-CASTELL O, GALINDO-ALFARO D, SÁNCHEZ-BALLESTER S, et al. Crosslinked sulfonated poly(vinyl alcohol)/graphene oxide electrospun nanofibers as polyelectrolytes. Nanomaterials-Basel. 2019;9(3):397.
[14] SHAO W, HE J, SANG F, et al. Enhanced bone formation in electrospun poly(l-lactic-co-glycolic acid)-tussah silk fibroin ultrafine nanofiber scaffolds incorporated with graphene oxide. Mater Sci Eng C. 2016;62:823-834.
[15] Raslan A, Saenz DBL, Ciriza J, et al. Graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide-based scaffolds in regenerative medicine. Int J Pharm. 2020;580:119226.
[16] ZHANG Q, DU Q, ZHAO Y, et al. Graphene oxide-modified electrospun polyvinyl alcohol nanofibrous scaffolds with potential as skin wound dressings. Rsc Adv. 2017;7(46):28826-28836.
[17] ZHANG L, WANG Z, XU C, et al. High strength graphene oxide/polyvinyl alcohol composite hydrogels. J Mater Chem. 2011;21(28):10399-10406.
[18] KIM H, NAMGUNG R, SINGHA K, et al. Graphene oxide-polyethylenimine nanoconstruct as a gene delivery vector and bioimaging tool. Bioconjugate Chem. 2015;22:2558-2567.
[19] CHEN W, LIU X, CHEN Q, et al. Angiogenic and osteogenic regeneration in rats via calcium phosphate scaffold and endothelial cell co-culture with human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (mscs),human umbilical cord mscs,human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mscs and human embryonic stem cell-derived mscs. J Tissue Eng Regen M. 2018;12:191-203.
[20] DENG Y, JIANG C, LI C, et al. 3D printed scaffolds of calcium silicate-doped β-TCP synergize with co-cultured endothelial and stromal cells to promote vascularization and bone formation. Sci Rep. 2017;7:5588.
[21] WU J, WU Z, XUE Z, et al. Phbv/bioglass composite scaffolds with co-cultures of endothelial cells and bone marrow stromal cells improve vascularization and osteogenesis for bone tissue engineering. Rsc Adv. 2017;7(36):22197-22207.
[22] JING X, MI HY, SALICK MR, et al. Electrospinning thermoplastic polyurethane/graphene oxide scaffolds for small diameter vascular graft applications. Mater Sci Eng C. 2015;49:40-50.
[23] DE CARA SPHM, ORIGASSA CST, DE SÁ SILVA F, et al. Angiogenic properties of dental pulp stem cells conditioned medium on endothelial cells in vitro and in rodent orthotopic dental pulp regeneration. Heliyon. 2019;5(4):e01560.
[24] LI M, ZHANG X, JIA W, et al.Improving in vitro biocompatibility on biomimetic mineralized collagen bone materials modified with hyaluronic acid oligosaccharide. Mater Sci Eng C.2019;104:110008.
[25] WANG Y, CUI W, ZHAO X, et al. Bone remodeling-inspired dual delivery electrospun nanofibers for promoting bone regeneration. Nanoscale. 2018;11:60-71.
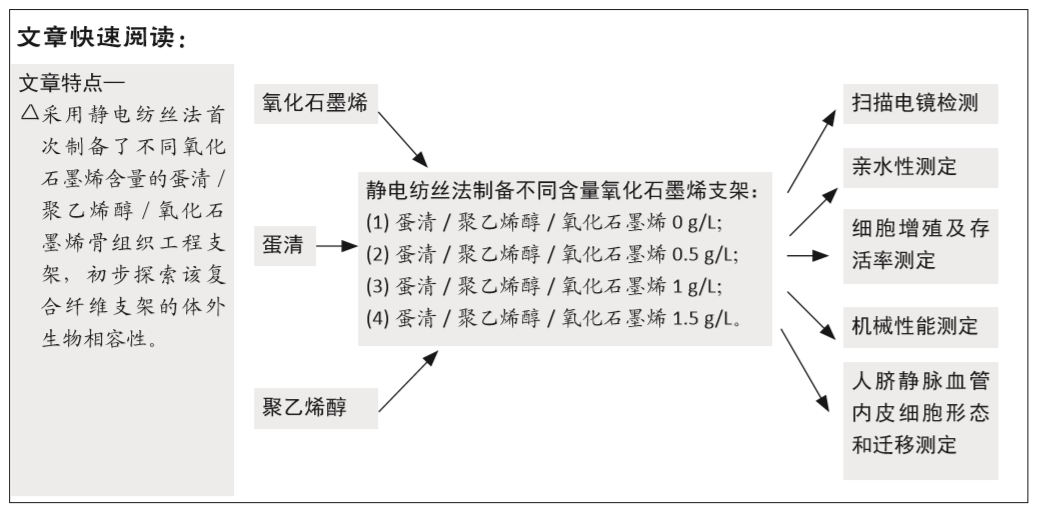
[26] 孙宇,邹强,李轩泽,等.基于静电纺丝技术的血液生物膜的构建初探及生物相容性评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(6):901-905.
[27] CHEN H, XIE S, YANG Y, et al. Multiscale regeneration scaffold in vitro and in vivo. J Biomed Mater Res Part B Appl Biomater. 2018;106:1218-1225.
[28] WANG C, LU WW, WANG M. Multifunctional fibrous scaffolds for bone regeneration with enhanced vascularization. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8:636-647.
[29] WU V, HELDER MN, BRAVENBOER N, et al. Bone tissue regeneration in the oral and maxillofacial region:a review on the application of stem cells and new strategies to improve vascularization. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:6279721.
[30] WANG C, WANG M. Electrospun multicomponent and multifunctional nanofibrous bone tissue engineering scaffolds. J Mater Chem B. 2017;5(7):1388-1399.
|