[1] KIM YH, HA KY, KIM SI. Spinal Cord Injury and Related Clinical Trials. Clin Orthop Surg. 2017;9(1):1-9.
[2] SANIVARAPU R, VALLABHANENI V, VERMA V. The Potential of Curcumin in Treatment of Spinal Cord Injury. Neurol Res Int. 2016;2016:9468193.
[3] YUAN J, LIU W, ZHU H, et al. Curcumin inhibits glial scar formation by suppressing astrocyte-induced inflammation and fibrosis in vitro and in vivo. Brain Res. 2017; 1655:90-103.
[4] MENON VP, SUDHEER AR. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of curcumin. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;595:105-125.
[5] GORABI AM, HAJIGHASEMI S, KIAIE N, et al. Anti-fibrotic effects of curcumin and some of its analogues in the heart. Heart Fail Rev. 2020;25(5):731-743.
[6] MORADI-MARJANEH R, HASSANIAN SM, RAHMANI F, et al. Phytosomal Curcumin Elicits Anti-tumor Properties Through Suppression of Angiogenesis, Cell Proliferation and Induction of Oxidative Stress in Colorectal Cancer. Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24(39):4626-4638.
[7] NERY-FLORES SD, RAMÍREZ-HERRERA MA, MENDOZA-MAGAÑA ML, et al. Dietary Curcumin Prevented Astrocytosis, Microgliosis, and Apoptosis Caused by Acute and Chronic Exposure to Ozone. Molecules. 2019;24(15):2839.
[8] METZLER M, PFEIFFER E, SCHULZ SI, et al. Curcumin uptake and metabolism. Biofactors. 2013;39(1):14-20.
[9] DENDE C, MEENA J, NAGARAJAN P, et al. Nanocurcumin is superior to native curcumin in preventing degenerative changes in Experimental Cerebral Malaria. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):10062.
[10] UMERSKA A, GAUCHER C, OYARZUN-AMPUERO F, et al. Polymeric Nanoparticles for Increasing Oral Bioavailability of Curcumin. Antioxidants (Basel). 2018 ;7(4):46.
[11] NAEIMI R, SAFARPOUR F, HASHEMIAN M, et al. Curcumin-loaded nanoparticles ameliorate glial activation and improve myelin repair in lyolecithin-induced focal demyelination model of rat corpus callosum. Neurosci Lett. 2018;674:1-10.
[12] XIAO J, SI N, HUANG Q. Assembly of kafirin / carboxymethyl chitosan nanoparticles to enhance the cellular uptake of curcumin. Food Hydrocolloids. 2015;51(1):166-175.
[13] ADITYA NP, YANG H, KIM S, et al. Fabrication of amorphous curcumin nanosuspensions using β-lactoglobulin to enhance solubility, stability, and bioavailability. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2015;127(1):114-121.
[14] BARAKAT C, PATRA D. Combining time-resolved fluorescence with synchronous fluorescence spectroscopy to study bovine serum albumin-curcumin complex during unfolding and refolding processes. Luminescence. 2013;28(2):149-155.
[15] LV L, SHEN Y, LIU J, et al. Enhancing curcumin anticancer efficacy through di-block copolymer micelle encapsulation. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2014;10(2):179-193.
[16] MADHAVI M, MADHAVI K, JITHAN AV. Preparation and in vitro / in vivo characterization of curcumin microspheres intended to treat colon cancer. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2012;4(2):164-171.
[17] 李然,赵燕娜,王婷,等.基于新型树枝状大分子姜黄素纳米粒的制备及体外释放[J].医药导报,2017,36(5):538-543.
[18] KAPOOR DN, BHATIA A, KAUR R, et al. PLGA: a unique polymer for drug delivery. Ther Deliv. 2015;6(1):41-58.
[19] MIR M, AHMED N, REHMAN AU. Recent applications of PLGA based nanostructures in drug delivery. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017;159:217-231.
[20] MOBARRA N, SOLEIMANI M, PAKZAD R, et al. Three-dimensional nanofiberous PLLA/PCL scaffold improved biochemical and molecular markers hiPS cell-derived insulin-producing islet-like cells. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018;46(sup3): S685-S692.
[21] 张贺龙,王慧燕,李卓,等.壳聚糖-明胶/聚乳酸-羟基乙酸联合载药水凝胶的体外抗结核作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(22):3480-3485.
[22] 朱雯洁,黄莉君,叶曾联,等.姜黄素微球制备工艺研究[J].广州化工,2017, 45(23):66-68.
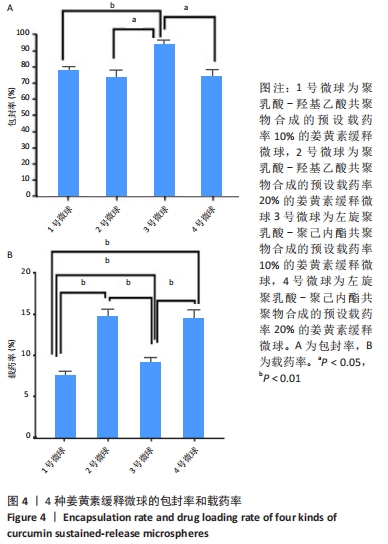
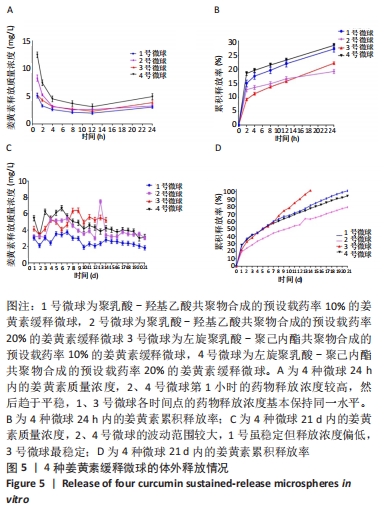
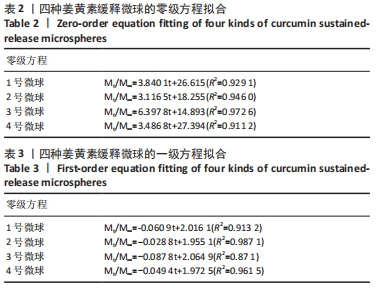
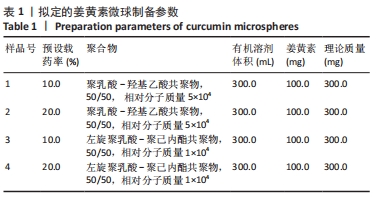
|