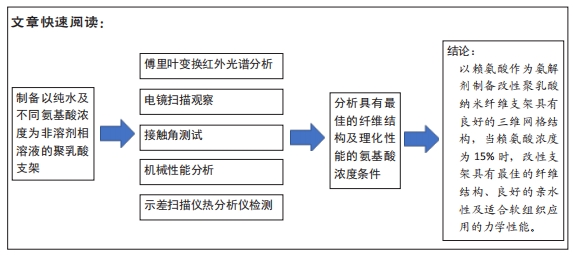
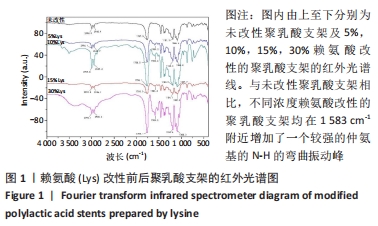
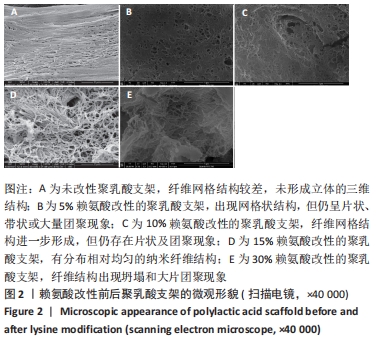
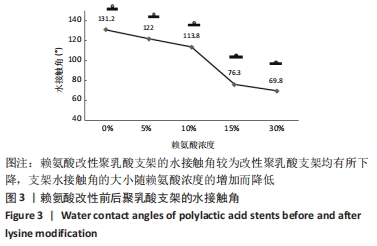
[1] MA H, HU J, MA PX. Polymer scaffolds for small-diameter vascular tissue engineering. Adv Funct Mater. 2010;20(17):2833-2841.
[2] HU J, SUN X, MA H, et al. Porous nanofibrous PLLA scaffolds for vascular tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2010;31(31):7971-7977.
[3] HU J, FENG K, LIU X, et al. Chondrogenic and osteogenic differentiations of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells on a nanofibrous scaffold with designed pore network. Biomaterials. 2009; 30(28):5061-5067.
[4] STEVENS MM. Biomaterials for bone tissue engineering. Mater Today. 2008;11(5):18-25.
[5] ESTHER JL, KASPER FK, ANTONIOS GM. Biomaterials for tissue engineering. Ann Biomed Eng. 2014;42(2):323-337.
[6] MARK W, NICHOLAS JC. Long-term in vivo degradation of poly-L-lactide (PLLA) in bone. J Biomater Appl. 2007;21(4):395-411.
[7] CHEN VJ, MA PX. The effect of surface area on the degradation rate of nano-fibrous poly(L-lactic acid) foams. Biomaterials. 2006;27(20): 3708-3715.
[8] LIU XH, MA PX. The nanofibrous architecture of poly(L-lactic acid)-based functional copolymers. Biomaterials. 2010;31(2):259-269.
[9] LANGER R, VACANTI JP. Tissue engineering. Science. 1993;260(5110): 920-926.
[10] MA PX. Biomimetic materials for tissue engineering. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008;60(2):184-198.
[11] HENCH, LARRY L, POTAK, et al. Third-generation biomedical materials. Science. 2002;295(5557):1014-1017.
[12] LIU X, MA PX. Polymeric scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Ann Biomed Eng. 2004;32(3):9622-9629.
[13] LI J, CHEN Y, MAK AT, et al. A one-step method to fabricate PLLA scaffolds with deposition of bioactive hydroxyapatite and collagen using ice-based microporogens. Acta Biomater. 2010;6(6):2013-2019.
[14] SHIN H, JO S, MIKOS AG. Biomimetic materials for tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2003;24(24):4353-4364.
[15] WEI G, MA PX. Nanostructured biomaterials for regeneration. Adv Funct Mater. 2010;18(22):3568-3582.
[16] WOO KM, CHEN VJ, MA PX. Nano-fibrous scaffolding architecture selectively enhances protein adsorption contributing to cell attachment. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2003;67(2):531-537.
[17] WOO KM, JUN JH, CHEN VJ, et al. Nano-fibrous scaffolding promotes osteoblast differentiation and biomineralization. Biomaterials. 2007; 28(2):335-343.
[18] HU J, LIU X, MA PX. Induction of osteoblast differentiation phenotype on poly(L-lactic acid) nanofibrous matrix. Biomaterials. 2008;29(28): 3815-3821.
[19] EPPLEY BL, REILLY M. Degradation characteristics of PLLA-PGA bone fixation devices. J Craniofac Surg. 1997;8(2):116-120.
[20] QUIRK RA, CHAN WC, DAVIES MC, et al. Poly(L-lysine)-GRGDS as a biomimetic surface modifier for poly(lactic acid). Biomaterials. 2001; 22(8):865-872.
[21] NIU X, LI X, LIU H, et al. Homogeneous chitosan/poly(L-lactide) composite scaffolds prepared by emulsion freeze-drying. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2012;23(1-4):391-404.
[22] KALIVA M, GEORGOPOULOU A, DRAGATOGIANNIS DA, et al. Biodegradable Chitosan-graft-Poly(l-lactide) copolymers for bone tissue engineering. Polymers (Basel). 2020;12(2):316.
[23] 王雪红,陈智,魏杰,等.赖氨酸改性聚乳酸/聚乙二醇共聚物的制备及表征[J].高分子材料科学与工程,2016,32(9):1-6.
[24] WU JZ, ZHAO JJ, ZHANG B, et al. Polyethylene glycol–polylactic acid nanoparticles modified with cysteine–arginine–glutamic acid–lysine–alanine fibrin-homing peptide for glioblastoma therapy by enhanced retention effect. Int J Nanomedicine. 2013;9(1):5261-5271.
[25] 周炳华,廖文波.改性聚乳酸-羟基乙酸/Ⅰ型胶原复合支架的细胞亲和性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(29):5687-5690.
[26] LI WJ, TULI R, HUANG X, et al. Multilineage differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells in a three-dimensional nanofibrous scaffold. Biomaterials. 2005;26(25):5158-5166.
[27] MA Z, HE W, YONG T, et al. Grafting of gelatin on electrospun poly(caprolactone) nanofibers to improve endothelial cell spreading and proliferation and to control cell Orientation. Tissue Eng. 2005;11(7): 1149-1158.
[28] YOSHIMOTO H, SHIN YM, TERAI H, et al. A biodegradable nanofiber scaffold by electrospinning and its potential for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2003;24(12):2077-2082.
[29] LIU X, SMITH L, WEI G, et al. Surface engineering of Nano-Fibrous Poly(L-Lactic acid) scaffolds via Self-Assembly technique for bone tissue engineering. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2005;1(1):54-60.
[30] SHAO J, CHEN C, WANG Y, et al. Early stage structural evolution of PLLA porous scaffolds in thermally induced phase separation process and the corresponding biodegradability and biological property. Polym Degrad Stabil.2012;97(6):955-999.
|