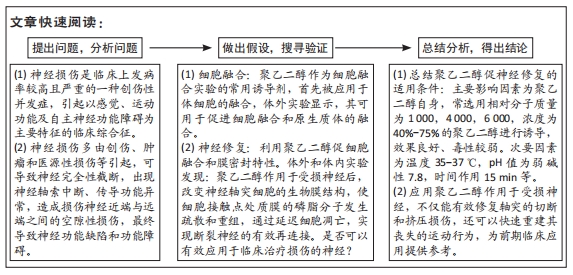
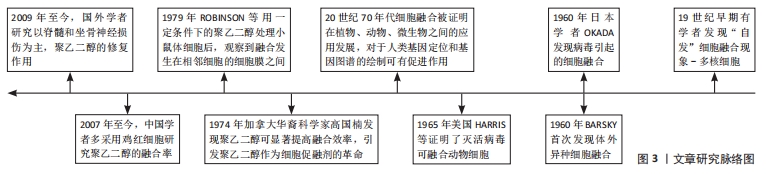
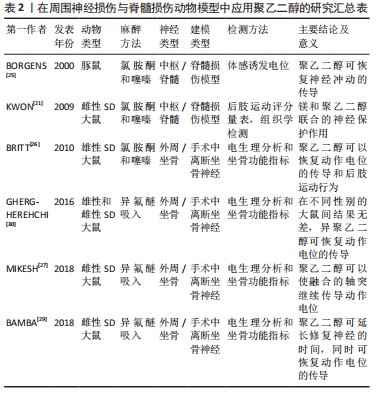
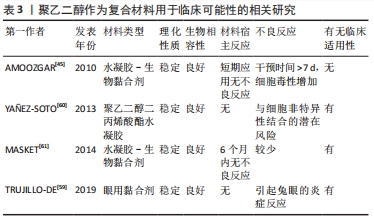
[1] Fitzharris M, Cripps RA, Lee BB. Estimating the global incidence of traumatic spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord. 2014;52(2):117-122.
[2] Karsy M, Watkins R, Jensen MR, et al. Trends and cost analysis of upper extremity nerve Injury using the national (nationwide) inpatient sample. World Neurosurg. 2019;123:e488-e500.
[3] Foster CH, Karsy M, Jensen MR, et al. Trends and cost-analysis of lower extremity nerve injury using the national inpatient sample. Neurosurg. 2019;85(2):250-256.
[4] Palispis WA, Gupta R. Surgical repair in humans after traumatic nerve injury provides limited functional neural regeneration in adults. Exp Neurol. 2017;290:106-114.
[5] PASKAL AM, PASKAL W, PIETRUSKI P, et al. Polyethylene glycol: the future of posttraumatic nerve repair? systemic review. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(6): 1478.
[6] ABDOU SA, Henderson PW. Fusogens: chemical agents that can rapidly restore function after nerve injury. J Surg Res. 2019;233:36-40.
[7] Bittner GD, Sengelaub DR, Ghergherehchi CL. Conundrums and confusions regarding how polyethylene glycol-fusion produces excellent behavioral recovery after peripheral nerve injuries. Neural Regen Res. 2018; 13(1):53-57.
[8] Bamba R, Waitayawinyu T, Nookala R, et al. A novel therapy to promote axonal fusion in human digital nerves. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2016;81(5 Suppl 2 Proceedings of the 2015 Military Health System Research Symposium):S177-S183.
[9] Pasut G, Panisello A, Folch-Puy E, et al. Polyethylene glycols: an effective strategy for limiting liver ischemia reperfusion injury. World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22(28):6501-6508.
[10] Mokarizadeh A, Mehrshad A, Mohammadi R. Local polyethylene glycol in combination with chitosan based hybrid nanofiber conduit accelerates transected peripheral nerve regeneration. J Invest Surg. 2016; 29(3):167-174.
[11] 陈军,沈华.神经导管内支架修复周围神经缺损的研究应用与进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(8):1273-1279.
[12] 肖立伟,戴富才,李政,等.聚乙二醇:绿色有机合成的新媒介[J].有机化学,2019,39(3):648-660.
[13] Hunckler MD, Medina JD, Coronel MM, et al. Linkage groups within thiol-ene photoclickable peg hydrogels control in vivo stability. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019;8(14):e1900371.
[14] 李玲,刘欢,贺亚玲,等.聚乙二醇诱导鸡红细胞融合实验方案的优化[J].农垦医学,2020,42(2):164-169.
[15] 李秀兰,姜曰水.聚乙二醇诱导细胞融合影响因素探究 [J].菏泽学院学报,2007,29(5):79-82.
[16] 仇燕,李朝炜,苗芳. 聚乙二醇诱导鸡红细胞融合条件的优化[J].生物技术,2011,21(3):50-53.
[17] 吴绍函,许辰琪,温馨,等.Mg-(2+)浓度对细胞融合效果的影响[J].现代生物医学进展,2013,13(11):2037-2039,2099.
[18] 杨明轩,游孟昊,王美文,等.葡萄糖浓度对细胞融合效果的影响[J].现代生物医学进展,2014,14(17):3236-3239.
[19] 侯元,霍德胜,温得中. 提高细胞融合率的实验方法探讨[J].实验室研究与探索,2017,36(10):28-30, 95.
[20] Robinson JM, Roos DS, Davidson RL, et al. Membrane alterations and other morphological features associated with polyethylene glycol-induced cell fusion. J Cell Sci. 1979;40:63-75.
[21] Kwon BK, Roy J, Lee JH, et al. Magnesium chloride in a polyethylene glycol formulation as a neuro-protective therapy for acute spinal cord injury:preclinical refinement and optimization. J Neurotrauma. 2009;26:1379-1393.
[22] Gafarov FM. Neural electrical activity and neural network growth. Neural Netw. 2018;101:15-24.
[23] Koh JY, Choi DW. Quantitative determination of glutamate mediated cortical neuronal injury in cell culture by lactate dehydrogenase efflux assay. J Neurosci Methods.1987;20(1):83-90.
[24] Luo J, Borgens R, Shi RY. Polyethylene glycol immediately repairs neuronal membranes and inhibits free radical production after acute spinal cord injury. J Neurochem. 2002;83(2):471-480.
[25] Borgens RB, Shi R. Immediate recovery from spinal cord injury through molecular repair of nerve membranes with polyethylene glycol. FASEB J. 2000;14(1):27-35.
[26] Britt JM, Kane JR, Spaeth CS, et al. Polyethylene glycol rapidly restores axonal integrity and improves the rate of motor behavior recovery after sciatic nerve crush injury. J Neurophysiol. 2010;104(2):695-703.
[27] Mikesh M, Ghergherehchi CL, Hastings RL, et al. Polyethylene glycol solutions rapidly restore and maintain axonal continuity, neuromuscular structures, and behaviors lost after sciatic nerve transections in female rats. J Neurosci Res 2018;96(7):1223-1242.
[28] Spaeth CS, Robison T, Fan JD, et al. Cellular mechanisms of plasmalemmal sealing and axonal repair by polyethylene glycol and methylene blue. J Neurosci Res. 2012;90(5):955-966.
[29] Bamba R, Riley DC, Kim JS, et al. Evaluation of a nerve fusion technique with polyethylene glycol in a delayed setting after nerve injury. J Hand Surg Am. 2018;43(1):82.e81-82.e87.
[30] Ghergherehchi CL, Bittner GD, Hastings RL, et al. Effects of extracellular calcium and surgical techniques on restoration of axonal continuity by polyethylene glycol fusion following complete cut or crush severance of rat sciatic nerves. J Neurosci Res 2016;94(3):231-245.
[31] Riley DC, Boyer RB, Deister CA, et al. Immediate enhancement of nerve function using a novel axonal fusion device after neurotmesis. Ann Plast Surg. 2017;79(6):590-599.
[32] Panagopoulos GN, Megaloikonomos PD, Mavrogenis AF. The present and future for peripheral nerve regeneration. Orthopedics. 2017;40(1):e141-e156.
[33] Giordano-Santini R, Linton C, Hilliard MA. Cell-cell fusion in the nervous system:alternative mechanisms of development, injury, and repair. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2016;60:146-154.
[34] Hoffman AN, Bamba R, Pollins AC, et al. Analysis of polyethylene glycol (PEG) fusion in cultured neuroblastoma cells via flow cytometry: techniques & optimization. J Clin Neurosci. 2017;36:125-128.
[35] Filous AR, Silver J. “Targeting astrocytes in CNS injury and disease: a translational research approach”. Prog Neurobiol. 2016;144:173-187.
[36] HE ZJ, JIN YS. Intrinsic control of axon regeneration. Neuron. 2016;90(3): 437-451.
[37] Rodemer W, Selzer ME. Role of axon resealing in retrograde neuronal death and regeneration after spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2019; 14(3):399-404.
[38] Lin YF, Xie Z, Zhou J, et al. Effect of exogenous spastin combined with polyethylene glycol on sciatic nerve injury. Neural Regen Res. 2019;14(7): 1271-1279.
[39] Messineo E, Pollins A, Thayer W. Optimization and evaluation of an in vitro model of PEG-mediated fusion of nerve cell bodies. J Clin Neurosci. 2019;63:189-195.
[40] Vázquez-Cuevas FG, Martínez-Ramírez AS, Robles-Martínez L, et al. Paracrine stimulation of P2X7 receptor by ATP activates a proliferative pathway in ovarian carcinoma cells. J Cell Biochem. 2014;115(11):1955-1966.
[41] Rodriguez-Feo CL, Sexton KW, Boyer RB, et al. Blocking the P2X7 receptor improves outcomes after axonal fusion. J Surg Res. 2013;184(1): 705-713.
[42] Iglesias R, Locovei S, Roque A, et al. P2X7 receptor-Pannexin1 complex: pharmacology and signaling. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008; 295(3):C752-C760.
[43] Pannuzzo M, De Jong DH, Raudino A, et al. Simulation of polyethylene glycol and calcium-mediated membrane fusion. J Chem Phys. 2014;140(12):124905.
[44] Arbeloa J, Pérez-Samartín A, Gottlieb M, et al. P2X7 receptor blockade prevents ATP excitotoxicity in neurons and reduces brain damage after ischemia. Neurobiol Dis. 2012;45(3):954-961.
[45] Amoozgar Z, Rickett T, Park J, et al. Semi-interpenetrating network of polyethylene glycol and photocrosslinkable chitosan as an in-situ-forming nerve adhesive. Acta Biomater. 2012;8(5):1849-1858.
[46] Scott R, Marquardt L, Willits RK. Characterization of poly (ethylene glycol) gels with added collagen for neural tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;93(3):817-823.
[47] Oveissi F, Naficy S, Lee A, et al. Materials and manufacturing perspectives in engineering heart valves:a review. Mater Today Bio. 2020;5:100038.
[48] Wang JZ, You ML, Ding ZQ, et al. A review of emerging bone tissue engineering via PEG conjugated biodegradable amphiphilic copolymers. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;97:1021-1035.
[49] Im GI. Application of kartogenin for musculoskeletal regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018;106(4):1141-1148.
[50] Cattin AL, Burden JJ, Van Emmenis L, et al. Macrophage-induced blood vessels guide schwann cell-mediated regeneration of peripheral nerves. Cell. 2015;162(5):1127-1139.
[51] Parrinello S, Napoli I, Ribeiro S, et al. EphB signaling directs peripheral nerve regeneration through Sox2-dependent Schwann cell sorting. Cell. 2010;143(1):145-155.
[52] Dadsetan M, Knight AM, Lu L, et al. Stimulation of neurite outgrowth using positively charged hydrogels. Biomaterials. 2009;30(23-24):3874-3881.
[53] Hilliard MA. Axonal degeneration and regeneration:a mechanistic tug-of-war. J Neurochem. 2009;108(1):23-32.
[54] Tuszynski MH, Steward O. Concepts and methods for the study of axonal regeneration in the CNS. Neuron. 2012;74(5):777-791.
[55] Bittner GD, Sengelaub DR, Trevino RC, et al. The curious ability of polyethylene glycol fusion technologies to restore lost behaviors after nerve severance. J Neurosci Res. 2016;94(3):207-230.
[56] Vargas SA, Bittner GD. Natural mechanisms and artificial PEG-induced mechanism that repair traumatic damage to the plasmalemma in eukaryotes. Curr Top Membr. 2019;84:129-167.
[57] Lu X, Perera TH, Aria AB, et al. Polyethylene glycol in spinal cord injury repair:a critical review. J Exp Pharmacol. 2018;10:37-49.
[58] Ghergherehchi CL, Mikesh M, Sengelaub DR, et al. Polyethylene glycol (PEG) and other bioactive solutions with neurorrhaphy for rapid and dramatic repair of peripheral nerve lesions by PEG-fusion. J Neurosci Methods. 2019;314:1-12.
[59] Trujillo-de Santiago G, Sharifi R, Yue K, et al. Ocular adhesives: design, chemistry, crosslinking mechanisms, and applications. Biomaterials. 2019;197:345-367.
[60] Yañez-Soto B, Liliensiek SJ, Murphy CJ, et al. Biochemically and topographically engineered poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate hydrogels with biomimetic characteristics as substrates for human corneal epithelial cells. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2013;101(4):1184-1194.
[61] Masket S, Hovanesian JA, Levenson J, et al. Hydrogel sealant versus sutures to prevent fluid egress after cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2014;40(12):2057-2066.
|