[1] 杨春晖,容新宗.病毒灭活技术及产业发展报告[J].中国医药生物技术,2020,15(4):440-448.
[2] 陈强,周丽媚,张伟.动物源性医疗器械的病毒灭活方案及结果分析[J].中国卫生检验杂志,2018,28(21):2592-2595.
[3] 白玉龙,高玉凤,衷鸿宾,等.同种异体及异种组织修复材料:如何选用适宜的病毒灭活工艺[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(14): 2261-2268.
[4] 周沫,李幼忱,张乃丽,等.过氧乙酸-乙醇联合辐照灭菌对同种肌腱力学强度的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2011,19(22):1898-1900.
[5] 李玉佳,段晓琼,王艳翠,等.四种病毒灭活方法用于登革病毒灭活效果的比较[J].中国输血杂志,2020,33(2):109-113.
[6] 黄荣强,李海,梁睿姝.巴氏消毒法对乙型肝炎人免疫球蛋白病毒灭活效果的验证[J].中国生物制品学杂志,2010,23(3):320-322.
[7] 钟昱文,张磊,刘哲,等.乙醇对脊髓灰质炎病毒的灭活效果及对病毒超微结构影响的研究[J].中国消毒学杂志,2019,36(4):246-249.
[8] 华岩.在乙醇分级分离血浆过程中Ⅲ型人类嗜T淋巴细胞病毒的灭活和消除[J].国外医学.预防.诊断.治疗用生物制品分册,1987 (3):140-141.
[9] 鱼园.不同病毒灭活工艺对脱细胞牛皮基质性能的影响[J].陕西农业科学,2018,64(7):33-35.
[10] 李幼忱,周沫,李宝兴,等.过氧乙酸-乙醇法对同种软组织移植物病毒灭活研究进展[J].中国消毒学杂志,2010,27(6):743-745.
[11] 吴振强,张冠群,张福强.环氧乙烷混合气体对乙型肝炎病毒灭活效果研究[J].广东医药学院学报,1987(1):57-60.
[12] 宋永超.用过氧化氢气态等离子体灭活法灭活人类免疫缺陷性病毒Ⅰ型、甲型肝炎病毒、呼吸道合胞病毒、牛痘病毒、单纯疱疹病毒Ⅰ型、脊髓灰质炎病毒Ⅱ型[J].国外医学.输血及血液学分册, 1999(1):68.
[13] 刘育京.爱滋病病毒的消毒与灭活[J].解放军医学杂志,1986,11(3): 177.
[14] ZHOU M, ZHANG NL, LIU XM, et al. Tendon allograft sterilized by peracetic acid/ethanol combined with gamma irradiation. J Orthop Sci. 2014;19(4):627-636.
[15] AXEL P, ARNE H, MOUJAHED K, et al. Comparison of the efficacy of virus inactivation methods in allogeneic avital bone tissue transplants. Cell Tissue Bank. 2001;2(4):201-215.
[16] SVEN S, SUSANN T, MARK S, et al. No influence of collagenous proteins of Achilles tendon, skin and cartilage on the virus-inactivating efficacy of peracetic acid–ethanol. Biologicals. 2007;35(4): 355-359.
[17] BRIAN OE, DAN LB, DAVID AL. Quantification of Sulfated Glycosaminoglycans in Chondrocyte/Alginate Cultures, by Use of 1,9-Dimethylmethylene. Anal Biochem. 1996;243(1):189-191.
[18] 何红振,李韶峰,于文杰,等.过氧乙酸测定方法综述[J].化学推进剂与高分子材料,2017,15(2):52-55.
[19] 刘斌,朱加亮.同种异体移植材料病毒灭活及其验证[J].中国骨肿瘤病,2011,10(2):184-187.
[20] GȔNTER K. Efficacy of ethanol against viruses in hand disinfection. J Hosp Infect. 2018;98(4):331-338.
[21] 方哲翔,王建华,袁平,等.医用胶原修复膜病毒灭活/去除工艺的验证和评价[J].中国生物制品学杂志,2016,29(12):1341-1345.
[22] EDUARD AE, MARILISA B, ROSA M, et al. Effectiveness of Consumers Washing with Sanitizers to Reduce Human Norovirus on Mixed Salad. Foods. 2019;8(12):637.
[23] AMTMANN A, AHMED I, ZAHNER-RIMMEL P, et al. Virucidal effects of various agents-including protease-against koi herpesvirus and viral haemorrhagic septicaemia virus. J Fish Dis. 2020;43(2):185-195.
[24] JEONG MI, PARK SY, HA SD. Effects of sodium hypochlorite and peroxyacetic acid on the inactivation of murine norovirus-1 in Chinese cabbage and green onion. Lwt-Food Sci Technol. 2018;96,663-670.
[25] JASON H, MICHAEL H. Virus safety of a porcine‐derived medical device: Evaluation of a viral inactivation method. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2002;79(2):211-216.
[26] 刘明,张旗,王蕊,等.过氧乙酸-乙醇对同种骨植入材料中病毒的灭活效果研究[J].中国消毒学杂志,2010,27(3):241-243.
[27] YU I, SEIJI H, KATSUMA M, et al. Development of 3D imaging technique of reconstructed human epidermis with immortalized human epidermal cell line. Exp Dermatol. 2018;27(5):563-570.
[28] SHIUHYANG K, HYUNGJIN MK, ZJIFA W, et al. Comparison of two decellularized dermal equivalents. J Tissue Eng. 2018;12(4):983-990.
[29] ELENA B, VALERIA P, CATUSCIA O, et al. The use of an acellular matrix derived from human dermis for the treatment of full-thickness skin wounds. Cell Tissue Bank. 2019;20(2):183-192.
[30] WANG HJ, PIEPER J, SCHOTEL R, et al. Stimulation of skin repair is dependent on fibroblast source and presence of extracellular matrix. Tissue Eng. 2004;10(7-8):1054-1064.
[31] 张帅.过氧乙酸对池塘水体的增氧抑菌抑藻效果研究[D].上海:上海海洋大学,2016.
[32] 陈博.新生小牛与成人皮肤组织学及生物力学性能的比较和牛异体脱细胞真皮基质的制备[D].重庆:第三军医大学,2012
[33] GRECO KV, FRANCIS L, HUANG H, et al. Is quercetin an alternative natural crosslinking agent to genipin for long-term dermal scaffolds implantation? J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(3):E1716-E1724.
[34] HEONJUNE R, GIANLUCA T, LORENZO B, et al. On the stiffness of demineralized dentin matrices. Dent Mater J. 2016;32(2):161-170.
[35] PURI S, COULSON-THOMAS YM. Distribution and Function of Glycosaminoglycans and Proteoglycans in the Development, Homeostasis and Pathology of the Ocular Surface. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:731.
[36] KELLT DJ, CRAWFORD A, DICKINSON SC, et al. Biochemical markers of the mechanical quality of engineered hyaline cartilage. J Mater Sci Med. 2007; 18(2):273-281.
[37] SCHEFFLER SU, SCHERLER J, PRUSS A, et al. Biomechanical comparison of human bone-patellar tendon-bone grafts after sterilization with peracetic acid-ethanol. Cell Tissue Bank. 2005;6(2):109-115.
[38] 周沫,李幼忱,李宝明,等.微量过氧乙酸溶液细胞毒性研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2010,24(8):958-961. |
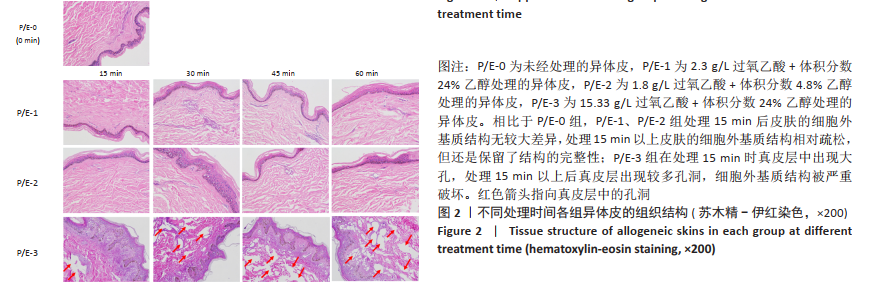
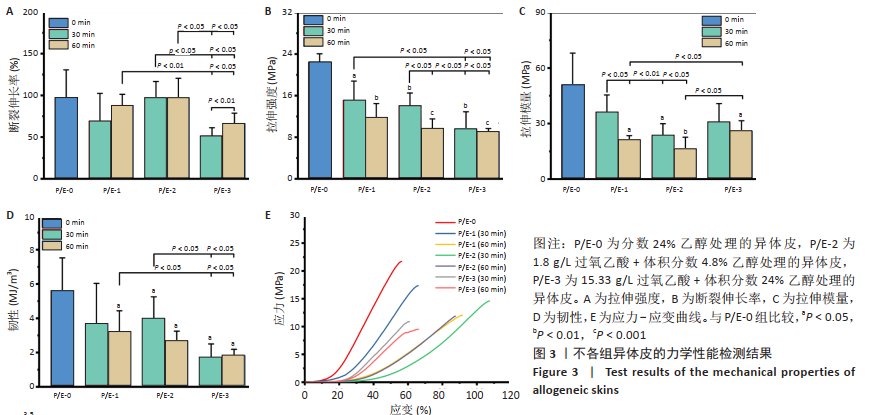
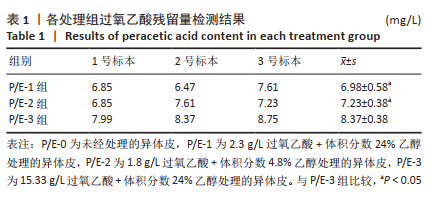
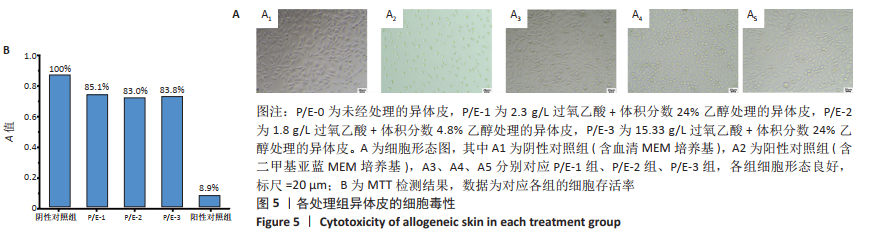
 文题释义:
文题释义: