中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (36): 5897-5904.doi: 10.12307/2021.360
• 骨与关节循证医学 evidence-based medicine of the bone and joint • 上一篇
后稳定型与后交叉韧带保留型膝关节假体在全膝关节置换中的疗效:系统综述和Meta分析
万大地1,2,段祥瑞1,2,范鑫超1,3,袁 野1,3,黄 腾1,潘迪康2,刘静艳2,李西成1
- 1河北省人民医院骨科,河北省石家庄市 050051;2华北理工大学研究生院,河北省唐山市 063210;3河北北方学院,河北省张家口市 075000
Efficacy of posterior cruciate ligament retaining versus posterior stabilized prostheses in total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and a meta-analysis
Wan Dadi1,2, Duan Xiangrui1,2, Fan Xinchao1,3, Yuan Ye1,3, Huang Teng1, Pan Dikang2, Liu Jingyan2, Li Xicheng1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Hebei General Hospital, Shijiazhuang 050051, Hebei Province, China; 2Graduate School of North China University of Science and Technology, Tangshan 063210, Hebei Province, China; 3Hebei North University, Zhangjiakou 075000, Hebei Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
CR假体:即posterior cruciate ligament retaining,应用CR假体进行全膝关节置换时保留了后交叉韧带,假体限制程度小,但是后髁截骨要求高,容易出现股骨髁反常前移。PS假体:即posterior stabilized,为后稳定型假体,应用PS假体进行全膝关节置换时切除了后交叉韧带。
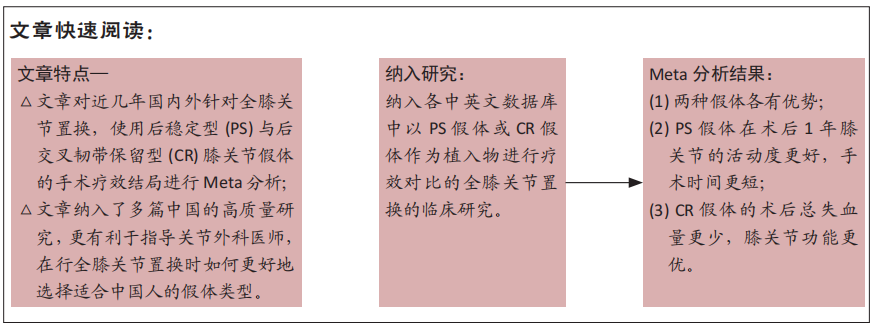
目的:临床上医生在进行全膝关节置换时常用到后稳定型(posterior stabilized,PS)与后交叉韧带保留型(posterior cruciate ligament retaining,CR)膝关节假体,而哪一种假体更具有优势还不能完全确定。文章探讨CR假体与PS假体应用于全膝关节置换的安全性和有效性。
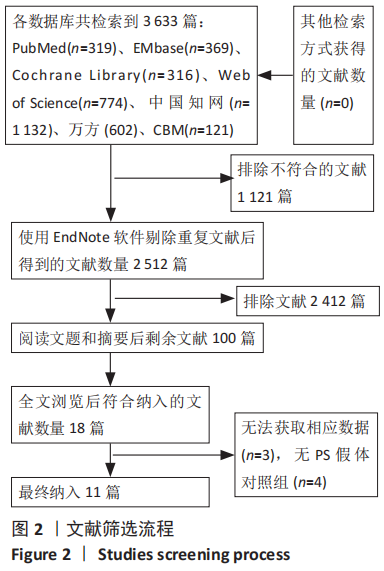
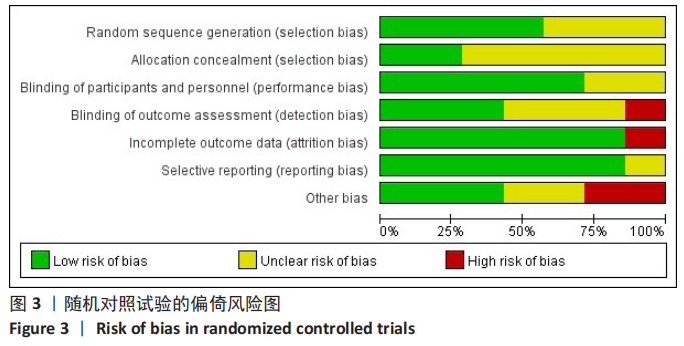
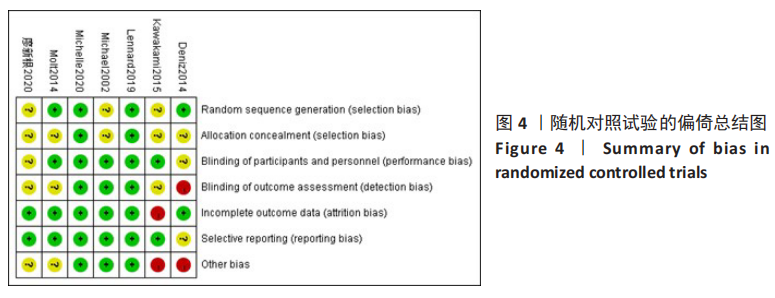
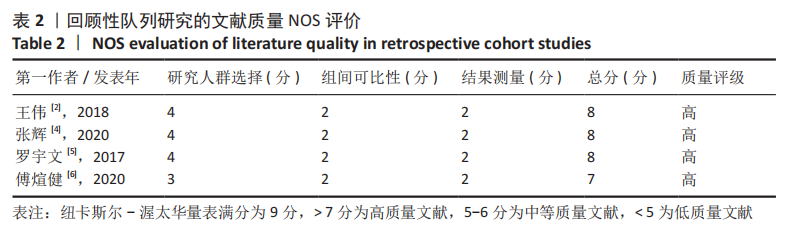
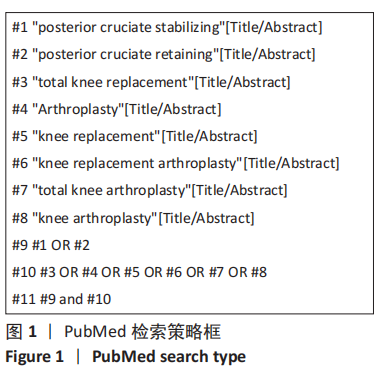
方法:在Cochrane library、PubMed、Web of Science、EMbase、中国知网、万方、维普、CBM数据库检索CR假体与PS假体应用于全膝关节置换的临床研究。使用Cochrane偏倚风险评估工具对随机对照试验的偏倚风险进行评估,对回顾性队列研究的文献质量评价参考纽卡斯尔-渥太华量表评估,使用RevMan 5.3软件进行Meta数据分析。
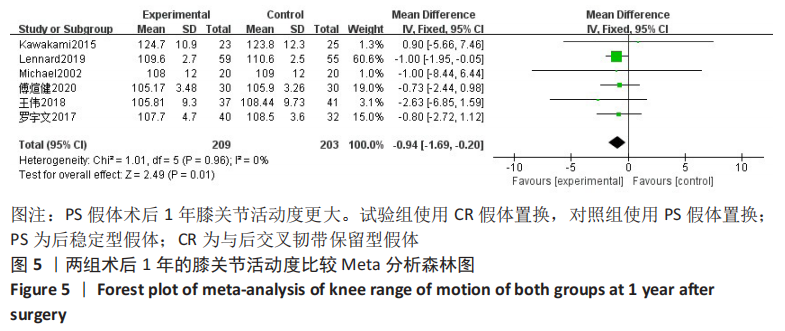
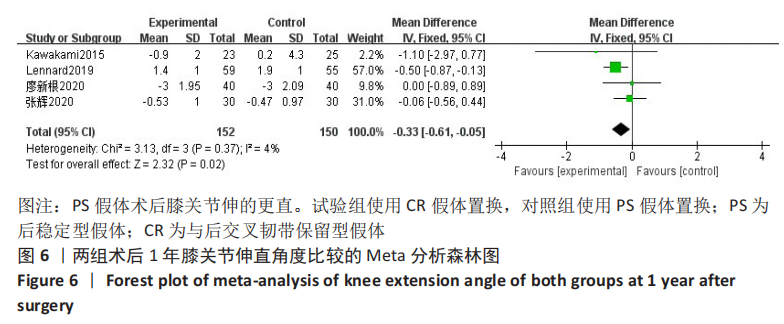
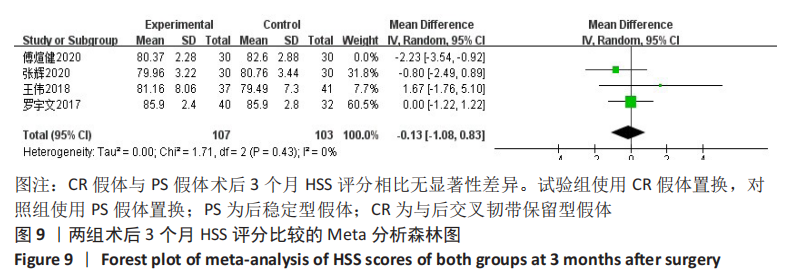
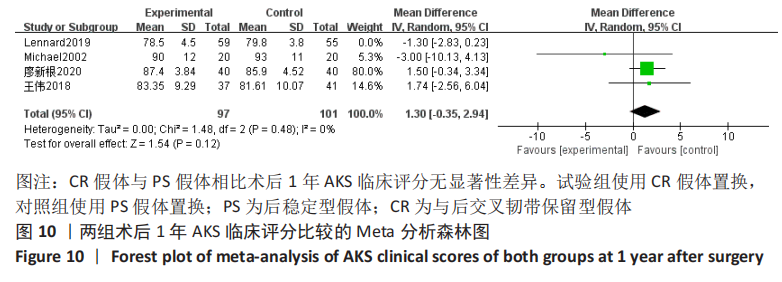
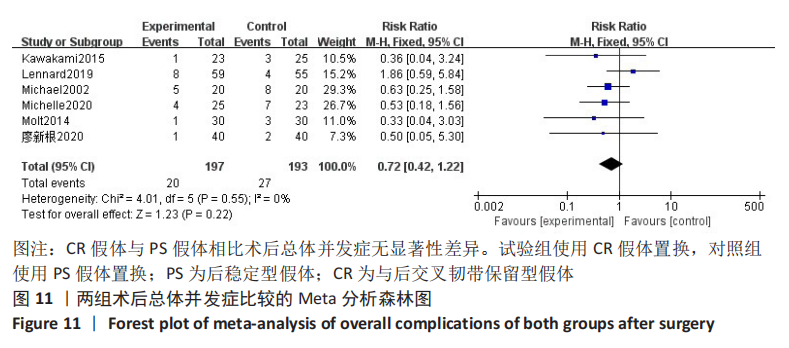
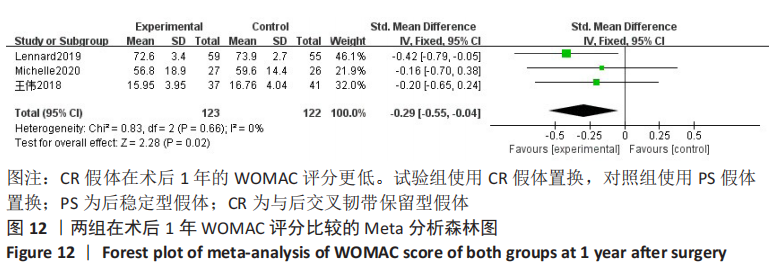
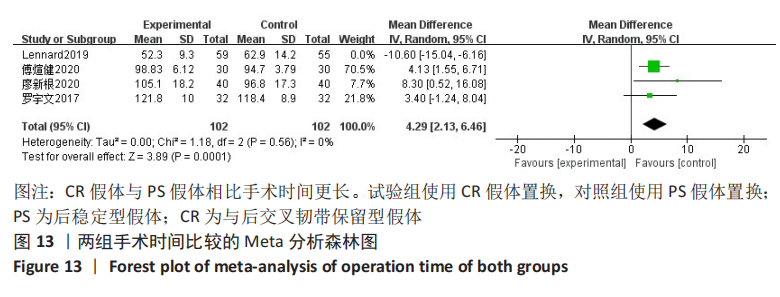
结果:共纳入11篇文献,包括7项随机对照试验,4项回顾性队列研究,均为高质量文献,包括765例行全膝关节置换的患者,其中386例应用CR假体,379例应用PS假体。Meta分析的结果表明:两种假体相比较,①PS假体术后1年膝关节活动度更大(WMD=-0.94,95%CI:-1.69至-0.20,P=0.01),术后1年膝关节伸直角度更小(WMD=-0.33,95%CI:-0.61至-0.05,P=0.02),术后1年的屈曲角度更大(SMD=-0.62,95%CI:-1.20至-0.04,P=0.03);②CR假体在术后的总失血量较少(WMD=-126.86,95%CI:-231.03至-22.69,P=0.02),术后1年的WOMAC评分更低(SMD=-0.29,95%CI:-0.55至-0.04,P=0.02),手术时间更长(WMD=4.29,95%CI:2.13-6.46,P=0.000 1);③两组术后3个月HSS评分、术后1年AKS临床评分、术后总体并发症发生率差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。
结论:行全膝关节置换时,PS假体在术后1年膝关节的活动度更好,手术时间更短;CR假体的术后总失血量更少,膝关节功能恢复更好;两种假体各有其优势,术者可以根据患者的个体差异进行选择。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6548-841X (万大地)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: