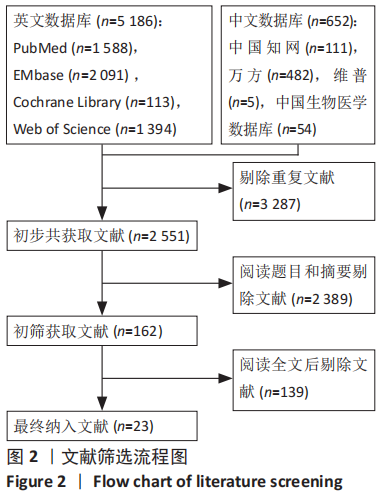
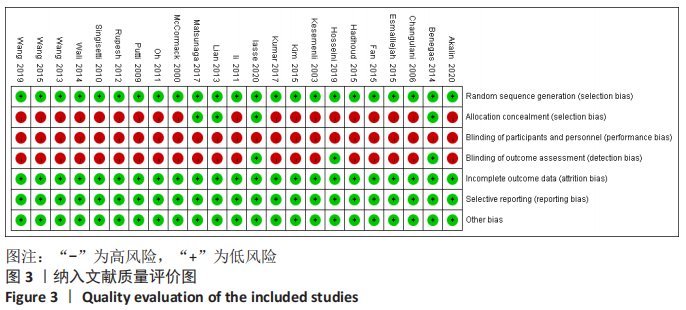
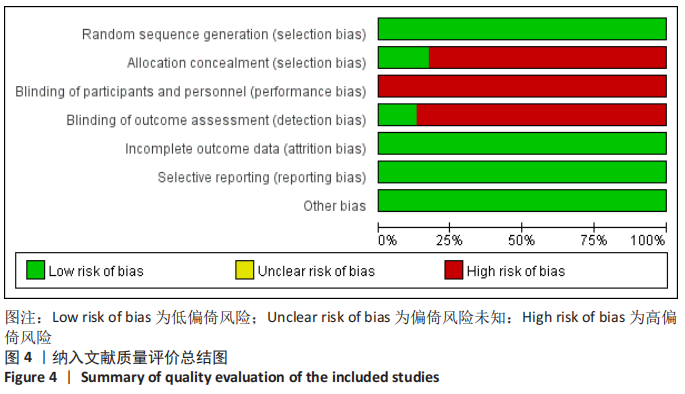
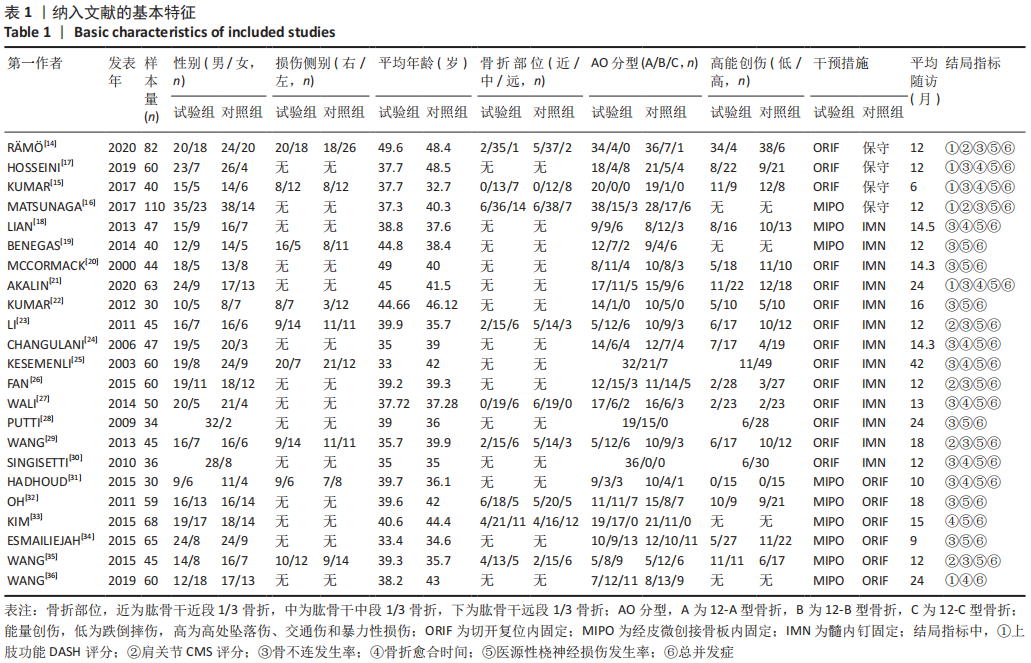
[1] COURT-BROWN CM, CAESAR B. Epidemiology of adult fractures: a review. Injury. 2006;37(8):691-697.
[2] EKHOLM R, ADAMI J, TIDERMARK J, et al. Fractures of the shaft of the humerus. An epidemiological study of 401 fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88(11):1469-1473.
[3] OLIVER WM, SEARLE HKC, NG ZH, et al. Fractures of the proximal- and middle-thirds of the humeral shaft should be considered as fragility fractures. Bone Joint J. 2020;102(11):1475-1483.
[4] UPDEGROVE GF, MOURAD W, ABBOUD JA. Humeral shaft fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2018;27(4):87-97.
[5] WALKER M, PALUMBO B, BADMAN B, et al. Humeral shaft fractures: a review. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011;20(5):833-844.
[6] BEERES FJ, DIWERSI N, HOUWERT MR, et al. ORIF versus MIPO for humeral shaft fractures: a meta-analysis and systematic review of randomized clinical trials and observational studies. Injury. 2020;1383(20):30939-30936.
[7] 王磊,李子龙,袁斌斌,等.锁定钢板与顺行髓内钉治疗成人肱骨干骨折临床效果的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2019,23(24):3924-3930.
[8] 曹春风,马坤龙,栾和旭,等.钢板内固定与髓内钉治疗肱骨干骨折的Meta分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24(12): 1080-1087.
[9] 王伟,陈永佳,沈磊,等.微创钢板内固定与传统手术治疗成人肱骨干骨折的系统评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2018, 22(35):5715-5723.
[10] 薛镜,黄富国,项舟,等.顺行锁定髓内钉和动力加压钢板治疗肱骨干骨折的系统评价[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2017, 25(22):2055-2060.
[11] 邱皓,卢旻鹏,栾富钧,等.三种不同手术方式治疗肱骨干骨折的网络Meta分析[J].重庆医科大学学报,2017,42(2):163-168.
[12] SCHOCH BS, PADEGIMAS EM, MALTENFORT M, et al. Humeral shaft fractures: national trends in management. J Orthop Traumatol. 2017;18(3):259-263.
[13] 赵益峰,王满宜.肱骨干骨折的治疗进展[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2010,12(10): 973-975.
[14] RÄMÖ L, SUMREIN BO, LEPOLA V, et al. Effect of surgery vs functional bracing on functional outcome among patients with closed displaced humeral shaft fractures: the FISH randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2020;323(18):1792-1801.
[15] KUMAR S, SHANMUGAM N, KUMAR S, et al. Comparison between operative and non operative treatment of fracture shaft of humerus: an outcome analysis. Int J Res Orthop. 2017;3:445-450.
[16] MATSUNAGA FT, TAMAOKI MJ, MATSUMOTO MH, et al. Minimally invasive osteosynthesis with a bridge plate versus a functional brace for humeral shaft fractures: a randomized controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017;99(7):583-592.
[17] HOSSEINI KHAMENEH SM, ABBASIAN M, ABRISHAMKARZADEH H, et al. Humeral shaft fracture: a randomized controlled trial of nonoperative versus operative management (plate fixation). Orthop Res Rev. 2019;11:141-147.
[18] LIAN K, WANG L, LIN D, et al. Minimally invasive plating osteosynthesis for mid-distal third humeral shaft fractures. Orthopedics. 2013;36(8):1025-1032.
[19] BENEGAS E, FERREIRA NETO AA, GRACITELLI ME, et al. Shoulder function after surgical treatment of displaced fractures of the humeral shaft: a randomized trial comparing antegrade intramedullary nailing with minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014;23(6):767-774.
[20] MCCORMACK RG, BRIEN D, BUCKLEY RE, et al. Fixation of fractures of the shaft of the humerus by dynamic compression plate or intramedullary nail. A prospective, randomised trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000; 82(3):336-339.
[21] AKALIN Y, ŞAHIN İG, ÇEVIK N, et al. Locking compression plate fixation versus intramedullary nailing of humeral shaft fractures: which one is better? A single-centre prospective randomized study. Int Orthop. 2020;44(10):2113-2121.
[22] KUMAR R, SINGH P, CHAUDHARY LJ, et al. Humeral shaft fracture management, a prospective study; nailing or plating. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2012;3(1):37-42.
[23] LI Y, WANG C, WANG M, et al. Postoperative malrotation of humeral shaft fracture after plating compared with intramedullary nailing. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011;20(6): 947-954.
[24] CHANGULANI M, JAIN UK, KESWANI T. Comparison of the use of the humerus intramedullary nail and dynamic compression plate for the management of diaphyseal fractures of the humerus. A randomised controlled study. Int Orthop. 2007;31(3):391-395.
[25] KESEMENLI CC, SUBAŞI M, ARSLAN H, et al. Comparison between the results of intramedullary nailing and compression plate fixation in the treatment of humerus fractures. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2003;37(2):120-125.
[26] FAN Y, LI YW, ZHANG HB, et al. Management of humeral shaft fractures with intramedullary interlocking nail versus locking compression plate. Orthopedics. 2015;38(9):825-829.
[27] WALI MG, BABA AN, LATOO IA, et al. Internal fixation of shaft humerus fractures by dynamic compression plate or interlocking intramedullary nail: a prospective, randomised study. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2014;9(3):133-140.
[28] PUTTI AB, UPPIN RB, PUTTI BB. Locked intramedullary nailing versus dynamic compression plating for humeral shaft fractures. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2009; 17(2):139-141.
[29] WANG C, DAI G, WANG S, et al. The function and muscle strength recovery of shoulder after humeral diaphysis fracture following plating and intramedullary nailing. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013;133(8):1089-1094.
[30] SINGISETTI K, AMBEDKAR M. Nailing versus plating in humerus shaft fractures: a prospective comparative study. Int Orthop. 2010;34(4):571-576.
[31] HADHOUD MM, DARWISH AE, MESRIGA M MK. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis versus open reduction and plate fixation of humeral shaft fractures. Menoufia Med J. 2015;28(1):154.
[32] OH CW, BYUN YS, OH JK, et al. Plating of humeral shaft fractures: comparison of standard conventional plating versus minimally invasive plating. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2012;98(1):54-60.
[33] KIM JW, OH CW, BYUN YS, et al. A prospective randomized study of operative treatment for noncomminuted humeral shaft fractures: conventional open plating versus minimal invasive plate osteosynthesis. J Orthop Trauma. 2015;29(4):189-194.
[34] ESMAILIEJAH AA, ABBASIAN MR, SAFDARI F, et al. Treatment of humeral shaft fractures: minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis versus open reduction and internal fixation. Trauma Mon. 2015; 20(3):262-271.
[35] WANG C, LI J, LI Y, et al. Is minimally invasive plating osteosynthesis for humeral shaft fracture advantageous compared with the conventional open technique? J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2015;24(11):1741-1748.
[36] WANG Z, SONG S, GUO Q, et al. Therapeutic effect of anterior approach MIPO combined with LCP in the treatment of humeral shaft fracture. Acta Medica Mediterranea. 2019;35(5):2765-2768.
[37] SARMIENTO A, ZAGORSKI JB, ZYCH GA, et al. Functional bracing for the treatment of fractures of the humeral diaphysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82(4):478-486.
[38] ALI E, GRIFFITHS D, OBI N, et al. Nonoperative treatment of humeral shaft fractures revisited. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2015;24(2):210-214.
[39] 赵峰峰.普通加压钢板与锁定钢板内固定修复老年复杂性肱骨干中下段骨折的生物力学比较[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(26):3909-3915.
[40] 王陶然,袁志,裴国献,等.可膨胀髓内钉与锁定加压钢板治疗肱骨干骨折的疗效比较[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2017, 19(7):566-571.
[41] PAPASOULIS E, DROSOS GI, VERVERIDIS AN, et al. Functional bracing of humeral shaft fractures. A review of clinical studies. Injury. 2010;41(7):21-27.
[42] HOHMANN E, GLATT V, TETSWORTH K. Minimally invasive plating versus either open reduction and plate fixation or intramedullary nailing of humeral shaft fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2016;25(10): 1634-1642.
[43] SARGEANT HW, FARROW L, BARKER S, et al. Operative versus non-operative treatment of humeral shaft fractures: a systematic review. Shoulder Elbow. 2020;12(4): 229-242.
|