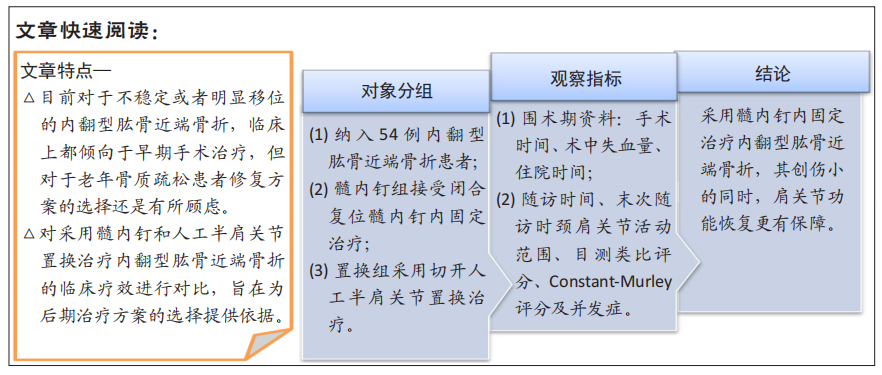
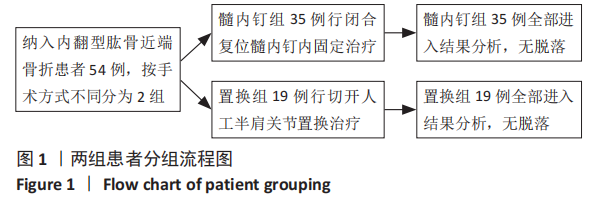
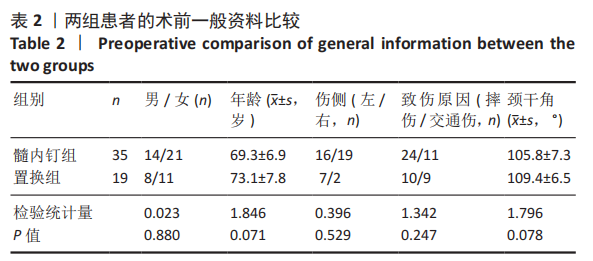
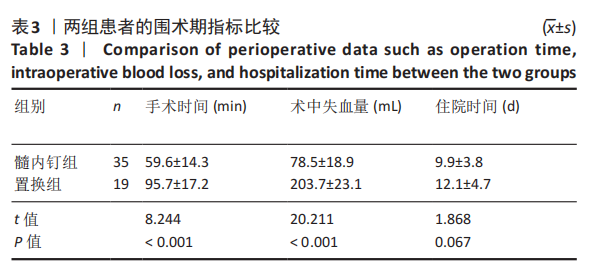
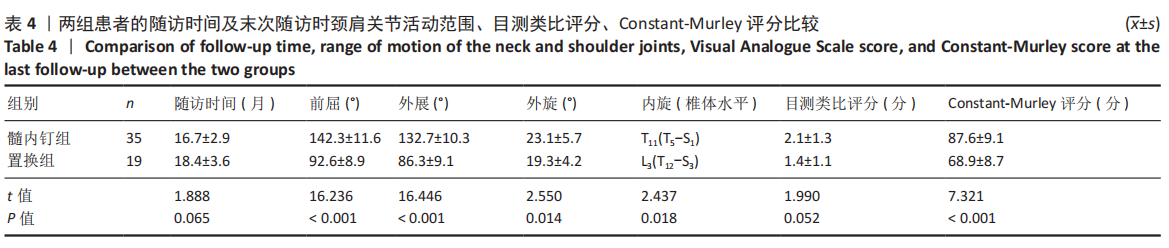
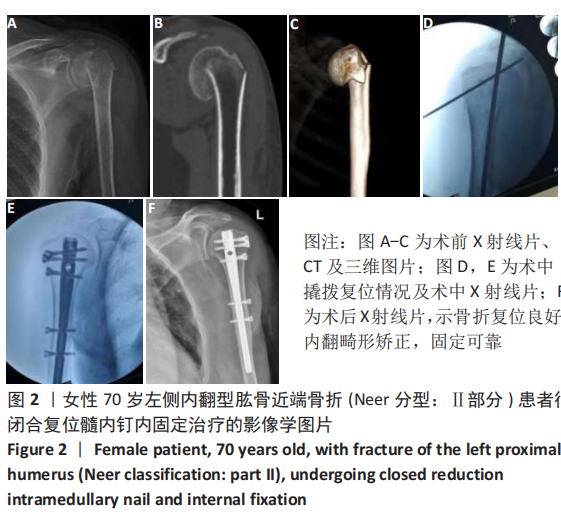
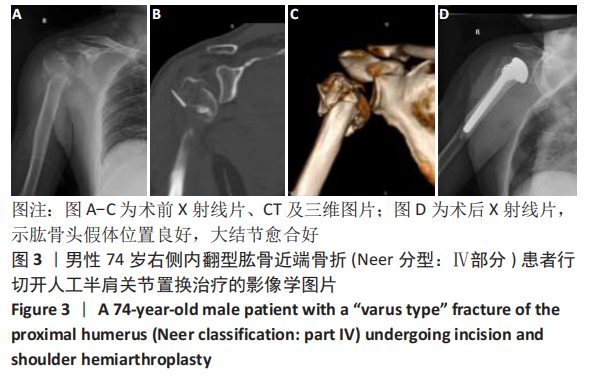
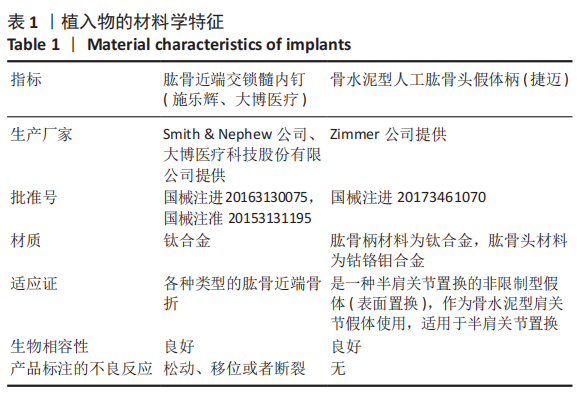
[1] MARAVIC M, BRIOT K, ROUX C. Burden of proximal humerus fractures in the French National Hospital Database. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2014;100(8): 931-934.
[2] 谢麟臻, 陈春慧, 陈华. 肱骨近端骨折的治疗进展[J]. 中华肩肘外科电子杂志, 2020,8(2):186-190.
[3] JOCKEL JA, BRUNNER A, THORMANN S, et al. Elastic stabilization of proximal humeral fractures with a new percutaneous angular stable fixation device: a preliminary report. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2010;130(11):1397-1403.
[4] 王华松, 杨晨曦, 吴刚,等. 经三角肌入路锁定钢板内固定治疗老年外展嵌插型肱骨近端骨折[J]. 中华创伤杂志,2020,36(3):228-232.
[5] LESCHEID J, ZDERO R, SHAH S, et al. The biomechanics of locked plating for repairing proximal humerus fractures with or without medial cortical support. J Trauma. 2010;69(5):1235-1242.
[6] 何继业, 张家红, 蔡贵泉,等. 锁定钢板治疗不稳定肱骨近端骨折术后内翻的危险因素分析[J]. 中华创伤杂志,2020,36(5):448-454.
[7] 周君琳, 王东. 肱骨近端骨折切开复位锁定接骨板治疗后内固定失效的预防策略[J]. 中国医刊,2020,55(7):700-703.
[8] 石华峰, 王庆伟, 王华松, 等. 钢板与髓内钉治疗“内翻型”肱骨近端骨折的对比[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2019,27(12):1078-1082.
[9] 石华峰, 王庆伟, 黄继锋,等. 闭合复位Trigen髓内钉治疗”内翻型”肱骨近端骨折[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2020,26(4):64-67.
[10] 刘磊, 邵佳申, 郭家良, 等. 2010年至2011年中国东部和西部地区成人肱骨近端骨折的流行病学对比分析[J] . 中华创伤骨科杂志,2017,19(1):70-74.
[11] 向明, 胡晓川, 姜春岩. 重视整体观念,提高肱骨近端骨折诊治水平[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2017,37(21):1313-1317.
[12] 李刚, 魏万富, 刘欣,等. 髓内钉与锁定钢板治疗老年肱骨近端骨折疗效比较[J]. 中华医学杂志,2020,100(41):3240-3245.
[13] 鲁谊, 朱以明, 姜春岩,等. 锁定钢板治疗肱骨近端骨折的并发症分析[J]. 中华创伤杂志,2008,24(10):808-813.
[14] 石华峰, 王庆伟, 王华松,等. 青壮年患者肱骨近端严重骨折脱位的内固定治疗[J]. 中华肩肘外科电子杂志,2019,7(4):26-31.
[15] 田旭, 向明, 王广宇,等. 反肩关节假体置换治疗老年复杂肱骨近端骨折的早期疗效评价[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2020,40(1):10-16.
[16] 李奉龙, 姜春岩, 鲁谊,等. 采用分期反肩置换手术治疗肱骨近端骨折术后感染的疗效分析[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版),2016,48(2):263-267.
[17] BOILEAU P, KRISHNAN SG, TINSI L, et al. Tuberosity malposition and migration: reasons for poor outcomes after hemiarthroplasty for displaced fractures of the proximal humerus. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2002;11(5):401-412.
[18] CASTRICINI R, BENEDETTO MD, PIRANI P, et al. Shoulder hemiarthroplasty for fractures of the proximal humerus. Musculoskeletal Surg. 2011;95(Suppl 1): 49-54.
[19] NEER CS. Four-segment classification of proximal humeral fractures: Purpose and reliable use. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2002;11(4):389-400.
[20] JO MJ, GARDNER MJ. Proximal humerus fractures. Tech Orthop. 2012;5(3): 192-198.
[21] 葛鸿庆, 郑沐欣, 管华. 锁定钢板联合异体腓骨支撑治疗老年内翻型肱骨近端骨折[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2019,21(5):440-442.
[22] 郭家良, 王海立, 董维冲,等. 老年肱骨近端骨折的治疗与康复研究进展[J]. 中华老年骨科与康复电子杂志 ,2020,5(4):233-237.
[23] 李刚, 魏万富, 刘欣,等. 髓内钉与锁定钢板治疗老年肱骨近端骨折疗效比较[J]. 中华医学杂志,2020,100(41):3240-3245.
[24] 曾浪清, 陈云丰, 唐三元, 等. 不同内侧柱支撑重建对锁定钢板固定治疗肱骨近端骨折的影响[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2014,16(1):6-11.
[25] 葛鸿庆, 刘炎, 管华,等. 肱骨近端骨折3种不同固定方式重建内侧柱的有限元分析[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2021,36(1):25-28.
[26] CHOI S, KANG H, BANG H. Technical tips: Dualplate fixation technique for comminuted proximal humerus fractures. Injury. 2014;45(8):1280-1282.
[27] HE Y, ZHANG Y, WANG Y, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of a novel dualplate fixation method for proximal humeral fractures without medial support. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1):72-81.
[28] GARDNER MJ, BORAIAH S, HELFET DL, et al. Indirect medial reduction and strut Support of proximal humerus fractures using an endosteal implant. J Orthop Trauma. 2008;22(3):195-200.
[29] HINDS RM, GARNER MR, TRAN WH, et al. Geriatric proximal humeral fracture patients show similar clinical outcomes to non-geriatric patients after osteosynthesis with endosteal fibular strut allograft augmentation. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2015;24(6):889-896.
[30] 张军, 庄云强, 李东贞, 等. 锁定钢板结合异体腓骨支撑治疗老年肱骨近端Neer三、四部分骨折[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2018,20(11):946-952.
[31] 游小军, 路考生, 韩月起, 等. 锁定钢板结合自体大块髂骨治疗老年复杂肱骨近端骨折的疗效[J]. 中华创伤杂志,2020,36(3):222-227.
[32] 向成浩,刘鸿,杨朝晖,等. 内侧柱支撑重建在肱骨近端骨折稳定性中的生物力学研究[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2020,35(11):35-37.
[33] 向明, 杨国勇, 邹义源, 等. 锁定钢板与髓内钉治疗肱骨近端骨折的疗效比较 [J] . 中华骨科杂志,2017,37(21):1333-1341.
[34] 崔崟, 王秀会, 王明辉,等. TriGen交锁髓内钉联合带线锚钉治疗Neer eer型肱骨近端骨折[J]. 中华手外科杂志,2020,36(1):16-19.
[35] 杨旭庆,王庆贤. 肱骨近端骨折的解剖学研究进展及治疗现状[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2020,35(11):113-115.
[36] LANTING B, MACDERMID J, DROSDOWECH D, et al. Proximal humeral fractures: a systematic review of treatment modalities. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008;17(1): 42-54.
[37] 王华松, 王庆伟, 丁然,等. 锁定钢板与髓内钉治疗肱骨近端骨折的疗效对比[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2017,25(20):1899-1901.
[38] 安庆, 张敬标, 李伟峰,等. 半肩置换治疗老年肱骨近端骨折疗效分析[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2020,14(1):92-96.
[39] 姜春岩. 关于人工肩关节置换的相关热点问题[J]. 中华创伤杂志,2017,33(8): 684-686.
[40] 袁礼波, 金涛, 徐永清. 肱骨头置换术中肱骨大结节固定及肩袖修复研究进展[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2020,34(2):127-130.
|