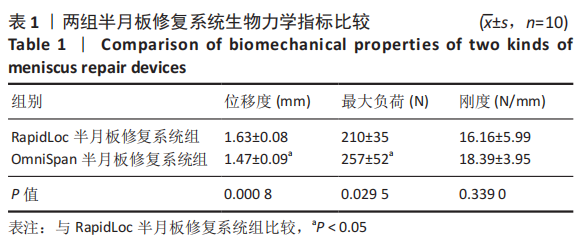
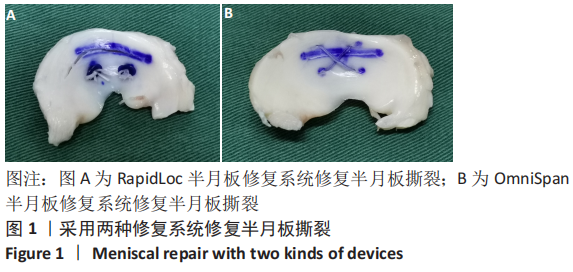
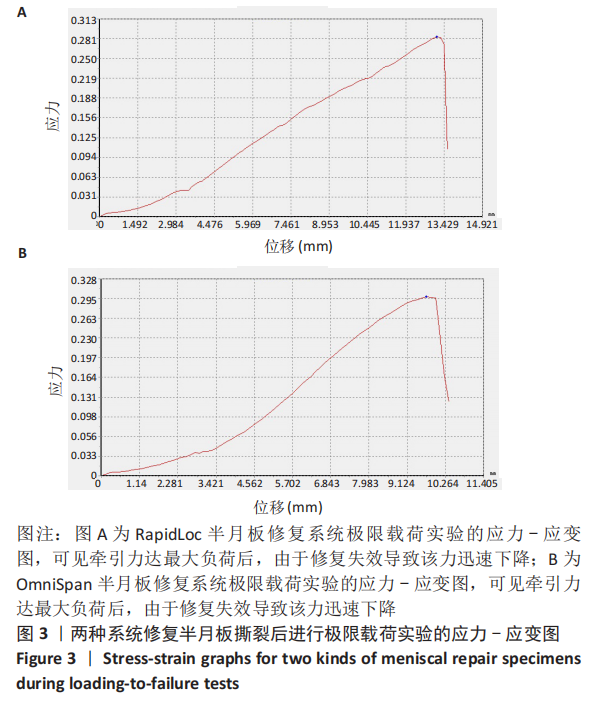
[1] MAFFULLI N, LONGO UG, CAMPI S, et al. Meniscal tears. Open Access J Sports Med. 2010;1:45-54.
[2] BADLANI JT, BORRERO C, GOLLA S, et al. The effects of meniscus injury on the development of knee osteoarthritis: data from the osteoarthritis initiative. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(6):1238-1244.
[3] ENGLUND M, LOHMANDER LS. Risk factors for symptomatic knee osteoarthritis fifteen to twenty-two years after meniscectomy. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50(9): 2811-2819.
[4] BARBER FA, HERBERT MA, RICHARDS DP. Load to failure testing of new meniscal repair devices. Arthroscopy. 2004;20(1):45-50.
[5] HUPPERICH A, SALZMANN GM, NIEMEYER P, et al. What are the factors to affect outcome and healing of meniscus bucket handle tears? Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2018;138(10):1365-1373.
[6] ROSSO C, MÜLLER S, BUCKLAND DM, et al. All-inside meniscal repair devices compared with their matched inside-out vertical mattress suture repair: introducing 10,000 and 100,000 loading cycles. Am J Sports Med. 2014;42(9):2226-2233.
[7] NAKAMA GY, KALEKA CC, FRANCIOZI CE, et al. Biomechanical comparison of vertical mattress and cross-stitch suture techniques and single- and double-row configurations for the treatment of bucket-handle medial meniscal tears. Am J Sports Med. 2019;47(5):1194-1202.
[8] 陆伟,王大平,韩云,等.关节镜下RapidLoc与FasTFix缝合器修复内侧半月板后角损伤40例[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(48):9465-9468.
[9] 刘聚,明立德,许建中,等.关节镜下Omnispan系统与FAST-fix 360°系统缝合修复内外侧半月板损伤[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2019,34(2):165-167.
[10] 刘晓晖,华国军,王星亮,等.关节镜下Omnispan缝合技术治疗半月板损伤[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2020,35(12):1304-1306.
[11] RAMAPPA AJ, CHEN A, HERTZ B, et al. A biomechanical evaluation of all-inside 2-stitch meniscal repair devices with matched inside-out suture repair. Am J Sports Med. 2014;42(1):194-199.
[12] 耿云航,刘晓阳,徐强.半月板损伤修复的研究进展[J].青岛大学医学院学报, 2017,53(6):727-732.
[13] ARNOCZKY SP, WARREN RF. Microvasculature of the human meniscus. Am J Sports Med. 1982;10(2):90-95.
[14] 李箭,蒋欣,裴福兴,等.膝关节半月板血供的应用解剖学研究[J].临床外科杂志,2003,11(5):335-336.
[15] CHAHLA J, PAPALAMPROU A, CHAN V, et al. Assessing the resident progenitor cell population and vascularity of the adult human meniscus. Arthroscopy. 2021; 37(1):252-265.
[16] BARBER-WESTIN SD, NOYES FR. Clinical healing rates of meniscus repairs of tears in the central-third (red-white) zone. Arthroscopy. 2014;30(1):134-146.
[17] LEE CS, TASTO JP, HEALEY RM, et al. Radiofrequency stimulation for potential healing of meniscal injuries in the avascular zone. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2014;43(12):E292-E298.
[18] 周伟峰,朱琳,姜雪峰,等.射频联合富血小板血浆修复半月板白区撕裂[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(20):3123-3128.
[19] COHEN SB, BOYD L, MILLER MD. Vascular risk associated with meniscal repair using Rapidloc versus FasT-Fix: comparison of two all-inside meniscal devices. Knee Surg. 2007;20(3):235-240.
[20] KALLIAKMANIS A, ZOURNTOS S, BOUSGAS D, et al. Comparison of arthroscopic meniscal repair results using 3 different meniscal repair devices in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction patients. Arthroscopy. 2008;24(7):810-816.
[21] FISHER SR, MARKEL DC, KOMAN JD, et al. Pull-out and shear failure strengths of arthroscopic meniscal repair systems. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2002;10(5):294-299.
[22] RIMMER MG, NAWANA NS, KEENE GC, et al. Failure strengths of different meniscal suturing techniques. Arthroscopy.1995;11(2):146-150.
[23] UZUN E, MISIR A, KIZKAPAN TB, et al. Evaluation of midterm clinical and radiographic outcomes of arthroscopically repaired vertical longitudinal and bucket-handle lateral meniscal tears. Orthop J Sports Med. 2019;7(5):1-8.
[24] MATTHEWS JR, WANG J, ZHAO J, et al. The influence of suture materials on the biomechanical behavior of suture-meniscal specimens:a comparative study in a porcine model. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2020;32(1):42.
[25] SWEIGART MA, ZHU CF, BURT DM, et al. Intraspecies and interspecies comparison of the compressive properties of the medial meniscus. Ann Biomed Eng. 2004; 32(11):1569-1579.
[26] HANG G, YEW AKS, CHOU SM, et al. Biomechanical comparison of vertical suture techniques for repairing radial meniscus tear. J Exp Orthop. 2020;7(1):77.
[27] MATSUBARA H, OKAZAKI K, IZAWA T, et al. New suture method for radial tears of the meniscus biomechanical analysis of cross-suture and double horizontal suture techniques using cyclic load testing. Am J Sports Med. 2012;40(2):414-418.
[28] WARNECKE D, BALKO J, HAAS J, et al. Degeneration alters the biomechanical properties and structural composition of lateral human menisci. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(11):1482-1491.
[29] BARBER FA, HOWARD MS, ASHRAF W, et al. The Biomechanical performance of the latest all-inside meniscal repair devices. Arthroscopy. 2020;36(12):3001-3007.
[30] 王小武,黄晓华,张鹏,等.关节镜下应用FasT-Fix缝合器治疗半月板桶柄样撕裂损伤[J].临床骨科杂志,2019,22(4):437-439.
[31] BECKER R, STARKE C, HEYMANN M, et al. Biomechanical properties under cyclic loading of seven meniscus repair techniques. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;400: 236-245.
[32] DOIG T, FAGAN P, FRUSH T, et al. The all-inside all-suture technique demonstrated better biomechanical behaviors in meniscus radial tear repair. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020;28(11):3606-3612.
[33] ZANTOP T, EGGERS AK, MUSAHL V, et al. Cyclic testing of flexible all-inside meniscus suture anchors: biomechanical analysis. Am J Sports Med. 2005;33(3):388-394.
[34] ARDIZZONE CA, HOUCK DA, MCCARTNEY DW, et al. All-inside repair of bucket-handle meniscal tears:clinical outcomes and prognostic factors. Am J Sports Med. 2020;48(13):3386-3393.
[35] SOLHEIM E, HEGNA J, INDERHAUG E. Long-term outcome after all-inside meniscal repair using the RapidLoc system. 2016;24(5):1495-1500.
[36] GLIATIS J, KOUZELIS A, PANAGOPOULOS A, et al. Chondral injury due to migration of a Mitek RapidLoc meniscal repair implant after successful meniscal repair: a case report. Knee Surg Sports Traumatoi Arthrosc. 2005;13(4):280-282.
[37] VENJAKOB AJ, FÖHR P, HENKE F, et al. Influence of sutures on cartilage integrity: do meniscus sutures harm cartilage? An experimental animal study. Arthroscopy. 2019;35(5):1509-1516.
|