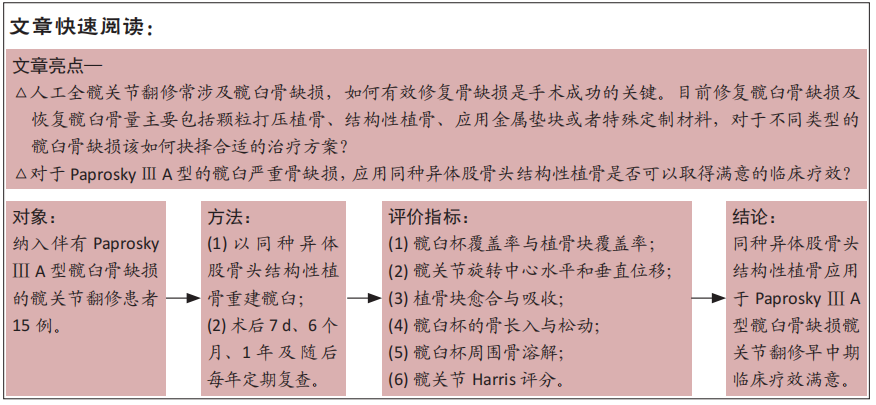
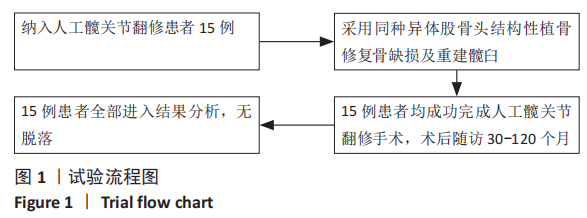
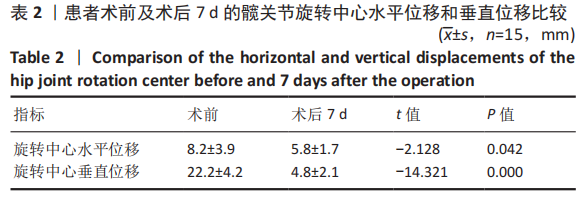
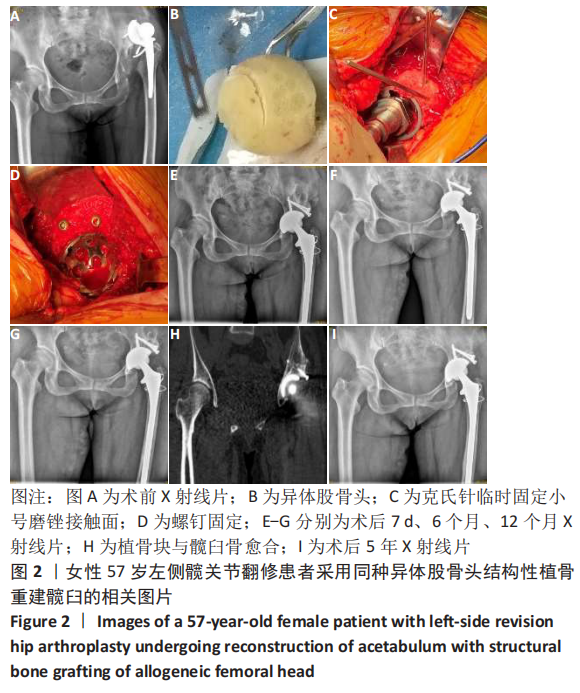
[1] KURTZ S, ONG K, LAU E, et al. Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89:780-785.
[2] HASENAUER MD, PAPROSKY WG, SHETH NP. Treatment options for chronic pelvic discontinuity. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2018;9(1):58-62.
[3] SHETH NP, PAPROSKY WG, MELNIC CM. Management of chronic pelvic discontinuity in revision total hip arthroplasty. Instr Course Lect. 2018;67: 215-222.
[4] 潘昭勋,孙超,杨振雷,等.全髋翻修髋臼骨缺损中颗粒打压植骨的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,35(17):6249-6253.
[5] BOZIC KJ, KURTZ SM, LAU E, et al. The epidemiology of revision total hip arthroplasty in the United States.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(1):128-133.
[6] 康鹏德,裴福兴.髋关节翻修中骨盆不连续的评估与重建[J].中华骨科杂志,2020,9(40):614-623.
[7] FERNANDEZ-VALENCIA JÁ, GALLART X, TOMÁS X, et al. Radiography versus multidetector computed tomography in assessing graft integration after acetabular reconstruction. J Orthop Surg. 2015;23(3):370-374.
[8] 吴浩波,朱晗晓,严世贵,等.Jumbo臼杯在全髋关节翻修术髋臼骨缺损重建中的应用[J].中华骨科杂志,2016,23(36):1471-1477.
[9] SHIBUYA N, JUPITER DC. Bone graft substitute:allograft and xenograft. Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 2015;32(1):21-34.
[10] KIM YL, NAM KW, YOO JJ, et al. Colyloplasty in cementless total hip arthroplasty for an insufficient acetabulum. Clin Orthop Surg. 2010;2(3):148-153.
[11] MARUYAMA M, WAKABAYASHI S, OTA H, et al. Reconstruction of the shallow acetabulum with a combination of autologous bulk and impaction bone grafting fixed by cement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017;475(2):387-395.
[12] VON ROTH P, ABDEL MP, HARMSEN WS, et al. Uncemented jumbo cups for revision total hip arthroplasty:a concise follow-up at a mean of twenty years of a previous report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97(4):284-287.
[13] MOORE MS, MCAULEY JP, YOUNG AM, et al. Radiographic signs of osseointegration in porous-coated acetabular components. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;(444):176-183.
[14] 查国春,孙俊英,冯硕,等.髋臼外上方结构性植骨在髋关节发育不良全髋关节置换术中的应用[J].中华骨科杂志,2017,23(37):1449-1455.
[15] 卢群山,张元凯.全髋关节置换后假体松动1例报道[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2018,11(3):219-221.
[16] DELEE JG, CHARNLEY J. Radiological demarcation of cemented sockets in total hip replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976;(121):20-32.
[17] 付君,李想,倪明,等.髋臼加强型抗生素骨水泥占位器在假体周围感染髋臼骨缺损翻修中的应用[J].中华骨科杂志,2018,38(3):143-149.
[18] 周建生,王志岩,肖玉周,等.人工髋关节翻修旋转中心重建的临床研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2011,31(5):475-480.
[19] REGIS D, MAGNAN B, SANDFI A, et al. Long-term results of antiprotrusion cage and massive allografts for the management of periprosthetie aeetabular bone loss. J Arthroplasty. 2008;23(6):826-832.
[20] 戴尅戎,朱振安,孙月华,等.翻修手术时髋臼巨大骨缺损的重建[J].中华骨科杂志,2001,21(6):332-336.
[21] HORSTMANN T, LISTRINGHAUS R, BRAUNER T, et al.Minimizing preoperative and postoperative limping in patients after total hip arthroplasty: Relevance of hip muscle strength and endurance. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2013;92(12):1060-1069.
[22] VON ROTH P, ABDEL MP, HARMSEN WS, et aI. Uncemented jumbo cups for revision total hip arthroplasty:a concise follow-up at a mean of twenty years of a previous report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97(4):284-287.
[23] LACHIEWICZ PF, SOILEAU ES. Fixation,survival,and dislocation of jumbo acetabular components in revision hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(6):543-548.
[24] GUSTKE KA, LEVERING MF, MIRANDA MA. Use of jumbo cups for revision of acetabulae with large bony defects. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(1):199-203.
[25] HORII M, KUBO T, INOUE S, et al. Coverage of the femoral head by the acetabular labrum in dysplastic hips: quantitative analysis with radial MR imaging. Acta Orthop Scand. 2003;74(3):287-292.
[26] WHITEHOUSE MR, MASRI BA, DUNCAN CP, et al. Continued good results with modular trabecalar metal augments for acetabular defects in hip rathroplast at 7 to 11 years. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473(2):521-527.
[27] SPORER SM, VALLE CJ. Porous metal augments:big hopers for big holes. Orthopedics. 2010;33(9):651.
[28] WADDELL BS, DELLA VALLE AG. Reconstruction of noncontained acetabular defects with impation grafting,a reinforement meshand a cemented polyetabular compomnet. Bone Joint J. 2017;99-B(1 supple A):25-30.
[29] GARIAREY E, MADERO R, GARACIACIMBRELO E. THA rebisions using impaction allografting with mesh is durable for medial but not lateral acrbular defects.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473(12):1-10.
[30] ZHA GC, SUN JY, GUO KJ, et al. Medial protrusio technique in cementless total hip arthroplasty for developmental dysplasia of the hip: a prospective 6- to 9-year follow-up of 43 Consecutive patients. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(8):1761-1766.
[31] MULROY JR RD, HARRIS WH. Failure of acetabular autogenous grafts in total hip arthroplasty. Increasing incidence: a follow-up note. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1990;72(10):1536-1540.
[32] 翟吉良,翁习生,林进,等.自体股骨头重建髋臼治疗髋关节发育不良的中期疗效[J].中华骨科杂志,2015,35(4):401-406.
[33] GAZDAG AR, LANE JM, GLASER D, et al. Alternatives to autogenous bone graft: efficacy and indications. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1995;3:1-8.
[34] KHAN SN, CAMMISA FP, SANDHU HS, et al. The biology of bone grafting. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2005;13:77-86.
[35] HERNAN A, PRIETO MD, MICHAEL E, et al. Structural Allograft Supporting a Trabecular Metal Cup Provides. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32:3488-3494.
[36] SCHUBERT AG, KEMPF J, HEIDERSCHEIT BC. Influence of stride frequency and length on running mechanics:a systematic review. Sports Health. 2014; 6(3):210-217.
[37] 周宗科,裴福兴,程惊秋,等.同种异体皮质骨板移植免疫学研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2005,13(3):201-203.
|