[1] TARRANT SM, BALOGH ZJ. The Global Burden of Surgical Management of Osteoporotic Fractures. World J Surg. 2020; 44(4):1009-1019.
[2] KHAN AM, TANG QO, SPICER D. The epidemiology of adult distal femoral shaft fractures in a central london major trauma centre over five years. Open Orthop J. 2017; 11:1277-1291.
[3] TSUDA T. Epidemiology of fragility fractures and fall prevention in the elderly: a systematic review of the literature. Curr Orthop Pract. 2017;28(6):580-585.
[4] LOOSEN A, FRITZ Y, DIETRICH M. Surgical treatment of distal femur fractures in geriatric patients. Geriatr Orthop Surg Rehabil. 2019;2;10:2151459319860723.
[5] 李英超,郝宝辉,王兵,等.股骨远端骨折治疗的研究进展[J].中国老年学杂志, 2018,38(7):1773-1175.
[6] CHEN J, LU H. Current status and progress of clinical research on distal femoral fractures. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018;15;32(2):242-247.
[7] 孙磊,李东.顺行交锁髓内钉内固定治疗股骨骨折疗效观察[J].中国药物经济学, 2013,(z1):123-124.
[8] 王笑磊. 顺行交锁髓内钉内固定治疗股骨骨折的疗效观察[J].中国医药科学,2011, 1(6):130-131.
[9] 吕宇明,蒋云楼,罗国富.顺行和逆行交锁髓内钉对股骨中下段骨折的疗效观察[J].当代医学,2019,25(20):50-51.
[10] 潘立波.逆行交锁髓内钉治疗股骨远端骨折的临床疗效[J].世界最新医学信息文摘,2018,18(78):62.
[11] HUSSAIN N, HUSSAIN FN, SERMER C, et al. Antegrade versus retrograde nailing techniques and trochanteric versus piriformis intramedullary nailing entry points for femoral shaft fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Can J Surg. 2017;60(1):19-29.
[12] HIGGINS J, GREEN S. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0. The Cochrane Collaboration 2011 [2012-03-30]. http://www.cochrane-handbook.org.
[13] 文进,李幼平.Meta分析中效应尺度指标的选择[J].中国循证医学杂志,2007, 7(8):606-613.
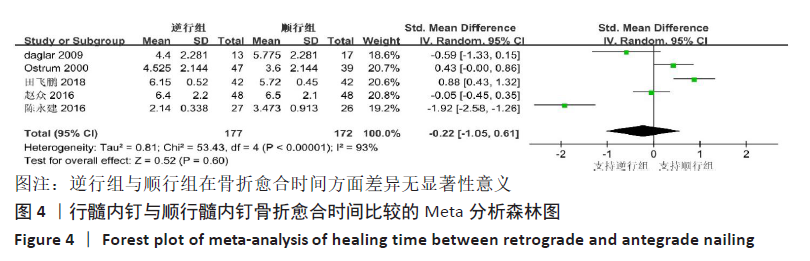
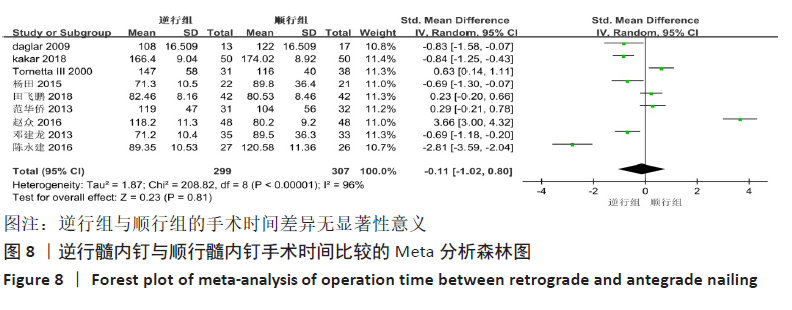
[14] 赵众.用顺行交锁髓内钉内固定术治疗股骨骨折的效果研究[J].当代医药论丛, 2016,14(18):33-34.
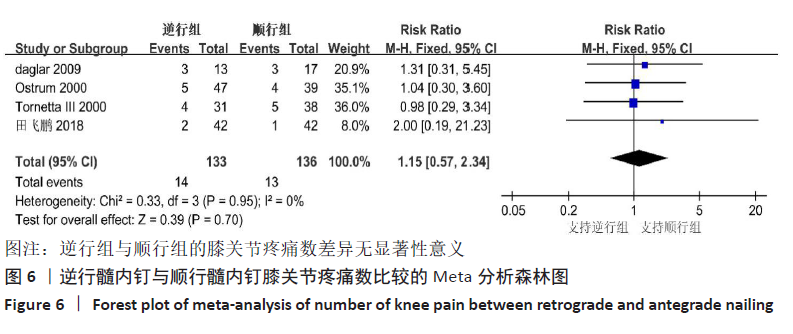
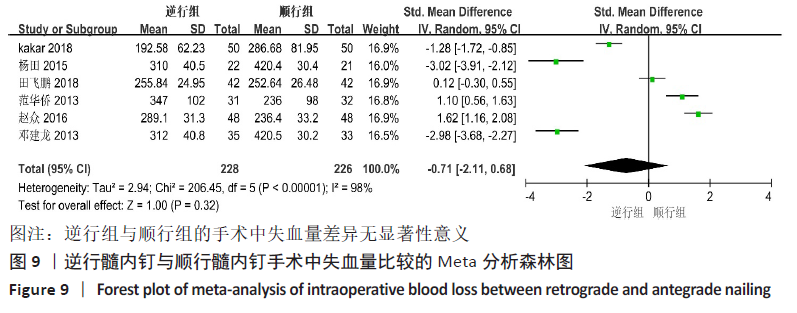
[15] 田飞鹏,高长奎,王喜娟,等.顺行交锁髓内钉内固定治疗股骨骨折的效果[J].临床医学研究与实践,2018,3(36):46-47.
[16] 范华侨.三种内固定方式治疗股骨远端骨折的疗效比较[J].中国医疗前沿,2013, 8(9):56-59.
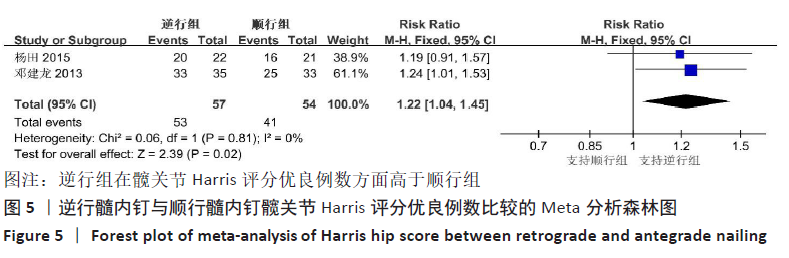
[17] 杨田.三种内固定处理股骨远端骨折的临床疗效比较[J].中国医学创新,2015, 12(35):148-150.
[18] 邓建龙,王剑敏,张茗慧,等.顺行髓内钉、逆行髓内钉及锁定加压钢板内固定治疗股骨远端骨折的对比研究[J].现代生物医学进展,2013,13(24):4687-4690.
[19] 陈永建.带锁髓内钉治疗新鲜四肢长骨干骨折疗效分析[J].中国农村卫生,2016 (18):20-21.
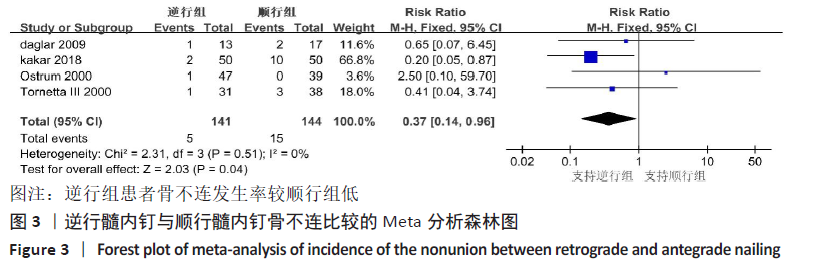
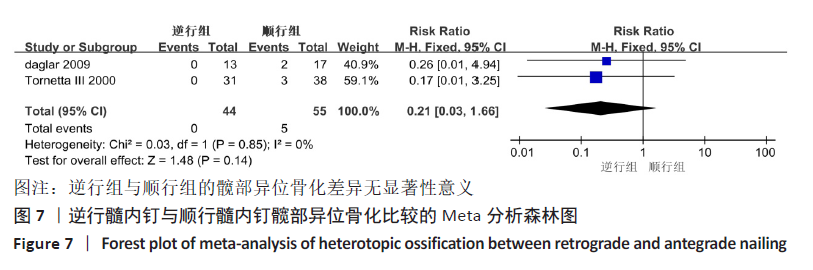
[20] TORNETTA P 3RD, TIBURZI D. Antegrade or retrograde reamed femoral nailing. A prospective, randomised trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br Vol. 2000;82(5):652-654.
[21] OSTRUM RF, AGARWAL A, LAKATOS R, et al. Prospective comparison of retrograde and antegrade femoral intramedullary nailing. J Orthop Trauma. 2000;14(7):496-501.
[22] DAGLAR B, GUNGOR E, DELIALIOGLU OM, et al. Comparison of knee function after antegrade and retrograde intramedullary nailing for diaphyseal femoral fractures: results of isokinetic evaluation. J Orthop Trauma. 2009;23(9):640-644.
[23] KAKAR LM, ISHAQ M, ANJUM RS. Management of diaphyseal fracture of femoral with antegrade and retrograde nailing: a comparative trial. Pak J Med Health Sci. 2018;12(4):1679-1681.
[24] RICCI WM, GALLAGHER B, HAIDUKEWYCH GJ. Intramedullary nailing of femoral shaft fractures: current concepts. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2009;17(5):296-305.
[25] SANDERS R, KOVAL KJ, DIPASQUALE T, et al. Retrograde reamed femoral nailing. J Orthop Trauma. 2014;28(8 SUPPL):S15-S24.
[26] RICCI WM, BELLABARBA C, EVANOFF B, et al. Retrograde versus antegrade nailing of femoral shaft fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2001;15(3):161-169.
[27] MURRAY P, BERGIN P, LABROPOULOS P, et al. Retrograde femoral nailing and knee function. Orthopedics. 2008;31(10):985.
[28] YU CK, SINGH VA, MARIAPAN S, et al. Antegrade versus retrograde locked intramedullary nailing for femoral fractures: which is better? Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2007;33(2):135-140.
[29] EL MOUMNI M, VOOGD EH, TEN DUIS HJ, et al. Long-term functional outcome following intramedullary nailing of femoral shaft fractures. Injury. 2012;43(7):1154-1158.
[30] DOUGHERTY PJ, GHEREBEH P, ZEKAJ M, et al. Retrograde versus antegrade intramedullary nailing of gunshot diaphyseal femoral fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(12):3974-3980.
[31] ANSARI MOEIN CM, VERHOFSTAD MH, BLEYS RL, et al. Soft tissue anatomy around the hip and its implications for choice of entry point in antegrade femoral nailing. Clin Anat. 2008;21(6):568-574.
[32] HELMY N, JANDO VT, LU T, et al. Muscle function and functional outcome following standard antegrade reamed intramedullary nailing of isolated femoral shaft fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2008;22(1):10-15.
[33] ARCHDEACON M, FORD KR, WYRICK J, et al. A prospective functional outcome and motion analysis evaluation of the hip abductors after femoral fracture and antegrade nailing. J Orthop Trauma. 2008; 22(1):3-9.
[34] 吕宇明,蒋云楼,罗国富.顺行和逆行交锁髓内钉对股骨中下段骨折的疗效观察[J].当代医学,2019,25(20):50-51.
[35] 关继奎. 股骨远端骨折不同内固定方法的生物力学分析[D]:长春:吉林大学,2005.
[36] DEY D, WHEATLEY BM, CHOLOK D, et al. The traumatic bone: trauma-induced heterotopic ossification. Transl Res. 2017; 186:95-111. |