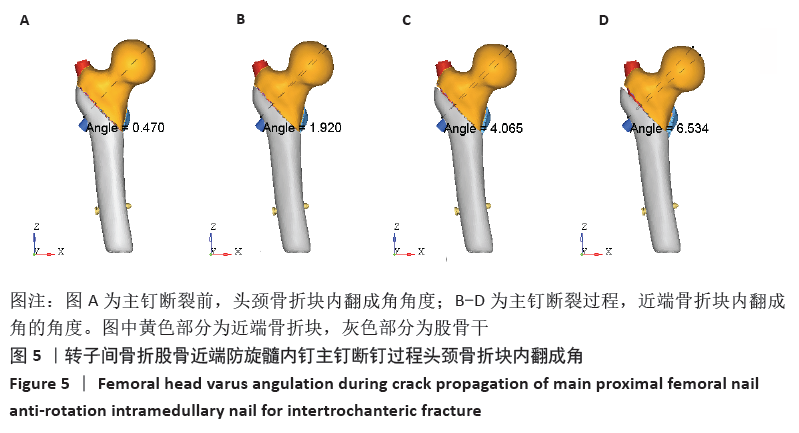
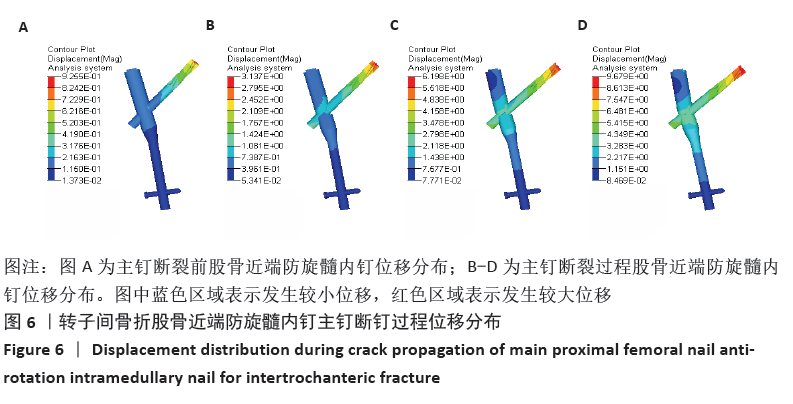
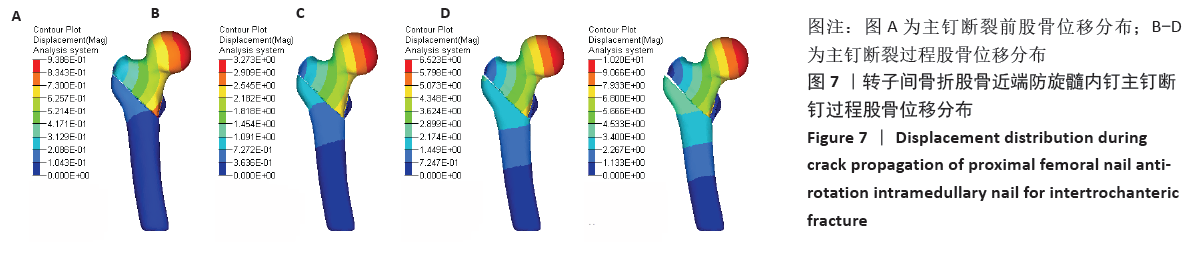
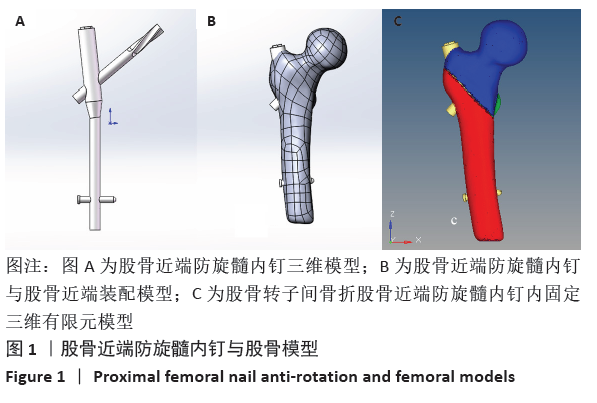
[1] WANG J, MA J, LU B, et al. Comparative finite element analysis of three implants fixing stable and unstable subtrochanteric femoral fractures: Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation (PFNA), Proximal Femoral Locking Plate (PFLP), and Reverse Less Invasive Stabilization System (LISS). Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2020;106(1):95-101.
[2] LI J, HAN L, ZHANG H, et al. Medial sustainable nail versus proximal femoral nail antirotation in treating AO/OTA 31-A2.3 fractures: Finite element analysis and biomechanical evaluation. Injury. 2019;50(3): 648-656.
[3] SHUANG L, SUN G, CHANG S, et al. Simulated postoperative weight-bearing after fixation of a severe osteoporotic intertrochanteric fracture. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2017;10(5):8438-8448.
[4] LEE PY, LIN KJ, WEI HW, et al. Biomechanical effect of different femoral neck blade position on the fixation of intertrochanteric fracture: a finite element analysis. Biomed Tech (Berl). 2016;61(3):331-336.
[5] 郑利钦,陈心敏,张彪,等.股骨转子间骨折股骨近端防旋髓内钉内固定切割失效的有限元仿真[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(36): 5794-5799.
[6] 于沂阳,李石伦,陈伟,等.中国北方和南方地区2010-2011年60岁以上人群股骨转子间骨折流行病学对比[J].中华老年骨科与康复电子杂志,2017,3(1):55-58.
[7] 林梓凌,李鹏飞,庞智晖,等.骨密度与老年髋部骨折股骨近端三维有限元模型密度的关系[J].中国老年学杂志,2015,35(11):3069-3070.
[8] 郑利钦,林梓凌,李鹏飞,等.动态载荷下松质骨对骨质疏松性股骨颈骨折断裂力学影响的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2019,23(12):1887-1892.
[9] LOTZ JC, GERHART TN, HAYES WC. Mechanical properties of trabecular bone from the proximal femur: a quantitative CT study. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1990;14(1):107-114.
[10] LOTZ JC, GERHART TN, HAYES WC. Mechanical properties of metaphyseal bone in the proximal femur. J Biomech. 1991;24(5):317-329.
[11] CHOY W, KIM KJ, LEE SK, et al. Implant failure of long proximal femoral nail antirotation in patient with subtrochanteric pathologic fracture. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2012;(22):609-612.
[12] LI Z, KINDIG MW, KERRIGAN JR, et al. Rib fractures under anterior–posterior dynamic loads: experimental and finite-element study. J Biomech. 2010;43(2):228-234.
[13] KHOR F, CRONIN DS, WATSON B, et al. Importance of asymmetry and anisotropy in predicting cortical bone response and fracture using human body model femur in three-point bending and axial rotation. J Mech Behav Biomed. 2018;87:213-229.
[14] EBERLE S, GERBER C, VON OLDENBURG G, et al. Type of hip fracture determines load share in intramedullary osteosynthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467(8):1972-1980.
[15] NUNO N, AMABILI M, GROPPETTI R, et al. Static coefficient of friction between Ti-6Al-4V and PMMA for cemented hip and knee implants. J Biomed Mater Res. 2002;59(1):191-200.
[16] MORGAN EF, KEAVENY TM. Dependence of yield strain of human trabecular bone on anatomic site. J Biomech. 2001;34:569-577.
[17] MA Z, CHEN J, LAN F. Biomechanical response and injury of occupant’s pelvis in side impacts: effects of the femoral head and loading conditions. J Mech Med Biol. 2014;14(6):1440001.
[18] BAYRAKTAR HH, MORGAN EF, NIEBUR GL, et al. Comparison of the elastic and yield properties of human femoral trabecular and cortical bone tissue. J Biomech. 2004;37(1):27-35.
[19] SHIBO G, XUANHUI Q, XINBO H, et al. Powder injection molding of Ti–6Al–4V alloy. J Mater Process Tech. 2006;173(3):310-314.
[20] NIINOMI M. Mechanical properties of biomedical titanium alloys. Mat Sci Eng A-Struct. 1998;243(1):231-236.
[21] CARNEY KS, PEREIRA JM, REVILOCK DM, et al. Jet engine fan blade containment using an alternate geometry. Int J Impact Eng. 2009;36(5): 720-728.
[22] HELGASON B, VICECONTI M, RÚNARSSON TP, et al. On the mechanical stability of porous coated press fit titanium implants: a finite element study of a pushout test. J Biomech. 2008;41(8):1675-1681.
[23] BOBBILI R, RAMAKRISHNA B, MADHU V. Dynamic compressive behavior and fracture modeling of Titanium alloy IMI 834. J Alloy Compd. 2017; 714:225-231.
[24] NAMJOSHI SA, MALL S, JAIN VK, et al. Fretting fatigue crack initiation mechanism in Ti–6Al–4V. Fatigue Fract Eng M. 2002;25(10):955-964.
[25] EDWARDS P, RAMULU M. Fatigue performance evaluation of selective laser melted Ti–6Al–4V. Mat Sci Eng A-Struct. 2014;598:327-337.
[26] KNOBE M, NAGEL P, MAIER KJ, et al. Rotationally stable screw-anchor with locked trochanteric stabilizing plate versus proximal femoral nail antirotation in the treatment of AO/OTA 31A2.2 fracture: a biomechanical evaluation. J Orthop Trauma. 2016;30(1):e12-e18.
[27] GOFFIN JM, PANKAJ P, SIMPSON AHRW, et al. Does bone compaction around the helical blade of a proximal femoral nail anti-rotation (PFNA) decrease the risk of cut-out? Bone Joint Res. 2013;2(5):79-83.
[28] HELWIG P, FAUST G, HINDENLANG U, et al. Finite element analysis of four different implants inserted in different positions to stabilize an idealized trochanteric femoral fracture. Injury. 2009;40(3):288-295.
[29] HUANG Y, ZHANG C, LUO Y. A comparative biomechanical study of proximal femoral nail (InterTAN) and proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures. Int orthop. 2013;37(12):2465-2473.
[30] WANG L, ZHAO F, HAN J, et al. Biomechanical study on proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA) for intertrochanteric fracture. J Mech Med Biol. 2012;12(4):1250075.
[31] YUAN GX, SHEN YH, CHEN B, et al. Biomechanical comparison of internal fixations in osteoporotic intertrochanteric fracture. A finite element analysis. Saudi Med J. 2012;33(7):732-739.
[32] SWART E, MAKHNI EC, MACAULAY W, et al. Cost-effectiveness analysis of fixation options for intertrochanteric hip fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96(19):1612-1620.
[33] KIM YS, HUR JS, HWANG KT, et al. The Comparison of compression hip screw and bipolar hemiarthroplasty for the treatment of AO Type A2 intertrochanteric fractures. Hip Pelvis. 2014;26(2):99-106.
[34] 郑利钦,林梓凌,陈心敏,等.载荷速率对股骨颈骨折裂纹扩展影响的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(20):3148-3152.
[35] 张强,孟凯.股骨粗隆间骨折术后不愈合并内固定物断裂1例分析[J].世界最新医学信息文摘,2018,18(9):226-229.
[36] MEINBERG EG, AGEL J, ROBERTS CS, et al. Fracture and dislocation classification compendium-2018. J Orthop Trauma. 2018;32 Suppl 1: S1-S170. |