[1] 陆艳红, 石晓兵. 膝骨关节炎国内外流行病学研究现状及进展[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志,2012,20(6):81-84.
[2] BREKELMANS WA, POORT HW, SLOOFF TJ. A New Method to Analyse the Mechanical Behaviour of Skeletal Parts. Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica. 1972;43(5):301-317.
[3] RYBICKI EF, SIMONEN FA, WEIS EB JR. On the mathematical analysis of stress in the human femur. J Biomech. 1972;5(2):203-215.
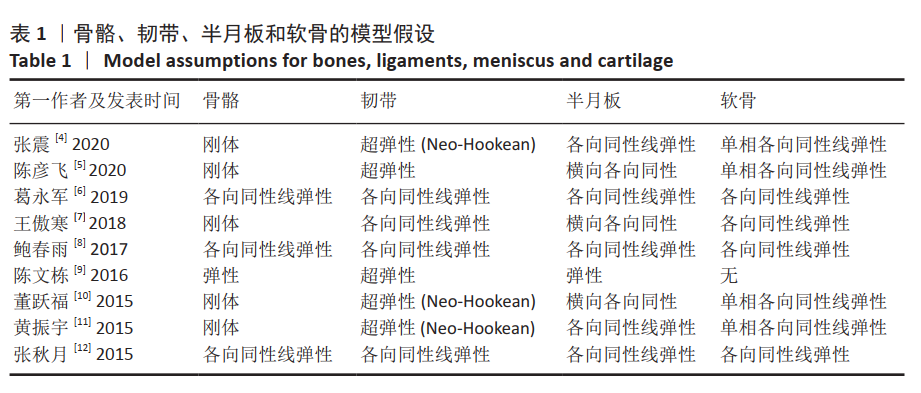
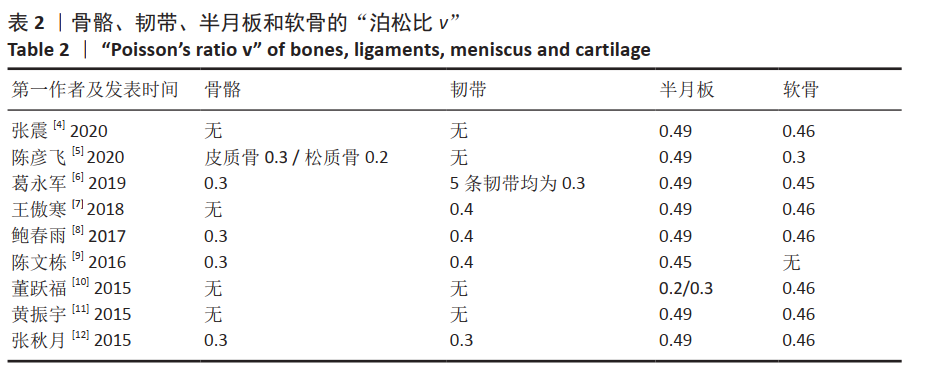
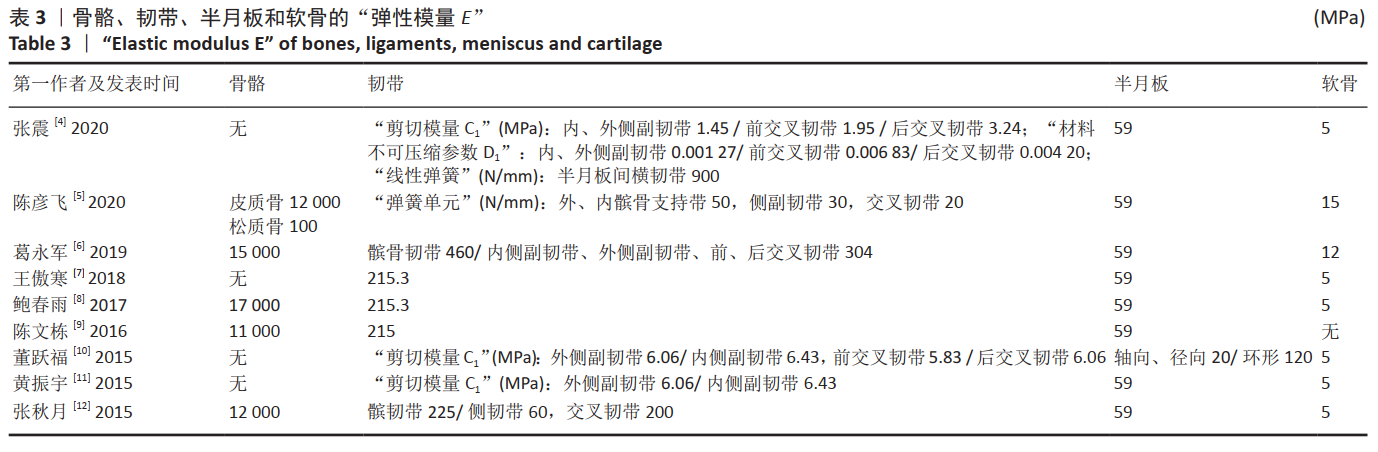
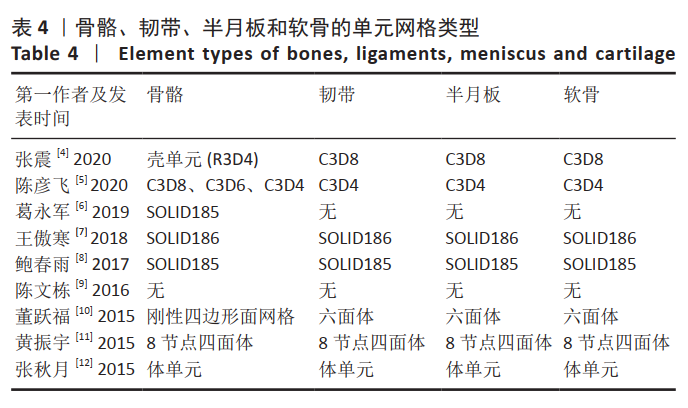
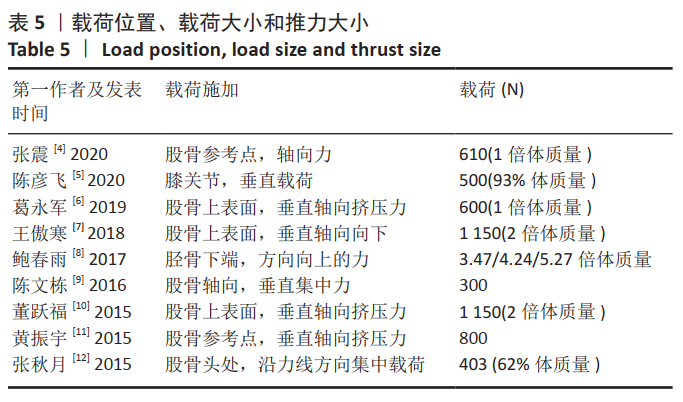
[4] 张震, 董跃福, 苏宏飞, 等. 轻度OA膝关节有限元解剖模型的构建及其力学分析[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(5):439-443.
[5] 陈彦飞, 鲁超, 赵勇, 等. 基于CT影像动态膝关节有限元模型的构建及仿真力学分析[J]. 中国骨伤,2020,33(5):479-484.
[6] 葛永军, 宣勇, 穆帅, 等. 膝关节盘状半月板有限元模型的构建及生物力学分析[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2019,27(22):2071-2075.
[7] 王傲寒, 董万鹏, 张震, 等. 膝关节三维有限元模型的建立和验证[J]. 计算机辅助工程,2018,27(Z1):68-71,76.
[8] 鲍春雨, 郭宝川, 孟庆华. 人体膝关节有限元模型建立及其有效性验证[J]. 应用力学学报,2017,34(3):559-563.
[9] 陈文栋, 杨光. 膝关节半月板三维有限元模型的动态仿真生物力学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2016,20(31):4658-4664.
[10] 董跃福, 牟志芳, 蒋胜波, 等. 膝关节有限元解剖模型的构建及其力学分析[J]. 临床骨科杂志,2015,18(6):686-692.
[11] 黄振宇, 董跃福, 胡广洪, 等. 基于有限元方法的正常和早期OA膝关节生物力学行为比较[J]. 中国数字医学,2015,10(5):6-9.
[12] 张秋月, 张春秋, 葛洪玉, 等. 膝关节三维有限元模型的建立及分析[J]. 天津理工大学学报,2015,31(3):27-30,34.
[13] PEÑA E, CALVO B, MARTÍNEZ MA, et al. Computer simulation of damage on distal femoral articular cartilage after meniscectomies. Comput Biol Med. 2008;38(1):69-81.
[14] DONAHUE TL, HULL ML, RASHID MM, et al. A finite element model of the human knee joint for the study of tibiofemoral contact. J Biomech Eng. 2002;124(3):273-280.
[15] DOBLARÉ M, CUETO E, CALVO B, et al. On the employ of meshless methods in biomechanics. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. 2005; 194(6-8):801-821.
[16] 李树虎, 贾华敏, 李茂东, 等. 超弹性体本构模型的理论和特种试验方法[J]. 弹性体,2011,21(1):58-64.
[17] 陈莲, 周海亭. 计算橡胶隔振器静态特性的数值分析方法[J]. 振动与冲击,2005,24(3):120-123.
[18] SPILKER RL, SUH JK. Formulation and evaluation of a finite element model for the biphasic model of hydrated soft tissues. Comput Struct. 1990;35(4):425-439.
[19] LEROUX MA, SETTON LA. Experimental and biphasic FEM determinations of the material properties and hydraulic permeability of the meniscus in tension. J Biomech Eng. 2002;124(3):315-321.
[20] HAUT DT, HULL ML, RASHID MM, et al. How the stiffness of meniscal attachments and meniscal material properties affect tibio-femoral contact pressure computed using a validated finite element model of the human knee joint. J Biomech. 2003;36(1):19-34.
[21] MOW VC, KUEI SC, LAI WM, et al. Biphasic Creep and Stress Relaxation of Articular Cartilage in Compression: Theory and Experiments. J Biomech Eng. 1980;102(1):73-84.
[22] GARCIA JJ, ALTIERO NJ, HAUT RC. An approach for the stress analysis of transversely isotropic biphasic cartilage under impact load. J Biomech Eng. 1998;120(5):608-613.
[23] DONZELLI PS, SPILKER RL, ATESHIAN GA, et al. Contact analysis of biphasic transversely isotropic cartilage layers and correlations with tissue failure. J Biomech. 1999;32(10):1037-1047.
[24] LI G, LOPEZ O, RUBASH H. Variability of a three-dimensional finite element model constructed using magnetic resonance images of a knee for joint contact stress analysis. J Biomech Eng. 2001;123(4): 341-346.
[25] PEÑA E, CALVO B, MARTÍNEZ MA, et al. Finite element analysis of the effect of meniscal tears and meniscectomies on human knee biomechanics. Clin Biomech. 2005;20(5):498-507.
[26] ASHMAN RB, COWIN SC, VAN BUSKIRK WC, et al. A continuous wave technique for the measurement of the elastic properties of cortical bone. J Biomech. 1984;17(5):349-361.
[27] WEISS JA, GARDINER JC. Computational modeling of ligament mechanics. Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 2001;29(3):1-70.
[28] BUTLER DL, SHEH MY, STOUFFER DC, et al. Surface strain variation in human patellar tendon and knee cruciate ligaments. J Biomech Eng. 1990;112(1):38-45.
[29] GARDINER JC, WEISS JA. Subject-specific finite element analysis of the human medial collateral ligament during valgus knee loading. J Orthop Res. 2003;21(6):1098-1106.
[30] WEISS JA, MAKER BN, GOVINDJEE S. Finite element implementation of incompressible, isotropic hyperelasticity. Comput. Methods Appl Mech Eng. 1996;135:107-128.
[31] ZIELINSKA B, DONAHUE TL. 3D finite element model of meniscectomy: changes in joint contact behavior. J Biomech Eng. 2006;128(1):115-123.
[32] MONONEN ME, JURVELIN JS, KORHONEN RK. Implementation of a gait cycle loading into healthy and meniscectomised knee joint models with fibril-reinforced articular cartilage. Comput Methods Biomecha Biomed Engin. 2013;18(2):141-152.
[33] SKAGGS DL, WARDEN WH, MOW VC. Radial tie fibers influence the tensile properties of the bovine medial meniscus. J orthop res. 1994; 12(2):176-185.
[34] TISSAKHT M, AHMED AM. Tensile stress-strain characteristics of the human meniscal material. J biomech. 1995;28(4):411-422.
[35] YANG NH, CANAVAN PK, NAYEB-HASHEMI H, et al. Protocol for constructing subject-specific biomechanical models of knee joint. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Eng. 2010;13(5):589-603.
[36] KEMPSON EG. 5-The Mechanical Properties of Articular Cartilage. Joints Synov Fluid. 1980;223(1):177-238.
[37] ASPDEN RM. A model for the function and failure of the meniscus. Eng Med. 1985;14(3):119-122.
[38] ARMSTRONG CG, LAI WM, MOW VC. An analysis of the unconfined compression of articular cartilage. J Biomech Eng. 1984;106(2):165-173.
[39] MAK AF, LAI WM, MOW VC. Biphasic indentation of articular cartilage-I. Theoretical analysis. J Biomech. 1987;20(7):703-714.
[40] BLANKEVOORT L, KUIPER JH, HUISKES R, et al. Articular contact in a thr ee-dim ensional model of the knee. J Biomech. 1991;24(11): 1019-1031.
[41] YAO J, SNIBBE J, MALONEY M, et al. Stresses and strains in the medial meniscus of an ACL deficient knee under anterior loading: a finite element analysis with image-based experimental validation. J Biomech Eng. 2006;128(1):135-141.
[42] CAPPOZZO A, CATANI F, CROCE UD, et al. Position and orientation in space of bones during movement:anatomical frame definition and determination. Clin Biomech. 1995;10(4):171-178.
[43] HALONEN KS, MONONEN ME, JURVELIN JS, et al. Deformation of articular cartilage during static loading of a knee joint – Experimental and finite element analysis. J Biomech. 2014;47(10):2467-2474.
[44] TAYLOR SJ, WALKER PS, PERRY JS, et al. The forces in the distal femur and the knee during walking and other activities measured by telemetry. J Arthroplasty. 1998;13(4):428-437.
[45] KUTZNER I, HEINLEIN B, GRAICHEN F, et al. Loading of the knee joint during activities of daily living measured in vivo in five subjects. J Biomech. 2010;43(11):2164-2173.
[46] 魏鸿文,郑诚功. 膝关节高屈曲假体的研究进展[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2009,3(4):524-528.
[47] 王岩, 周飞虎, 周勇刚, 等. 国人正常膝关节三维几何形态测量及相关研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2004,12(8):617-619.
[48] 王建平, 闫池辉, 张盼盼, 等. 基于Neo-Hookean本构模型的人体膝关节韧带力学性能测试分析[J]. 上海理工大学学报,2017,39(6): 580-585. |