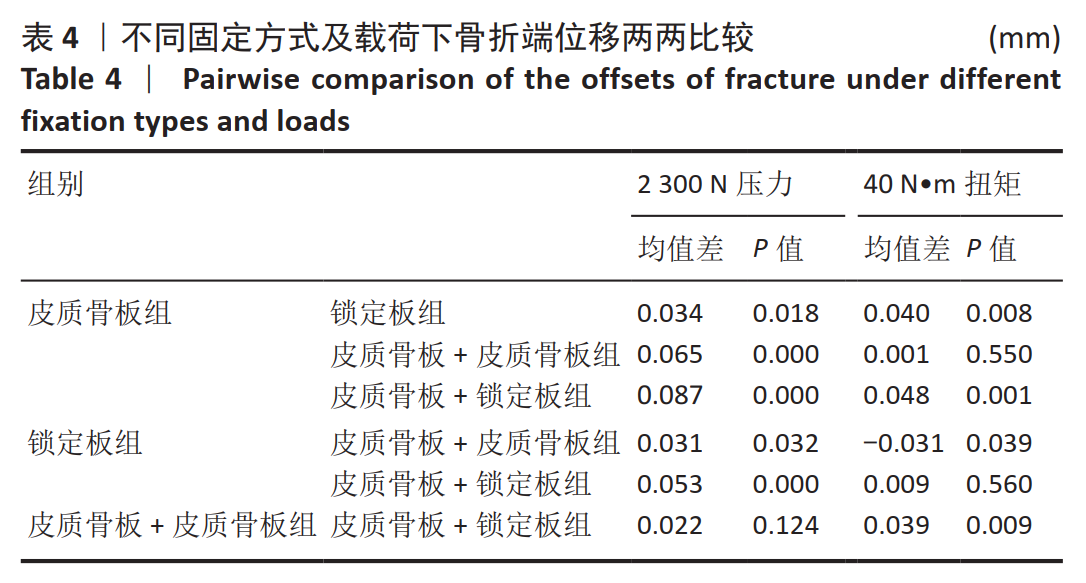
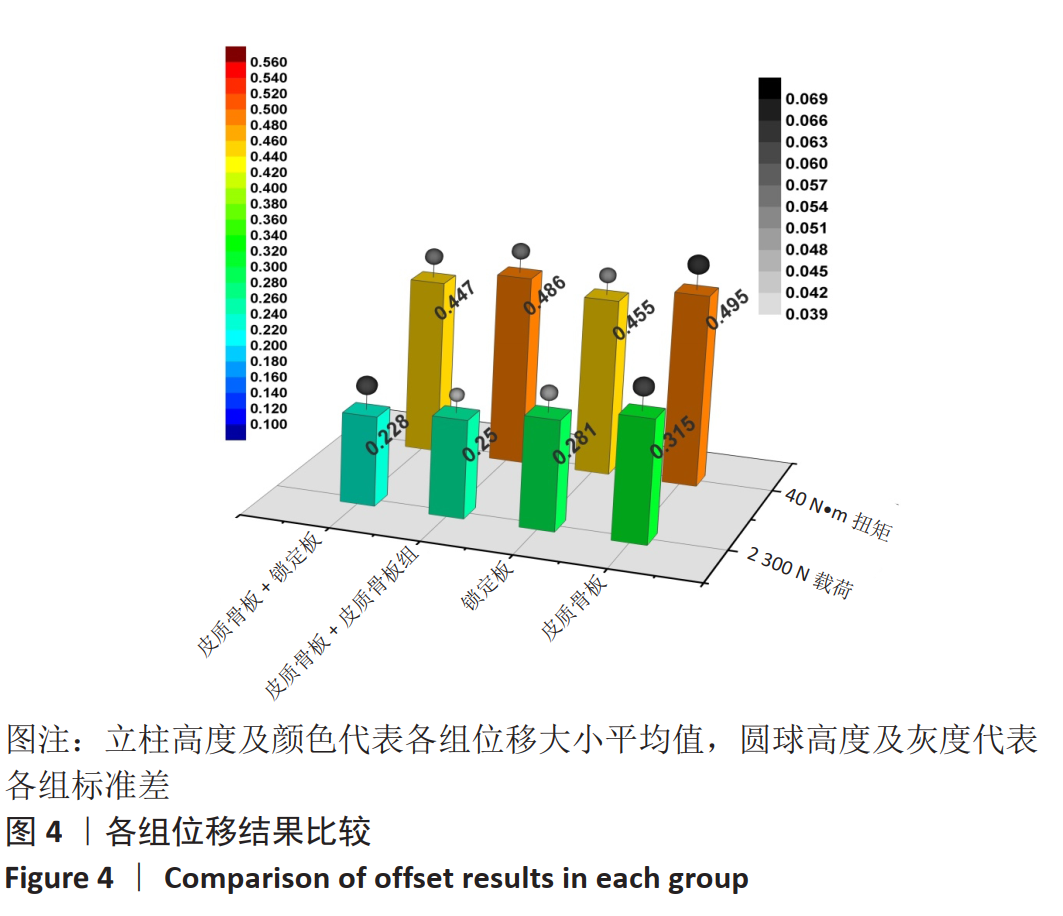
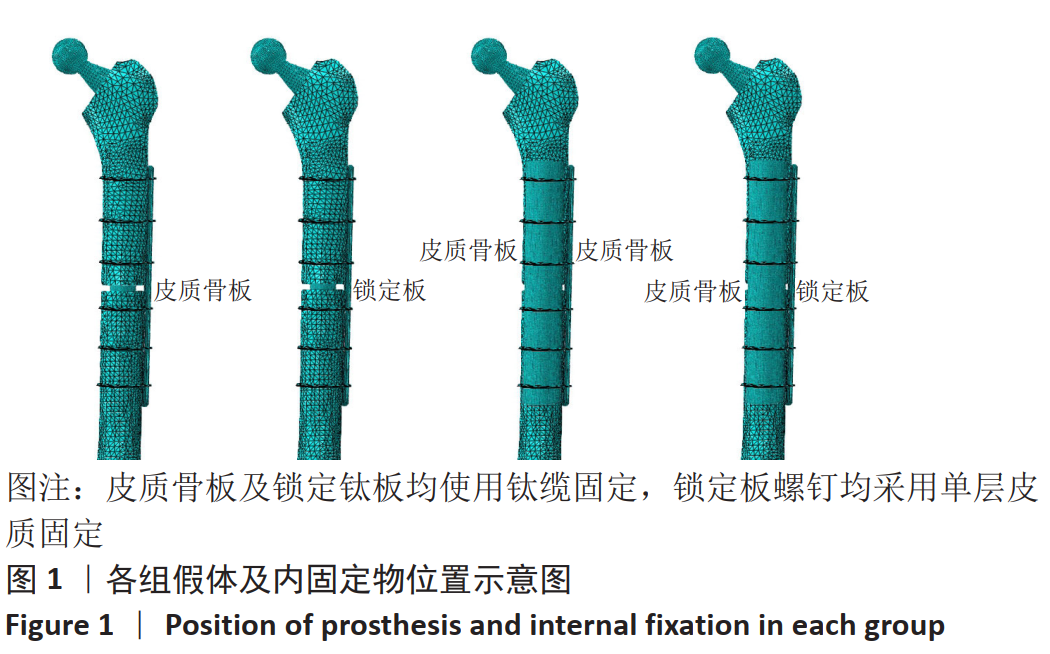
[1] BRODÉN C, MUKKA S, MUREN O, et al. High risk of early periprosthetic fractures after primary hip arthroplasty in elderly patients using a cemented, tapered, polished stem: An observational, prospective cohort study on 1,403 hips with 47 fractures after mean follow-up time of 4 years. Acta Orthopaedica. 2015;86(2):169-174.
[2] CIRIELLO V, CHIARPENELLO R, TOMARCHIO A, et al. The management of Vancouver B1 and C periprosthetic fractures: radiographic and clinic outcomes of a monocentric consecutive series. Hip Int. 2020;30(2): 94-100.
[3] OKUDERA Y, KIJIMA H, YAMADA S, et al. The location of the fracture determines the better solution, osteosynthesis or revision, in periprosthetic femoral fractures. J Orthop. 2020;22:220-224.
[4] CHATZIAGOROU G, LINDAHL H, KÄRRHOLM J, et al. Lower reoperation rate with locking plates compared with conventional plates in Vancouver type C periprosthetic femoral fractures: A register study of 639 cases in Sweden. Injury. 2019;50(12):2292-2300.
[5] LEGOSZ P, PLATEK AE, RYS-CZAPOROWSKA A, et al. Correlations between Vancouver type of periprosthetic femur fracture and treatment outcomes. J Orthop. 2019;16(6):517-521.
[6] SMITHAM PJ, CARBONE TA, BOLAM SM, et al. Vancouver B2 Peri-Prosthetic Fractures in Cemented Femoral Implants can be Treated With Open Reduction and Internal Fixation Alone Without Revision. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(7):1430-1434.
[7] MORETA J, URIARTE I, ORMAZA A, et al. Outcomes of Vancouver B2 and B3 periprosthetic femoral fractures after total hip arthroplasty in elderly patients. HIP Int. 2019;29(2):184-190.
[8] RHO JY, HOBATHO MC, ASHMAN RB. Relations of mechanical properties to density and CT numbers in human bone. Med Eng Phys. 1995;17(5): 347-355.
[9] ZDERO R, OLSEN M, BOUGHERARA H, et al. Cancellous bone screw purchase: a comparison of synthetic femurs, human femurs, and finite element analysis. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2008;222(H8):1175-1183.
[10] SHAH S, KIM SYR, DUBOV A, et al. The biomechanics of plate fixation of periprosthetic femoral fractures near the tip of a total hip implant: cables , screws , or both ? Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers. Part H. J Eng Med. 2011;225(9):845-856.
[11] MOAZEN M, MAK JH, ETCHELS LW, et al. Periprosthetic femoral fracture - a biomechanical comparison between vancouver type B1 and B2 fixation methods. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(3):495-500.
[12] RUEDI TP, BUCKLEY RE, MORAN CG. AO principles of fracture management. 2nd edition. Davos: AO Publishing, 2007:447.
[13] 马显志, 张伯松, 王满宜, 等. 辅助钢板治疗股骨干骨折髓内钉固定术后骨折不愈合的生物力学研究[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2016, 18(2):158-162.
[14] 王志强, 姜洪源, Roman Kamink, 等. 康复机器人辅助人体站立的关节力矩模拟与试验研究[J]. 中国康复医学杂志,2014,29(9): 847-850.
[15] 龚志兵,吴昭克,张焕堂,等.锁定钢板固定联合同种异体皮质骨板治疗髋关节置换后老年骨质疏松性Vancouver B1、C型股骨假体周围骨折[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(12):1812-1817.
[16] MUNRO JT, GARBUZ DS, MASRI BA, et al. Tapered fluted titanium stems in the management of vancouver B2 and B3 periprosthetic femoral fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;2:590-598.
[17] 李颖, 童梁成, 薛庆, 等. 有限元壁厚分析法诊断股骨干骨折术后骨愈合程度的应用价值[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2020,35(6): 569-572.
[18] 郑辉, 李璐兵, 李飞, 等. 距骨骨软骨损伤的有限元研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(14):1307-1310.
[19] 陈荣彬, 李勇, 白杰, 等. 三种骨水泥弥散类型对胸腰段椎体强化术后术椎应力影响的三维有限元分析[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2020, 30(7):628-637.
[20] 李文银, 尹红灵, 蒋钰钢. PVP术中腰椎不同骨水泥注入量的有限元分析[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(18):1695-1700.
[21] 肖永川, 许泽川, 梁川东, 等. 腰1椎体应力的有限元分析及分区[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2020,30(11):1016-1026.
[22] 陈宣煌, 郑锋, 蔡涵华, 等. AORI Ⅰ、Ⅱ型胫骨平台骨缺损对胫骨假体稳定性影响的有限元分析[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2019,27(21): 1982-1987.
[23] 王进, 赵广雷, 黄钢勇, 等. 3D打印金属垫块修复全膝关节置换(TKA)术中胫骨平台骨缺损的三维有限元分析[J]. 复旦学报(医学版),2020,47(2):232-239.
[24] 郭团茂, 陈忠宁, 行艳丽. 腰椎后路椎间植骨融合内固定术后邻近节段椎间盘退行性改变生物力学特点的有限元分析[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2020,35(3):232-235.
[25] 范勋健, 陈瑱贤, 曹卓, 等. 个体化骨肌多体动力学和有限元联合建模的肩胛骨锁定板生物力学评估方法[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2019,53(7):168-176.
[26] 张旭林, 徐永清, 何晓清,等. 手舟骨腰部骨折3种内固定方式的有限元分析[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志,2019,37(5):553-558.
[27] 郑利钦, 林梓凌, 李鹏飞,等. 动态载荷下松质骨对骨质疏松性股骨颈骨折断裂力学影响的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2019,23(12):1887-1892.
[28] 关玉龙, 吕春娥, 赵晓亮,等. 跗骨窦切口内固定治疗SandersⅡ型跟骨骨折临床疗效与有限元分析[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2020,35(12):1325-1327.
[29] 蔡凯文, 蒋国强, 卢斌, 等. 椎间隙骨水泥渗漏的不同分型对邻椎相邻终板应力分布的影响: 三维有限元研究[J]. 中华骨科杂志, 2019,39(6):364-373.
[30] SLEDGE JB 3RD, ABIRI A. An algorithm for the treatment of Vancouver type B2 periprosthetic proximal femoral fractures. J Arthroplasty. 2002;17(7):887-892.
[31] BRADY OH, GARBUZ DS, MASRI BA, et al. The treatment of periprosthetic fractures of femur using cortical onlay allograft struts. Orthop Clin North Am. 1999;30:249-257
[32] 董巍, 贾俊玲, 李真, 等.基于有限元方法的Vancouver B2型假体周围骨折治疗方法的比较[J]. 重庆医科大学学报,2016,41(5): 472-476. |