中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (34): 5439-5444.doi: 10.12307/2021.236
• 组织工程骨材料Tissue-engineered bone • 上一篇 下一篇
碱性成纤维细胞生长因子复合脱细胞骨基质/壳聚糖支架修复骨缺损
张志文1,黄玉良1,张理选2,王晓锋1,陈锐雄1
- 惠州市中心人民医院,1创伤骨科,2关节外科,广东省惠州市 516001
Acellular bone matrix/chitosan scaffold combined with basic fibroblast growth factor for repairing bone defects
Zhang Zhiwen1, Huang Yuliang1, Zhang Lixuan2, Wang Xiaofeng1, Chen Ruixiong1
- 1Department of Trauma and Orthopedics, 2Department of Joint Surgery, Huizhou Central People’s Hospital, Huizhou 516001, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
脱细胞骨基质:是通过物理、化学与酶等一系列的处理去除骨组织中的细胞与脂类等抗原成分,保留细胞外基质的主要成分与结构,具备正常骨组织生理结构与力学特征的骨修复材料,具有良好的骨传导与骨诱导性能,被广泛应用于骨修复中。
碱性成纤维细胞生长因子:为一种有效的促有丝分裂及促血管再生因子,可促进包括间质细胞、前成骨细胞及软骨细胞在内的多种细胞的增殖与分化,可刺激毛细血管内皮细胞迁移和增殖,促进骨形态发生蛋白、血管内皮生长因子等成骨因子的表达与释放,进而发挥促成骨作用。
背景:有研究显示,碱性成纤维细胞生长因子可促进间充质干细胞的增殖与成骨分化。
目的:对比脱细胞骨基质/壳聚糖支架复合碱性成纤维细胞生长因子前后修复兔股骨缺损的能力。
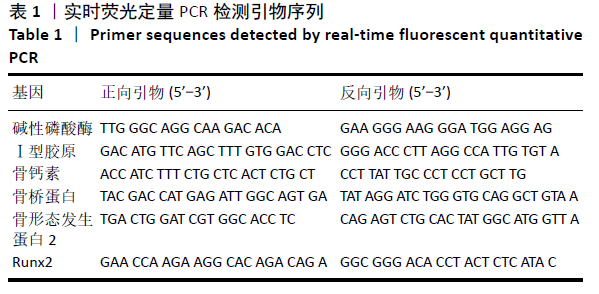
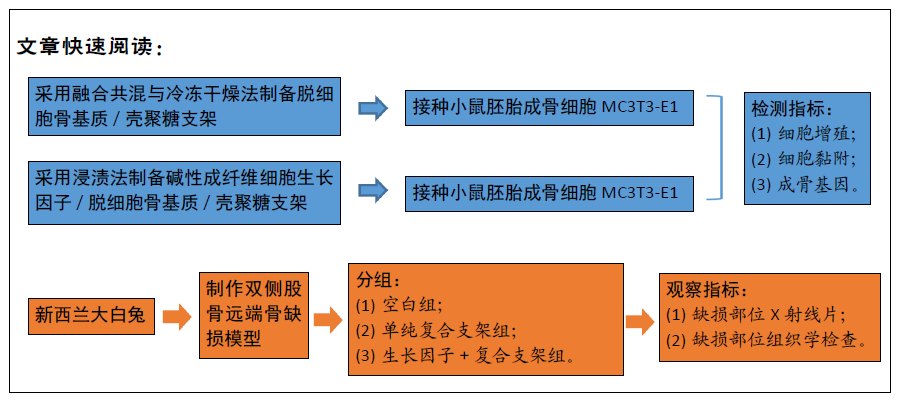
方法:采用融合共混与冷冻干燥法制备脱细胞骨基质/壳聚糖支架,采用浸渍法制备碱性成纤维细胞生长因子/脱细胞骨基质/壳聚糖支架。将小鼠胚胎成骨细胞MC3T3-E1分别接种于两种支架表面,以单独培养的细胞为对照,进行细胞增殖、细胞黏附与成骨基因检测。在36只6月龄新西兰大白兔双侧股骨远端制备直径5 mm的骨缺损模型,抽签法随机分3组,空白组不进行任何干预,单纯复合支架组、生长因子+复合支架组分别植入脱细胞骨基质/壳聚糖支架与碱性成纤维细胞生长因子/脱细胞骨基质/壳聚糖支架,进行骨缺损部位X射线片与组织学检查。
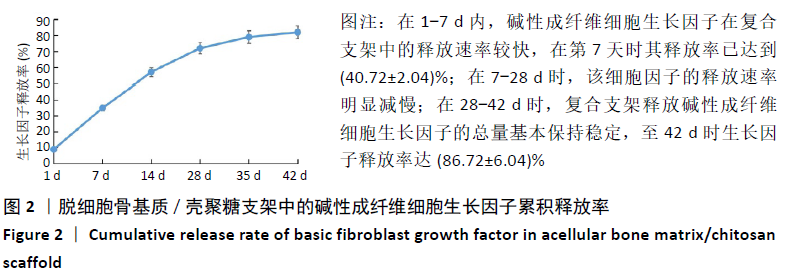
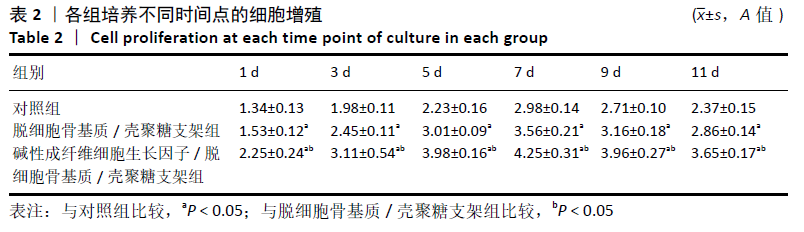
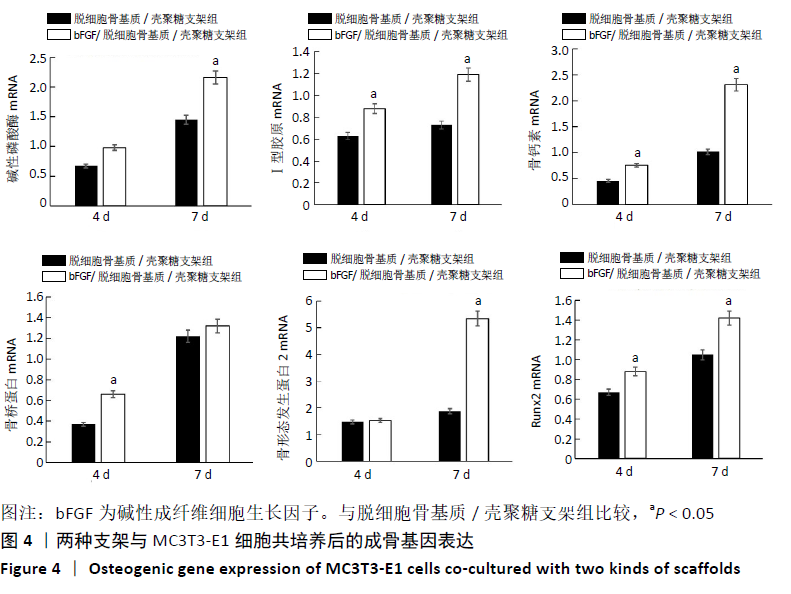
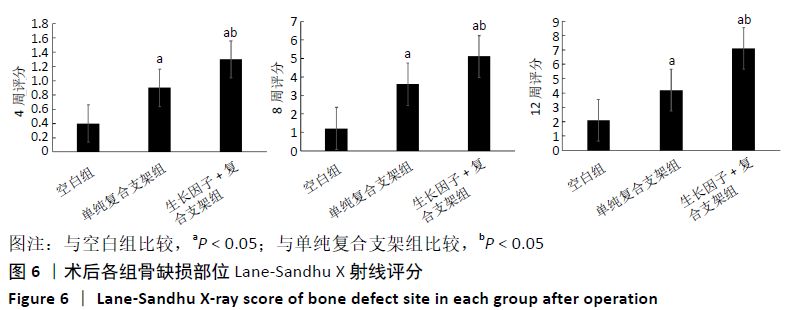
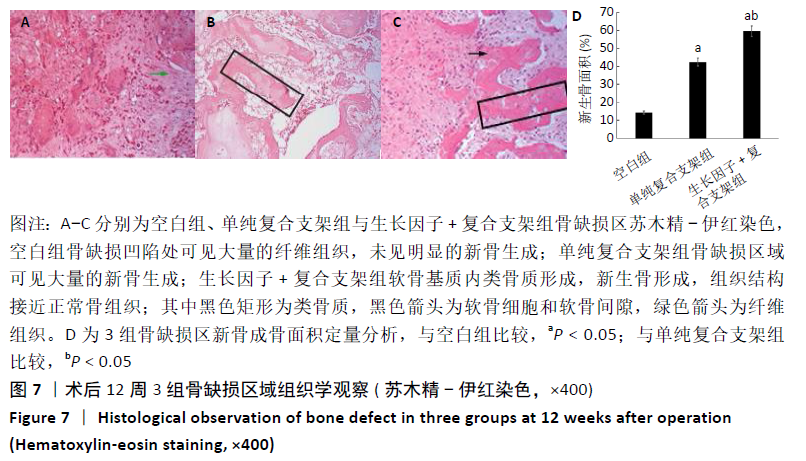
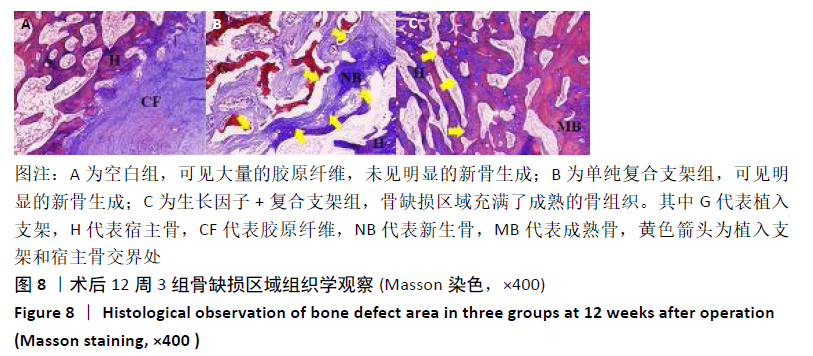
结果与结论:①在培养的1-11 d内,碱性成纤维细胞生长因子/脱细胞骨基质/壳聚糖支架组的细胞增殖快于脱细胞骨基质/壳聚糖支架组 (P < 0.05),脱细胞骨基质/壳聚糖支架组快于对照组(P < 0.05);②细胞与支架共培养4 d后,碱性成纤维细胞生长因子/脱细胞骨基质/壳聚糖支架组培养4,7 d的成骨基因Ⅰ型胶原、骨钙素、骨桥蛋白及Runx2 mRNA表达均高于脱细胞骨基质/壳聚糖支架组(P < 0.05),培养7 d后的碱性磷酸酶mRNA表达高于脱细胞骨基质/壳聚糖支架组(P < 0.05);③共培养7 d后的扫描电镜显示,两组支架均支持MC3T3-E1细胞的黏附;④动物实验X射线片显示,空白组术后12周时无明显的骨修复;单纯复合支架组术后8周时可见新骨生成,术后12周时可见明显新骨生成;细胞因子+复合支架组术后4周时即可见新骨生成,至术后12周时骨缺损部位几乎完全修复;⑤动物实验术后12周的缺损部位苏木精染色与Masson染色显示,空白组可见大量的纤维组织;两支架组可见大量的新骨生成,其中生长因子+复合支架组的新骨生成面积与成熟度高于单纯复合支架组;⑥结果表明,负载碱性成纤维细胞生长因子的脱细胞骨基质/壳聚糖复合支架是较为理想的骨组织修复材料,可促进骨形成。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3474-326X (张志文)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号: