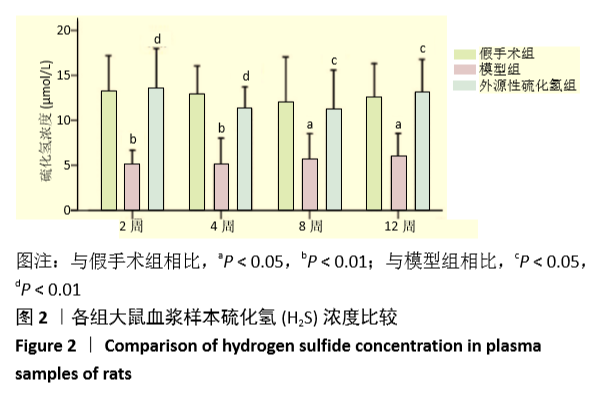
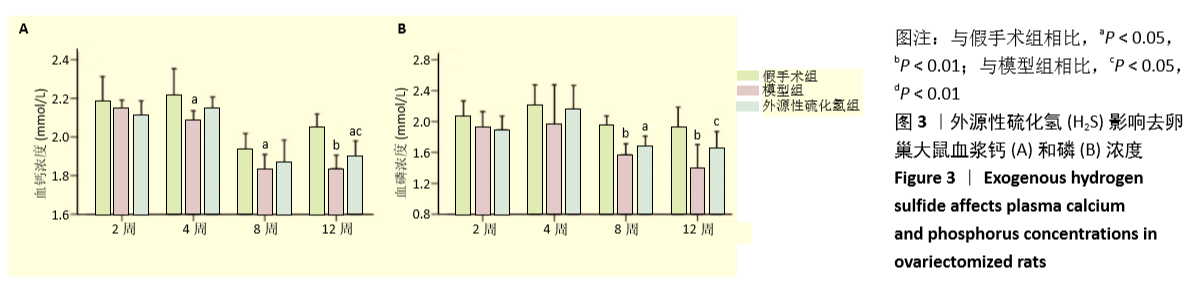
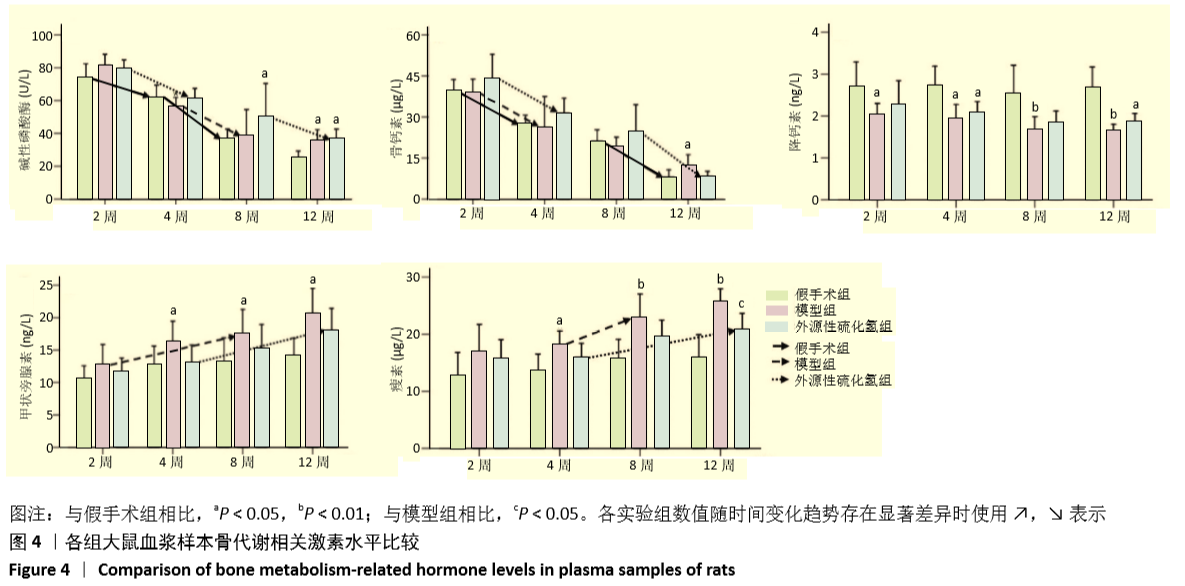
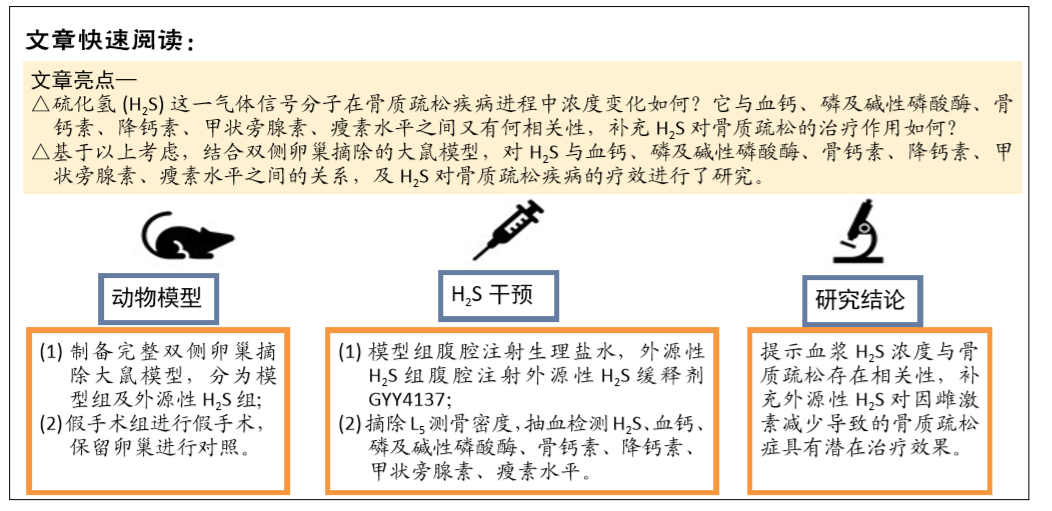
[1] FORCIEA MA , MCLEAN RM , QASEEM A. Treatment of Low Bone Density or Osteoporosis to Prevent Fractures in Men and Women: A Clinical Practice Guideline Update From the American College of Physicians. Ann Int Med. 2017;167(12):899.
[2] KANIS JA, COOPER C, RIZZOLI R, et al. European guidance for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. Osteoporos Int. 2019;30(1):3-44.
[3] KALU DN. The ovariectomized model of postmenopausal bone loss. Bone Miner. 1991;15:175-191.
[4] MARCUS R, FELDMAN D, KELSEY J. Osteoporosis. Academic Press, 1996: 677-679.
[5] MUTHUSAMI S, RAMACHANDRAN I, MUTHUSAMY B, et al. Ovariectomy induces oxidative stress and impairs bone antioxidant system in adult rats. Clin Chim Acta. 2005;360:81-86.
[6] ALMEIDA M, HAN L, MARTIN-MILLAN M, et al. Skeletal involution by ageassociated oxidative stress and its acceleration by loss of sex steroids. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(37):27285-27297.
[7] BASU S, MICHAËLSSON K, OLOFSSON H, et al. Association between oxidative stress and bone mineral density. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;288:275-279.
[8] MAGGIO D, BARABANI M, PIERANDREI M, et al. Marked decrease in plasma antioxidants in aged osteoporotic women: results of a cross-sectional study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88:1523-1527.
[9] FINKEL T, HOLBROOK NJ. Oxidants, oxidative stress and the biology of ageing. Nature. 2000;408:239-247.
[10] MANOLAGAS SC. From estrogen-centric to aging and oxidative stress:a revised perspective of the pathogenesis of osteoporosis. Endocr Rev. 2010;31(3):266-300.
[11] WEITZMANN MN, PACIFICI R. Estrogen deficiency and bone loss: an inflammatory tale. J Clin Invest. 2006;116(5):1186-1194.
[12] WHITEMAN M, ARMSTRONG JS, CHU SH, et al. The novel neuromodulator hydrogen sulfide: an endogenous peroxynitrite ‘scavenger’? J Neurochem. 2004;90:765-768.
[13] KIMURA Y, GOTO Y, KIMURA H. Hydrogen sulfide increases glutathione production and suppresses oxidative stress in mitochondria. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2010;12:1-13.
[14] ABE K, KIMURA H. The possible role of hydrogen sulfide as an endogenous neuromodulator. J Neurosci. 1996;16(3):1066-1071.
[15] WANG R. Two’s company, three’s a crowd: can H2S be the third endogenous gaseous transmitter? FASEB J. 2002;16:1792-1798.
[16] XU ZS,WANG XY,XIAO DM, et al. Hydrogen sulfide protects MC3T3-E1 osteoblastic cells against H2O2-induced oxidative damage-implications for the treatment of osteoporosis. Free Radic Biol Med. 2011;50(10) : 1314-1323.
[17] LELOVAS PP, XANTHOS TT, THORMA SE, et al. The laboratory rat as an animal model for osteoporosis research. Comp Med. 2008;58(5): 424-430.
[18] LIU XL, LI CL, LU WW, et al. Skeletal site-specific response to ovariectomy in a rat model: change in bone density and microarchitecture. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2015;26(4):392-398.
[19] JAIN S, CAMACHO P. Use of bone turnover markers in the management of osteoporosis. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2018;25(6): 366-372.
[20] SAHA MK, AGRAWAL P, SAHA SG, et al. Evaluation of Correlation between Salivary Calcium, Alkaline Phosphatase and Osteoporosis- A Prospective, Comparative and Observational Study. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017;11(3):ZC63-ZC66.
[21] BOYACIOGLU O, ORENAY-BOYACIOGLU S, YILDIRIM H, et al. Boron intake, osteocalcin polymorphism and serum level in postmenopausal osteoporosis. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2018;48:52-56.
[22] LEDER, BZ. Parathyroid Hormone and Parathyroid Hormone-Related Protein Analogs in Osteoporosis Therapy. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2017; 15(2):110-119.
[23] CREPALDI G, ROMANATO G, TONIN P, et al. Osteoporosis and body composition. J Endocrinol Invest. 2007;30(6 Suppl):42.
[24] RACHNER TD, KHOSLA S, HOFBAUER LC. Osteoporosis:now and the future. Lancet. 2011;377(9773):1276-1287.
[25] KOMM BS, TERPENING CM, BENZ DJ, et al. Estrogen binding,receptor mRNA,and biologic response in osteoblast-like osteosarcoma cells. Science. 1988;241(4861):81-84.
[26] ERIKSEN EF, COLVARD DS, BERQ NJ, et al. Evidence of estrogen receptors in normal human osteoblast-like cells. Science. 1988;241(4861):84-86.
[27] OURSLE MJ,OSDOBY P, PYFFEROEN J, et al. Alian osteoclast as estrogen target cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 1991;88(15):6613-6617.
[28] MANO H, YUASA T, KAMEDA T, et al. Mamnalian mature osteoclast as estrogen target cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996;223(3): 637-642.
[29] ASSEY HM, FLANAGAN AM. Humano steoelasts derive from CD14-Positive monoeytes. Br J Haematol. 1999;106:167-170.
[30] ADAEHI JD, PAPAIOANNOU A. Cortieosteroid-Indueed osteoporsis: detdetion and management. Drug Saf. 2001;24(8):607-624.
[31] LUMACHI F, ERMANI M, CAMOZZI V, et al. Changes of bone formation markers osteocalcin and bone-specific alkaline phosphatase in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009; 1173(1): 60-63.
[32] ALMEIDA M, HAN L, MARTIN-MILLAN M, et al. Skeletal involution by ageassociated oxidative stress and its acceleration by loss of sex steroids. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(37):27285-27297.
[33] LV M, LIU Y, XIAO TH, et al. GYY4137 stimulates osteoblastic cell proliferation and differentiation via an ERK1/2-dependent anti-oxidant mechanism. Am J Transl Res. 2017;9(3):1183.
[34] GAMBARI L, LISIGNOLI G, CATTINI L, et al. Sodium hydrosulfide inhibits the differentiation of osteoclast progenitor cells via NRF2-dependent mechanism. Pharmacol Res. 2014;87:99-112.
[35] LI J, YUAN YQ, ZHANG L, et al. Exogenous hydrogen sulfide protects against high glucoseinduced apoptosis and oxidative stress by inhibiting the STAT3/HIF1α pathway in H9c2 cardiomyocytes. Exp Ther Med. 2019;18(5):3948-3958.
[36] ZHOU Q, ZHU L, ZHANG D, et al. Oxidative Stress-Related Biomarkers in Postmenopausal Osteoporosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses. Dis Markers. 2016;2016:7067984.
[37] HINE C, HARPUTLUGIL E, ZHANG Y, et al. Endogenous hydrogen sulfide production is essential for dietary restriction benefits. Cell. 2015; 160(1-2):132-144. |