中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (26): 4183-4189.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2765
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
免疫调控受体TIGIT在“怒”模型大鼠胸腺及外周血单个核细胞表达的意义
陈俊贤1,李玮婷2,杨军平2,王 莹2,金桂林2
1江西中医药大学,江西省南昌市 330004;2江西中医药大学附属医院检验科,江西省南昌市 330004
The significance of immunoregulatory receptor TIGIT expression in thymus and peripheral blood mononuclear cells in an “anger” rat model
Chen Junxian1, Li Weiting2, Yang Junping2, Wang Ying2, Jin Guilin2
1Jiangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330004, Jiangxi Province, China; 2Clinical Laboratory, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330004, Jiangxi Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
TIGIT(T cell immunoglobulin and ITIM domain):是2005年由Abbas等发现的由免疫球蛋白(IgV)样结构、Ⅰ型跨膜结构和免疫受体酪氨酸基序(ITIM)组成的跨膜分子,其胞内的ITIM基因序列,后来被研究组定义为具有负性免疫调节的基因结构,并证实了TIGIT分子具有直接或间接抑制T细胞活化的作用;TIGIT在人与啮齿动物的同源性为58%。
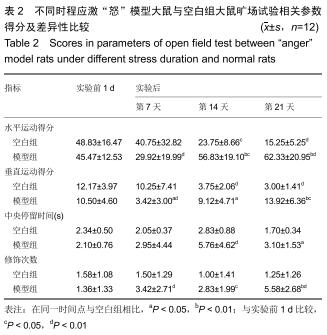
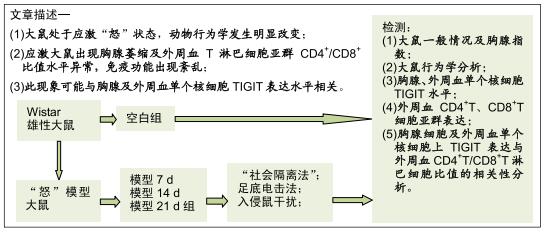
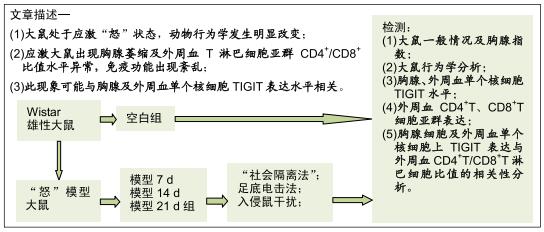
“怒”模型建立:“怒”动物模型的制备有多种方法,可采用刺激怒吼中枢的方法诱发怒反应、夹尾间接激怒法、颈部枷锁模具限制法、社会隔离与居住入侵法等。在复制精神心理应激“怒”模型方法中,尚未有明确的评断标准。实验通过孤立饲养及日夜颠倒改变模型大鼠的生存环境,提高了大鼠对环境应激因素的敏感性,旷场试验结果表明,随应激时间延长,模型大鼠水平和垂直活动活跃及修饰次数增多,说明大鼠心理焦虑度、紧张度升高,同时伴随攻击行为试验得分上升,提示大鼠处于易激易怒的应激状态,说明应激“怒”模型建立是有效的。
背景:既往研究表明,应激反应能引起机体免疫功能紊乱。免疫调控受体TIGIT能够抑制T细胞活性,促进T细胞凋亡及T细胞亚群分布失衡。应激反应的免疫反应机制是否与TIGIT的表达及作用相关,目前尚未明确。
目的:探讨免疫调控受体TIGIT在“怒”模型大鼠胸腺细胞及外周血单个核细胞中的表达情况及TIGIT与免疫功能的相关意义。
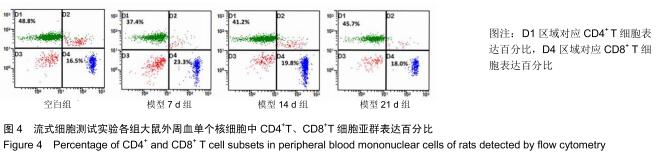
方法:将48只Wistar雄性大鼠随机分成空白组(正常大鼠)、模型7 d、14 d、21 d组,每组12只。除空白组外,其余各组以“社会隔离法”结合足底电击法进行“怒”模型大鼠复制。以旷场试验、攻击行为试验观察大鼠行为学变化,记录试验前后体质量变化及胸腺指数,应用免疫组织化学法观察各组大鼠胸腺及外周血单个核细胞中TIGIT阳性表达情况,流式细胞术测试外周血CD4+、CD8+ T细胞亚群表达水平,并进行胸腺细胞及外周血单个核细胞上TIGIT表达与外周血CD4+T/CD8+T淋巴细胞比值的相关性分析。实验方案经江西中医药大学动物实验伦理委员会批准。
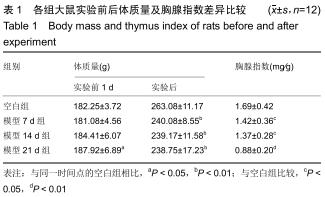
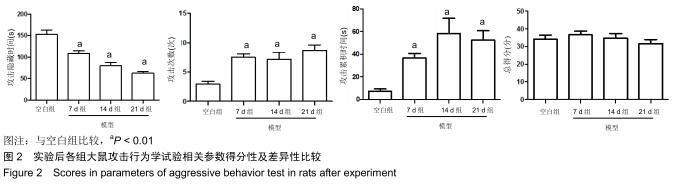
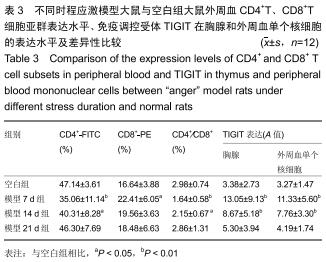
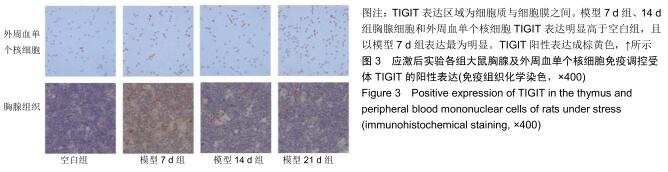
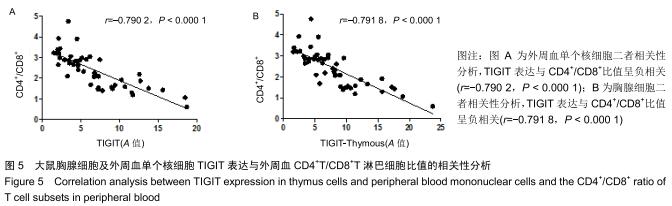
结果与结论:①模型14 d组、21 d组大鼠旷场试验水平活动、垂直活动得分,修饰动作次数较空白组升高(P < 0.05,或P < 0.01);②模型7 d组、14 d组、21 d组攻击行为试验的攻击隐藏时间较空白组明显缩短(P < 0.01),攻击次数和攻击累计时间明显增多(P < 0.01),体质量和胸腺指数明显下降(P < 0.05,或 P < 0.01);③模型7 d组、14 d组胸腺及外周血单个核细胞中TIGIT表达较空白组明显升高(P < 0.01);④模型7 d组、14 d组大鼠外周血T细胞亚群CD4+/CD8+比值较空白组明显下降(P < 0.05, 或P < 0.01);⑤大鼠外周血T细胞亚群CD4+/CD8+比值与胸腺T细胞上TIGIT表达呈负相关(r2=0.627 0,P < 0.00 01),与单个核细胞上TIGIT表达呈负相关(r2=0.624 4,P < 0.000 1);⑥结果提示,模型大鼠处于应激“怒”状态,动物行为学发生明显改变,应激大鼠出现胸腺萎缩及外周血T淋巴细胞亚群CD4+/CD8+比值水平异常,免疫功能出现紊乱,此现象可能与胸腺及外周血单个核细胞TIGIT表达水平相关,但其具体作用机制需进一步研究。
ORCID: 0000-0001-9886-5835(陈俊贤)中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: