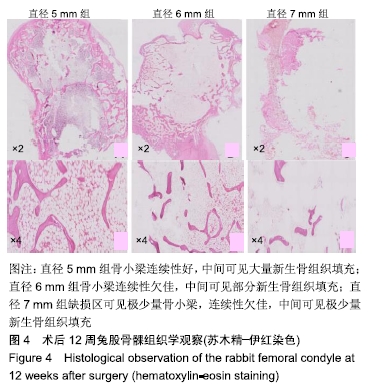
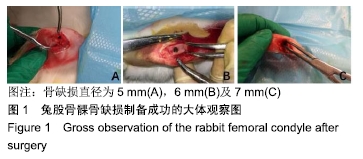
[1] GHAZAVI MT, STOCKLEY I, YEE G, et al. Reconstruction of massive bone defects with allograft in revision total knee arthroplasty.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1997;79(1):17-25.
[2] ZHANG J, JIA J, KIM JP, et al. Ionic Colloidal Molding as a Biomimetic Scaffolding Strategy for Uniform Bone Tissue Regeneration.Adv Mater. 2017;29(17).
[3] WILMOWSKY CV, SCHWARZ S, KERL JM, et al. Reconstruction of a mandibular defect with autogenous, autoclaved bone grafts and tissue engineering: An in vivo, pilot study. J Biomed Mater Res A.2010; 93 A(4):1510-1518.
[4] TANG C, JIN C, XU Y, et al. Chondrogenic differentiation could be induced by autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular matrix scaffolds without exogenous growth factor.Tissue Engineering Part A.2015; 22(3-4):222.
[5] 葛振林,何通文,徐庚池,等.构建兔颅顶骨临界骨缺损模型:确立颅顶临界骨缺损的参考值[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(18):2789-2794.
[6] NAITO Y, TERUKINA T, GALLI S, et al. The effect of simvastatin-loaded polymeric microspheres in a critical size bone defect in the rabbit calvaria.Int J Pharm.2014; 461(1-2):157-162.
[7] ALEXANDER GE, BERNASEK TL, CRANK RL, et al. Cementless Metaphyseal Sleeves Used for Large Tibial Defects in Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(4):604-607.
[8] DAINES BK, DENNIS DA. Management of bone defects in revision total knee arthroplasty. Instr Course Lect. 2013;62:341-348.
[9] ENGH GA, AMMEEN DJ. Bone loss with revision total knee arthroplasty: defect classification and alternatives for reconstruction. Instr Course Lect. 1999;48:167-175.
[10] LI X, NIU Y, GUO H, et al. Erratum: Preparation and osteogenic properties of magnesium calcium phosphate biocement scaffolds for bone regeneration. Journal of Instrumentation. 2013.
[11] HE D, DONG W, TANG S, et al.Tissue engineering scaffolds of mesoporous magnesium silicate and poly(ε-caprolactone)- poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(ε-caprolactone) composite.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2014;25(6):1415-1424.
[12] LIU YJ, YANG ZY, TAN LL, et al. An animal experimental study of porous magnesium scaffold degradation and osteogenesis.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2014;47(8):715-720.
[13] YU W, ZHAO H, DING Z, et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of MgF2 coated AZ31 magnesium alloy porous scaffolds for bone regeneration. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017;149:330-340.
[14] ZHAO Y, LEI C, HAO Y, et al. Synthesis and Characterization of an Injectable and Hydrophilous Expandable Bone Cement Based on Poly(methyl methacrylate). ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(46): 40846-40856.
[15] LIN KF,HE S,SONG Y,et al.Low-Temperature Additive Manufacturing of Biomimic Three-Dimensional Hydroxyapatite/Collagen Scaffolds for Bone Regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2016; 8(11):6905-6916.
[16] 邓威,郑欣,谌业帅,等.3D打印多孔钛材料修复兔股骨髁骨缺损的实验研究[J]. 实验动物与比较医学,2017,37(4):266-272.
[17] SCHMITZ JP, HOLLINGER JO. The critical size defect as an experimental model for craniomandibulofacial nonunions. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1986; 205(205):299.
[18] GOSAIN AK, SONG L, YU P, et al. Osteogenesis in cranial defects: reassessment of the concept of critical size and the expression of TGF-beta isoforms.Plast Reconstr Surg.2000;106(2):360.
[19] 周芳,李静,余磊,等.兔桡骨临界骨缺损模型的制备[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(50):9385-9388.
[20] NEYT JG, BUCKWALTER JA, CARROLL NC.Use of animal models in musculoskeletal research.Iowa Orthop J. 1998;18:118-123.
[21] RAVANETTI F, SCARPA E, FARINA V, et al.The effect of age, anatomical site and bone structure on osteogenesis in New Zealand White rabbit.Journal of Biological Research(1826-8838) .2015;88(2).
[22] PAN Z, JIANG P, XUE S, et al. Repair of a critical-size segmental rabbit femur defect using bioglass-β-TCP monoblock, a vascularized periosteal flap and BMP-2.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2018; 106(6):2148-2156.
[23] 黄鑫,孟国林,刘建,等.骨形态发生蛋白-2壳聚糖微球复合组织工程支架修复兔股骨髁部骨缺损的实验研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2010,12(4): 360-364.
[24] LIU J, MAO K, LIU Z, et al. Injectable Biocomposites for Bone Healing in Rabbit Femoral Condyle Defects. Plos One.2013; 8(10):e75668.
[25] LIN KF, HE S, SONG Y, et al. Low-Temperature Additive Manufacturing of Biomimic Three-Dimensional Hydroxyapatite/ Collagen Scaffolds for Bone Regeneration. Acs Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016; 8(11):6905-6916.
[26] CHANG B, SONG W, HAN T, et al. Influence of pore size of porous titanium fabricated by vacuum diffusion bonding of titanium meshes on cell penetration and bone ingrowth. Acta Biomaterialia. 2016; 33:311-321.
[27] SUN T, QU Y, CUI W, et al. Evaluation of osteogenic inductivity of a novel BMP2-mimicking peptide P28 and P28-containing bone composite.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018;106(1):210-220.
|