中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (7): 1016-1022.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2027
• 脐带脐血干细胞 umbilical cord blood stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
TDP43慢病毒载体转染人脐带间充质干细胞与软骨细胞共培养后的增殖与凋亡
黄永明1,黄启明2,刘焱杰3,王 竣3,曹振武3,田振江3,陈博鉴3,麦秀钧1,冯恩辉1
- 1广东省中医院骨科,广东省广州市 510120;2怡诺博(北京)生物医学技术有限公司,北京市 100088;3广州中医药大学附属第二临床医院,广东省广州市 510405
Proliferation and apoptosis of chondrocytes co-cultured with TDP43 lentivirus transfected-human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells
Huang Yongming1, Huang Qiming2, Liu Yanjie3, Wang Jun3, Cao Zhenwu3, Tian Zhenjiang3, Chen Bojian3, Mai Xiujun1, Feng Enhui1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China; 2Yinuobo (Beijing) Biomedical Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing 100088, China; 3the Second Clinical Medical College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:

文题释义:
TTDP43:一种高度保守、广泛表达的核蛋白,多功能地与DNA和RNA结合参与RNA转录、选择性剪接,并可调节细胞中mRNA的稳定性,可从细胞核到细胞质中形成泛素阳性包涵体,对肌萎缩侧索硬化症和额颞叶变性具有神经毒性。
RACK1:是G蛋白β亚基的同族体,一种胞浆内游离的支架蛋白,通过不同的WD40位点,结合、转运PKC到细胞内相应的位置,并使其保持活性状态;除可与细胞膜上活化的PKC结合发生反应外,还可结合多种胞浆蛋白或亚细胞结构,参与多条代谢通路,发挥不同的生理作用。
背景:在缺血缺氧条件下TDP43可能为MAPK信号通路关键的负调控因子,但其在骨性关节炎中对JNK及p38 MAPK信号通路的作用并不清楚。
目的:研究野生型TDP43介导骨性关节炎中软骨细胞病变的靶基因RACK1表达,分析其发挥应激作用的效应。
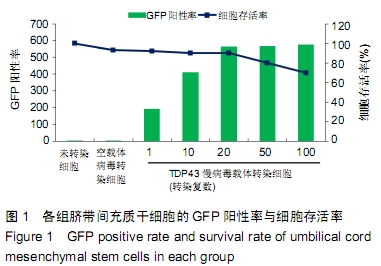
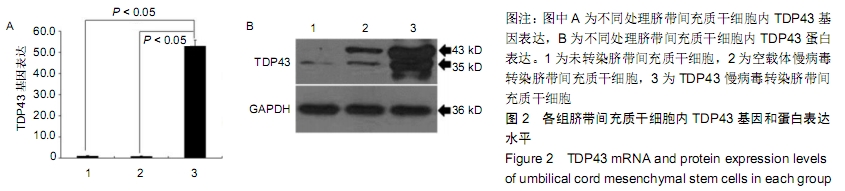
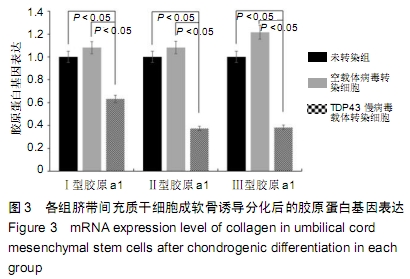
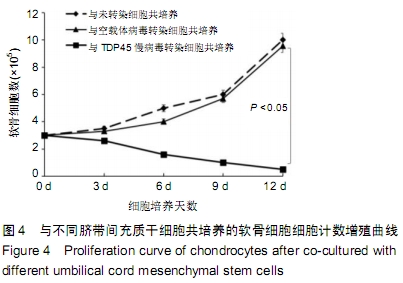
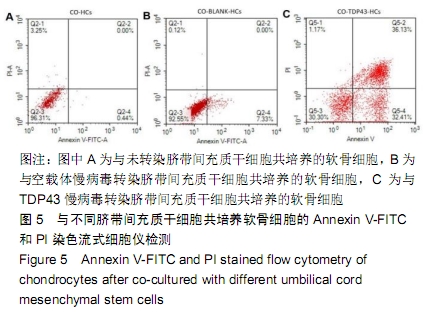
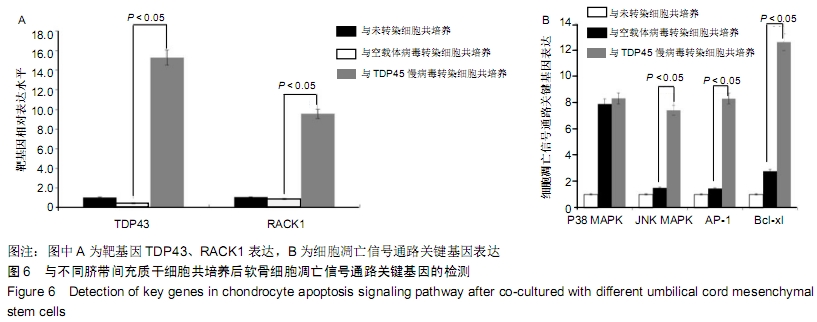
方法:以TDP43慢病毒载体转染人脐带间充质干细胞,分析其体外分化为软骨细胞的能力。将TDP43慢病毒转染脐带间充质干细胞、空载体慢病毒转染脐带间充质干细胞、未转染脐带间充质干细胞分别与人软骨细胞共培养12 d,倒置显微镜下观察软骨细胞形态变化;共培养第0,3,6,9,12天,分析软骨细胞增殖水平;共培养第3天,流式细胞仪检测软骨细胞凋亡率;共培养第3天,qRT-PCR检测软骨细胞内TDP43、RACK1、p38、JNK、AP-1和cl-xl的基因表达。
结果与结论:①TDP43慢病毒载体转染后,人脐带间充质干细胞可分化为软骨细胞;②与TDP43慢病毒转染脐带间充质干细胞共培养的软骨细胞形态发生显著改变,细胞变得粗大,并出现多个分枝情况;与空载体慢病毒转染脐带间充质干细胞、未转染脐带间充质干细胞共培养的软骨细胞形态未出现变化,呈梭形贴壁生长;③软骨细胞与TDP43慢病毒转染脐带间充质干细胞共培养后,促使软骨细胞凋亡而抑制了细胞增殖(P < 0.05);④软骨细胞与TDP43慢病毒转染脐带间充质干细胞共培养后,TDP43、RACK1、JNK、AP-1和Bcl-xl基因表达高于与未转染脐带间充质干细胞、空载体慢病毒转染脐带间充质干细胞共培养的软骨细胞(P < 0.05);⑤结果表明,软骨细胞高表达TDP43可激活RACK1的表达,进而调控软细胞增殖和凋亡。ORCID: 0000-0002-4563-8652(黄永明)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: