中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (26): 4121-4128.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1736
• 组织工程口腔材料 tissue-engineered oral materials • 上一篇 下一篇
颌骨缺损修复用多孔镁合金支架材料的生物安全性评价研究
王 亮1,郭玉兴1,黄 华2,袁广银2,张 雷1
- 1北京大学口腔医院口腔颌面外科,北京市 100081;2上海交通大学轻合金精密加工成型国家工程中心,上海市 200240
Evaluation of biosafety of porous magnesium alloy scaffolds for jaw defects
Wang Liang1, Guo Yuxing1, Huang Hua2, Yuan Guangyin2, Zhang Lei1
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Peking University Hospital of Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China; 2National Engineering Research Center of Light Alloys Net Forming and State Key Laboratory of Metal Matrix Composite, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
多孔镁合金支架材料:针对颌骨缺损设计的可降解金属修复支架材料,以Mg元素为主体,加入了Nd、Zn、Zr等元素,既有金属的优良机械学性能又可缓慢均匀降解,避免了二次手术取出问题;镁合金的诱导成骨性能及多孔支架形态设计有利于新骨形成。
医疗器械生物安全性评价:医疗器械是指直接或者间接用于人体的仪器、设备、器具、材料及其他类似或者相关的物品,其应用于临床必须保证安全性和有效性。医疗器械安全性评价一般需参照国标整理的方案,通用的包括细胞毒性、全身急性毒性、血液相容性评价、皮肤致敏实验等。
背景:研究已证实部分生物医用镁合金产品生物安全性及其他优势性能,但在其合金成分基础上改变制作工艺及产品形态制得的多孔支架材料生物安全性尚不明确。
目的:探讨生物医用多孔镁合金支架材料的生物安全性能。
方法:制取多孔镁合金支架材料浸提液,参照GB/T16886医疗器械生物学评价系列标准,进行体外细胞毒性实验、体外溶血实验、皮内反应实验、热源实验、急性全身毒性实验及遗传毒性实验,评估多孔镁合金支架材料浸提液对人骨髓间充质干细胞活性及血细胞胞膜结构完整性的影响,对动物皮内组织、体温、体质量、嗜多染红细胞染色体结构的影响;制备动物下颌骨缺损模型,将多孔镁合金材料植入缺损区,评估其对动物血清及尿液Mg2+浓度、血细胞数目和重要脏器等的影响。实验已通过北京大学医学部动物伦理委员会审核批准,批号为LA2017217。
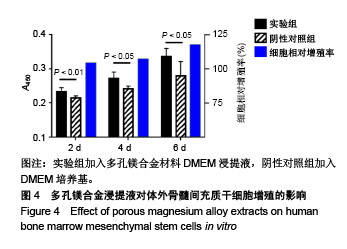
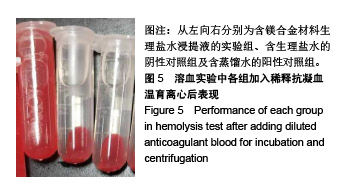
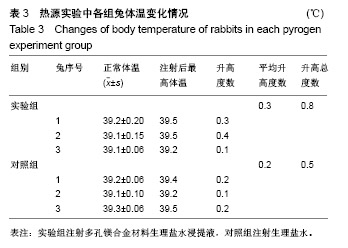
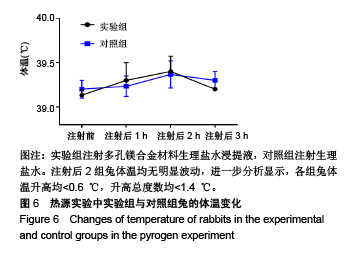
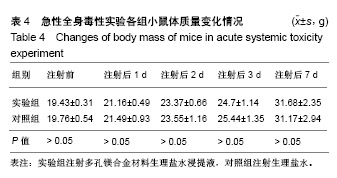
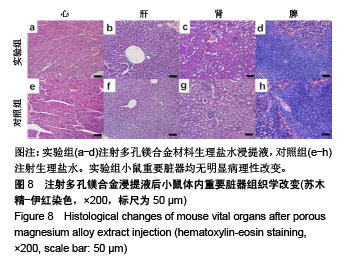
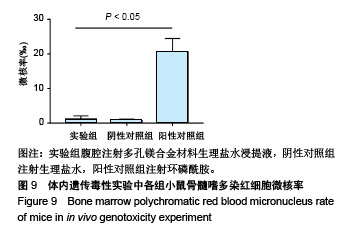
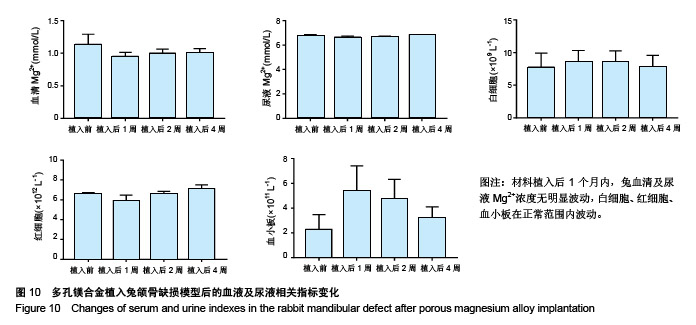
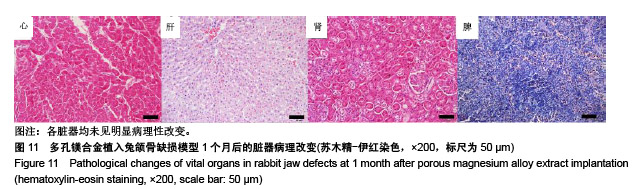
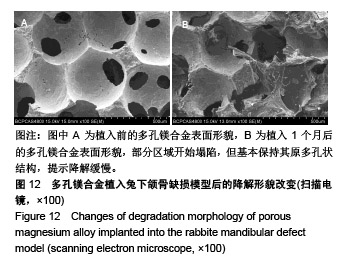
结果与结论:①多孔镁合金支架材料浸提液可促进骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖,细胞毒性为0级;②多孔镁合金支架材料浸提液的溶血率为0.94%,皮内刺激反应为0分,符合医疗器械溶血实验(<5%)及皮内反应实验(最终记分≤1.0)相关要求;③注射多孔镁合金浸提液后,所有动物体温升高均≤0.4 ℃,升高总度数≤0.8 ℃,符合医疗器械热源实验相关要求;④多孔镁合金浸提液未引起动物全身毒性反应,未破坏嗜多染红细胞染色体结构;⑤多孔镁合金支架材料植入动物骨缺损1个月内,动物血清及尿液Mg2+浓度无明显变化,红细胞、白细胞、血小板处在正常范围,未引起心、肝、肾、脾组织明显的病理性改变;⑥结果表明,多孔镁合金支架材料具备优良的生物安全性能。
中图分类号:

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)