中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (18): 2877-2883.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0876
• 组织工程口腔材料 tissue-engineered oral materials • 上一篇 下一篇
两种粘接剂的近中-合-远中洞型金合金嵌体三维有限元模型及应力分析
胡 杨1,冯 明2,祝 军3
- 1新疆医科大学第一附属医院口腔修复科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830054;2新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市口腔医院牙体牙髓科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830054;3上海市宝山区罗店医院口腔科,上海市 201908
Stress analysis of two kinds of adhesives used in a three-dimensional finite element model of mesio-occluso-distal cavity gold alloy inlay
Hu Yang1, Feng Ming2, Zhu Jun3
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Endodontics, Stomatological Hospital of Urumqi, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 3Department of Stomatology, Luodian Hospital of Baoshan District in Shanghai, Shanghai 201908, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
目的:建立右下颌第三磨牙近中-合-远中洞型金合金嵌体三维有限元模型,探究不同洞型深度下,3M RelyX Unicem和vario-link树脂粘接剂粘接金合金嵌体后,粘接界面和牙体组织应力分布规律及特点。
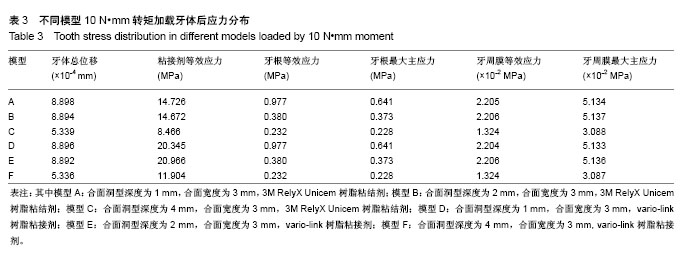
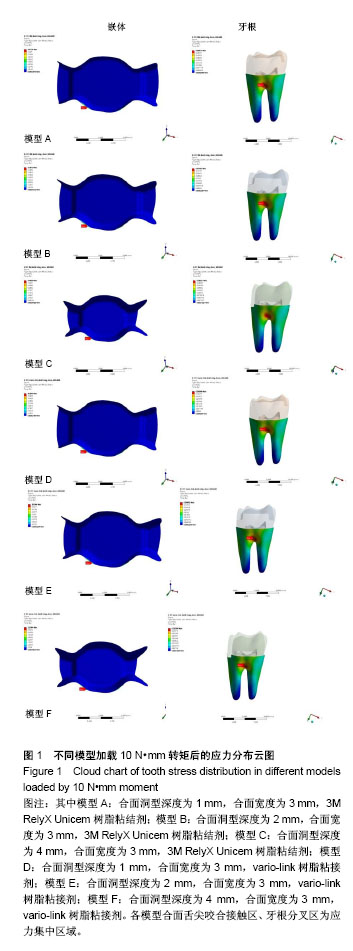
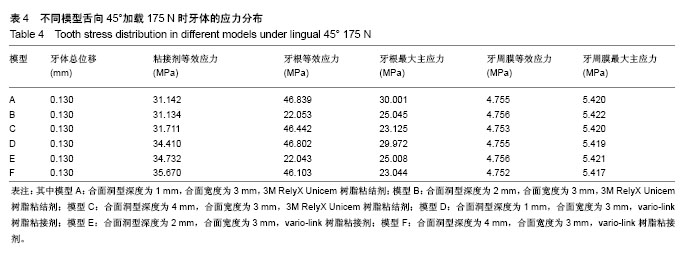
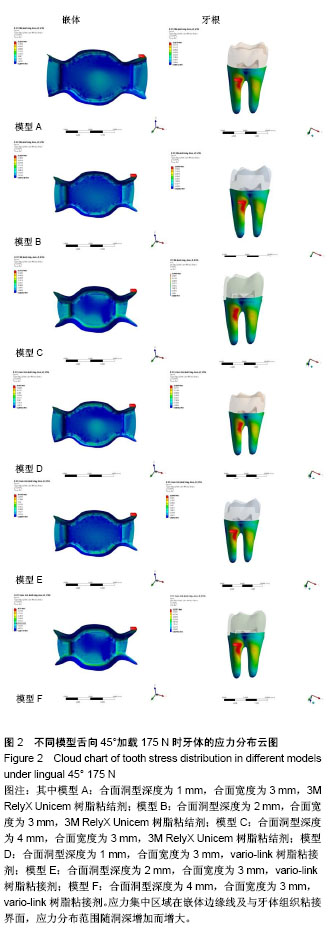
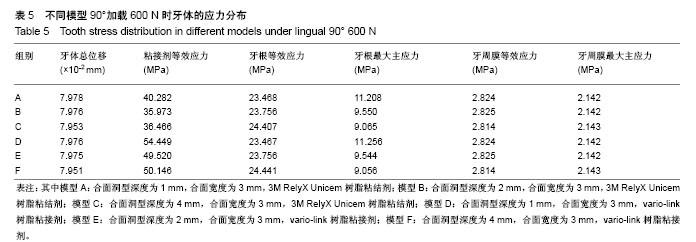
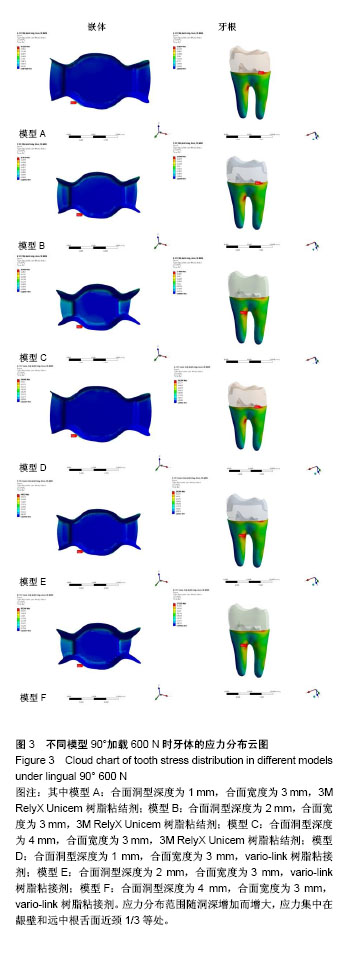
方法:采用Micro-CT扫描,Mimics、Goemagic Studio、NX 10.0等软件,建立不同深度和粘接剂的右下颌第三磨牙近中-合-远中洞型金合金嵌体三维有限元模型。其中模型A:合面洞型深度为1 mm,合面宽度为 3 mm,3M RelyX Unicem树脂粘结剂;模型B:合面洞型深度为2 mm,合面宽度为3 mm,3M RelyX Unicem树脂粘结剂;模型C:合面洞型深度为4 mm,合面宽度为3 mm,3M RelyX Unicem树脂粘结剂;模型D:合面洞型深度为1 mm,合面宽度为3 mm,vario-link树脂粘接剂;模型E:合面洞型深度为2 mm,合面宽度为3 mm,vario-link树脂粘接剂;模型F:合面洞型深度为4 mm,合面宽度为3 mm, vario-link树脂粘接剂。用ANSYS Workbench软件网格划分,并分析各模型在10 N•mm转矩、垂直载荷600 N和舌向45°加载175 N条件下应力分布情况。
结果与结论:不同洞深及粘接剂条件下,舌向45°加载175 N条件下各模型后,在洞深2 mm时,牙根等效应力最小,适宜金合金嵌体和vario-link粘接修复。垂直载荷600 N后,对于牙根等效应力,模型F高于模型C;对于牙根最大主应力,模型D高于模型A;对于粘接剂等效应力,vario-link树脂粘接剂模型较大。提示4 mm深度时,vario-link粘接界面产生的牙根部破坏性应力较大。各模型的应力集中区域为根分叉区、髓室顶、龈壁、近中或远中根颈1/3处。提示不同洞深、粘接剂和加载条件下,应力集中大小和区域有所不同,应避免过浅(< 1 mm)或过深近中-合-远中洞型(> 4 mm)洞型设计,3M RelyX Unicem 和vario-link均可作为金合金嵌体粘接剂,但需进一步临床实验验证三维有限元模型分析结果。
ORCID: 0000-0002-5014-6142(胡杨)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)