| [1] Werner N, Kosiol S, Schiegl T, et al. Circulating endothelial progenitor cells and cardiovascular outcomes.N Engl J Med. 2005;353(10):999-1007.[2] Yu P, Li Q, Liu Y, et al. Pro-angiogenic efficacy of transplanting endothelial progenitor cells for treating hindlimb ischemia in hyperglycemic rabbits.J Diabetes Complications. 2015;29(1):13-19.[3] Kim H, Kim S, Baek SH, et al. Pivotal Cytoprotective Mediators and Promising Therapeutic Strategies for Endothelial Progenitor Cell-Based Cardiovascular Regeneration.Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:8340257.[4] Suciu CF, Prete M, Ruscitti P, et al. Oxidized low density lipoproteins: The bridge between atherosclerosis and autoimmunity. Possible implications in accelerated atherosclerosis and for immune intervention in autoimmune rheumatic disorders.Autoimmun Rev. 2018;17(4):366-375.[5] Rajendran P, Rengarajan T, Thangavel J, et al. The vascular endothelium and human diseases.Int J Biol Sci. 2013;9(10): 1057-1069.[6] Zhang L, Xu Q.Stem/Progenitor cells in vascular regeneration. ArteriosclerThrombVasc Biol. 2014;34(6):1114-1119.[7] Avogaro A, Albiero M, Menegazzo L, et al. Endothelial dysfunction in diabetes: the role of reparatory mechanisms. Diabetes Care. 2011;34Suppl 2:S285-290.[8] Lee PS, Poh KK.Endothelial progenitor cells in cardiovascular diseases.World J Stem Cells. 2014;6(3):355-366.[9] Altabas V, Altabas K, Kirigin L.Endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) in ageing and age-related diseases: How currently available treatment modalities affect EPC biology, atherosclerosis, and cardiovascular outcomes.Mech Ageing Dev. 2016;159:49-62.[10] Alsheikh-Ali AA, Kitsios GD, Balk EM, et al. The vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque: scope of the literature.Ann Intern Med. 2010;153(6):387-395.[11] Bentzon JF, Otsuka F, Virmani R, et al. Mechanisms of plaque formation and rupture.Circ Res. 2014;114(12):1852-1866.[12] Sun Z.Atherosclerosis and atheroma plaque rupture: normal anatomy of vasa vasorum and their role associated with atherosclerosis.Scientific World Journal. 2014;2014:285058.[13] Alsheikh-Ali AA, Kitsios GD, Balk EM, et al. The vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque: scope of the literature.Ann Intern Med. 2010;153(6):387-395.[14] Bentzon JF, Otsuka F, Virmani R, et al. Mechanisms of plaque formation and rupture.Circ Res. 2014;114(12):1852-1866.[15] Libby P, Ridker PM, Hansson GK.Progress and challenges in translating the biology of atherosclerosis.Nature. 2011;473 (7347):317-325.[16] 王建礼,徐兴华,林娜. 氧化型低密度脂蛋白与动脉粥样硬化研究进展[J]. 医学综述, 2009, 15(9):1307-1310.[17] Trpkovic A, Resanovic I, Stanimirovic J, et al. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein as a biomarker of cardiovascular diseases.Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2015;52(2):70-85.[18] Orsó E, Grandl M, Schmitz G.Oxidized LDL-induced endolysosomalphospholipidosis and enzymatically modified LDL-induced foam cell formation determine specific lipid species modulation in human macrophages.Chem Phys Lipids. 2011;164(6):479-487.[19] Samson S, Mundkur L, Kakkar VV.Immune response to lipoproteins in atherosclerosis.Cholesterol. 2012;2012: 571846.[20] Steinberg D.The LDL modification hypothesis of atherogenesis: an update.J Lipid Res. 2009;50 Suppl: S376-381.[21] Pirillo A, Norata GD, Catapano AL.LOX-1, OxLDL, and atherosclerosis.Mediators Inflamm. 2013;2013:152786.[22] Ma FX, Zhou B, Chen Z, et al. Oxidized low density lipoprotein impairs endothelial progenitor cells by regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase.J Lipid Res. 2006;47(6): 1227-1237.[23] Chen J, Mehta JL, Haider N, et al. Role of caspases in Ox-LDL-induced apoptotic cascade in human coronary artery endothelial cells.Circ Res. 2004;94(3):370-376.[24] Auge N, Garcia V, Maupas-Schwalm F, et al. Oxidized LDL-induced smooth muscle cell proliferation involves the EGF receptor/PI-3 kinase/Akt and the sphingolipid signaling pathways.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2002;22(12): 1990-1995.[25] Yu BL, Zhao SP, Huang XS.Oxidized low-density lipoprotein: a double-edged sword on atherosclerosis.Med Hypotheses. 2007;69(3):553-556.[26] Fadini GP, Agostini C, Sartore S, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells in the natural history of atherosclerosis.Atherosclerosis. 2007;194(1):46-54.[27] Zampetaki A, Kirton JP, Xu Q.Vascular repair by endothelial progenitor cells.Cardiovasc Res. 2008;78(3):413-421.[28] Vasa M, Fichtlscherer S, Aicher A, et al. Number and migratory activity of circulating endothelial progenitor cells inversely correlate with risk factors for coronary artery disease.Circ Res. 2001;89(1):E1-7.[29] Tepper OM, Galiano RD, Capla JM, et al. Human endothelial progenitor cells from type II diabetics exhibit impaired proliferation, adhesion, and incorporation into vascular structures.Circulation. 2002;106(22):2781-2786.[30] Yamamoto K, Kondo T, Suzuki S, et al. Molecular evaluation of endothelial progenitor cells in patients with ischemic limbs: therapeutic effect by stem cell transplantation. Arterioscler ThrombVasc Biol. 2004;24(12):e192-196.[31] Stancu CS, Toma L, Sima AV.Dual role of lipoproteins in endothelial cell dysfunction in atherosclerosis.Cell Tissue Res. 2012;349(2):433-446.[32] Lin FY, Tsao NW, Shih CM, et al. The biphasic effects of oxidized-low density lipoprotein on the vasculogenic function of endothelial progenitor cells.PLoS One. 2015;10(5): e0123971.[33] Tie G, Yan J, Messina JA, et al. Inhibition of p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Enhances the Apoptosis Induced by Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein in Endothelial Progenitor Cells.J Vasc Res. 2015;52(6):361-371.[34] Li D, Chen H, Romeo F, et al. Statins modulate oxidized low-density lipoprotein-mediated adhesion molecule expression in human coronary artery endothelial cells: role of LOX-1.J Pharmacol ExpTher. 2002;302(2):601-605.[35] 马凤霞,任倩,韩忠朝. 植物血凝素样氧化型低密度脂蛋白受体介导氧化型低密度脂蛋白对内皮祖细胞存活和功能的影响[J]. 中国医学科学院学报, 2007, 29(3):336-341.[36] Li TB, Zhang YZ, Liu WQ, et al. Correlation between NADPH oxidase-mediated oxidative stress and dysfunction of endothelial progenitor cell in hyperlipidemic patients.Korean J Intern Med. 2018;33(2):313-322.[37] Li TB, Zhang JJ, Liu B, et al. Dysfunction of endothelial progenitor cells in hyperlipidemic rats involves the increase of NADPH oxidase derived reactive oxygen species production.Can J PhysiolPharmacol. 2017;95(5):474-480.[38] Lai P, Liu Y.Angelica sinensis polysaccharides inhibit endothelial progenitor cell senescence through the reduction of oxidative stress and activation of the Akt/hTERT pathway.Pharm Biol. 2015;53(12):1842-1849.[39] Ji KT, Qian L, Nan JL, et al. Ox-LDL induces dysfunction of endothelial progenitor cells via activation of NF-κB.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:175291.[40] Cheng J, Cui R, Chen CH, et al. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein stimulates p53-dependent activation of proapoptoticBax leading to apoptosis of differentiated endothelial progenitor cells.Endocrinology. 2007;148(5): 2085-2094.[41] Di Santo S, Diehm N, Ortmann J, et al. Oxidized low density lipoprotein impairs endothelial progenitor cell function by downregulation of E-selectin and integrin alpha(v)beta5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;373(4):528-532.[42] Ming GF, Tang YJ, Hu K, et al. Visfatin attenuates the ox-LDL-induced senescence of endothelial progenitor cells by upregulating SIRT1 expression through the PI3K/Akt/ERK pathway.Int J Mol Med. 2016;38(2):643-649. |
.jpg)
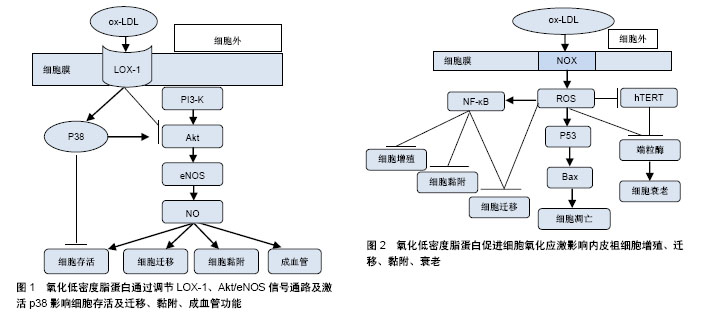
.jpg)
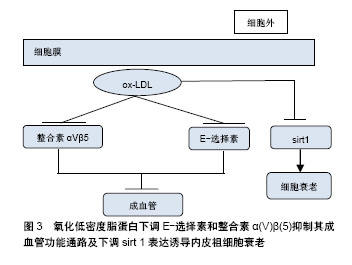
.jpg)