| [1] 肖德明,李伟,江捍平.骨科创伤流行病学研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2007,15(6):438-440.[2] Bekelis K, Desai A, Bakhoum SF, et al.A predictive model of complications after spine surgery: the National Surgical Quality Improvement Program (NSQIP) 2005-2010.Spine J.2014;14(7):1247-1255.[3] Curtis EM, van der Velde R,Moon RJ, et al.Epidemiology of fractures in the United Kingdom 1988-2012: Variation with age, sex, geography, ethnicity and socioeconomic status. Bone.2016;87:19-26.[4] Shi X,Yang J,Wang L,et al.Prospective study of serum uric acid levels and stroke in a Chinese hypertensive cohort.Clin Exp Hypertens.2017;39(6):527-531.[5] Sun S,Liu Z,Zhou H,et al.The role of fucosylation in the promotion of endothelial progenitor cells in neovascularization and bone repair.Biomaterials.2014;35(12):3777-3785.[6] Munsell EV,Kurpad DS,Freeman TA,et al.Histone-Targeted Gene Transfer of Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 Enhances Mesenchymal Stem Cell Chondrogenic Differentiation. Acta Biomater. 2018;71:156-167.[7] Walia B,Lingenheld E,Duong L,et al.A novel role for cathepsin K in periosteal osteoclast precursors during fracture repair. Ann N Y Acad Sci.2018;1415(1):57-68.[8] Patel KD, Cuvelier SL, Wiehler S. Selectins: critical mediators of leukocyte recruitment. Semin Immunol.2002;14(2):73-81.[9] Laird CT,Hassanein W,O'Neill NA,et al.P- and E-selectin receptor antagonism prevents human leukocyte adhesion to activated porcine endothelial monolayers and attenuates porcine endothelial damage. Xenotransplantation. 2018 ; 25(2):e12381. [10] Bell D, Zhao Y Y, Devine A B, et al. Influence of atenolol and nifedipine on nitric-oxide deficient cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and expression of the cardio-endocrine peptide intermedin and its receptor components. Cell Physiol Biochem.2008; 21(1-3):203-214.[11] Tonetti MS,D'Aiuto F,Nibali L,et al.Treatment of periodontitis and endothelial function.N Engl J Med.2007;356(9):911-920.[12] Pountos I,Georgouli T,Blokhuis TJ,et al. Pharmacological agents and impairment of fracture healing: what is the evidence?.Injury.2008;39(4):384-394.[13] Chan JK, Glass GE,Ersek A,et al.Low-dose TNF augments fracture healing in normal and osteoporotic bone by up-regulating the innate immune response.EMBO Mol Med. 2015;7(5):547-561.[14] Wiesenfeld HC,Hillier SL,Meyn LA,et al.Subclinical pelvic inflammatory disease and infertility. Obstet Gynecol.2012; 120(1):37-43.[15] Hiltunen A,Vuorio E, Aro HT.A standardized experimental fracture in the mouse tibia.J Orthop Res.1993;11(2):305-312.[16] Einhorn TA. The cell and molecular biology of fracture healing.Clin Orthop.1998,355S:S7-21.[17] Hankenson KD, Zimmerman G,Marcucio R.Biological perspectives of delayed fracture healing. Injury. 2014;45 Suppl 2:S8-S15 [18] 陈孝平. 外科学(下册)[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2005:986.[19] Kolar P,Schmidt-Bleek K,Schell H,et al.The early fracture hematoma and its potential role in fracture healing.Tissue Eng Part B Rev.2010;16(4):427-434.[20] Calori GM, Giannoudis PV.Enhancement of fracture healing with the diamond concept: the role of the biological chamber. Injury.2011;42(11):1191-1193.[21] Krause DS,Lazarides K,Lewis JB,et al.Selectins and their ligands are required for homing and engraftment of BCR-ABL1+ leukemic stem cells in the bone marrow niche. Blood.2014;123(9):1361-1371.[22] Silva M,Videira PA,Sackstein R.E-Selectin Ligands in the Human Mononuclear Phagocyte System: Implications for Infection, Inflammation, and Immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2017;8:1878.[23] Kon T,Cho TJ,Aizawa T, et al. Expression of osteoprotegerin, receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand (osteoprotegerin ligand) and related proinflammatory cytokines during fracture healing.J Bone Miner Res.2001;16(6):1004-1014.[24] 徐锡明,王飞,徐大启,等.低强度脉冲超声波促进脊柱融合的研究进展[J].第二军医大学学报,2015, 36(8):893-896.[25] Chou KJ,Lee PT,Chen CL,et al.CD44 fucosylation on mesenchymal stem cell enhances homing and macrophage polarization in ischemic kidney injury. Exp Cell Res. 2017; 350(1):91-102 [26] Obermeyer TS,Yonick D,Lauing K,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells facilitate fracture repair in an alcohol-induced impaired healing model.J Orthop Trauma.2012;26(12):712-718.[27] Alford AI,Reddy AB,Goldstein SA,et al.Two molecular weight species of thrombospondin-2 are present in bone and differentially modulated in fractured and nonfractured tibiae in a murine model of bone healing.Calcif Tissue Int. 2012;90(5): 420-428.[28] Nam D,Mau E,Wang Y,et al.T-lymphocytes enable osteoblast maturation via IL-17F during the early phase of fracture repair. PLoS One.2012;7(6):e40044.[29] Lauing KL,Roper PM,Nauer RK,et al.Acute alcohol exposure impairs fracture healing and deregulates beta-catenin signaling in the fracture callus. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2012; 36(12):2095-2103. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
E、P选择素:是一类由糖基化单链跨膜蛋白构成的细胞黏附分子,主要分布于血小板及内皮细胞上,介导细胞间选择性识别、迁移、黏附,并在炎症反应、肿瘤转移及血栓形成等中起重要作用。
酶联免疫吸附法(ELISA):是一类利用抗原抗体结合专一性进行的免疫反应,可定性、定量检测组织中的蛋白含量。ELISA的基础是抗原或抗体的固相化及抗原或抗体的酶标记。由于酶的催化效率很高,间接地放大了免疫反应的结果,使测定方法达到很高的灵敏度。
文题释义:
E、P选择素:是一类由糖基化单链跨膜蛋白构成的细胞黏附分子,主要分布于血小板及内皮细胞上,介导细胞间选择性识别、迁移、黏附,并在炎症反应、肿瘤转移及血栓形成等中起重要作用。
酶联免疫吸附法(ELISA):是一类利用抗原抗体结合专一性进行的免疫反应,可定性、定量检测组织中的蛋白含量。ELISA的基础是抗原或抗体的固相化及抗原或抗体的酶标记。由于酶的催化效率很高,间接地放大了免疫反应的结果,使测定方法达到很高的灵敏度。.jpg) 文题释义:
E、P选择素:是一类由糖基化单链跨膜蛋白构成的细胞黏附分子,主要分布于血小板及内皮细胞上,介导细胞间选择性识别、迁移、黏附,并在炎症反应、肿瘤转移及血栓形成等中起重要作用。
酶联免疫吸附法(ELISA):是一类利用抗原抗体结合专一性进行的免疫反应,可定性、定量检测组织中的蛋白含量。ELISA的基础是抗原或抗体的固相化及抗原或抗体的酶标记。由于酶的催化效率很高,间接地放大了免疫反应的结果,使测定方法达到很高的灵敏度。
文题释义:
E、P选择素:是一类由糖基化单链跨膜蛋白构成的细胞黏附分子,主要分布于血小板及内皮细胞上,介导细胞间选择性识别、迁移、黏附,并在炎症反应、肿瘤转移及血栓形成等中起重要作用。
酶联免疫吸附法(ELISA):是一类利用抗原抗体结合专一性进行的免疫反应,可定性、定量检测组织中的蛋白含量。ELISA的基础是抗原或抗体的固相化及抗原或抗体的酶标记。由于酶的催化效率很高,间接地放大了免疫反应的结果,使测定方法达到很高的灵敏度。
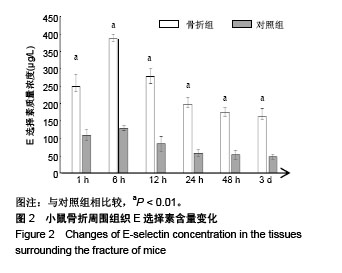
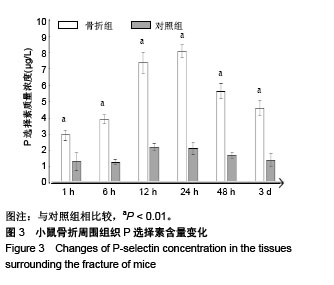
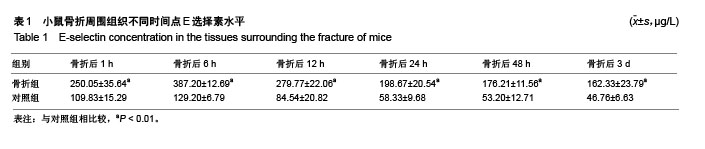
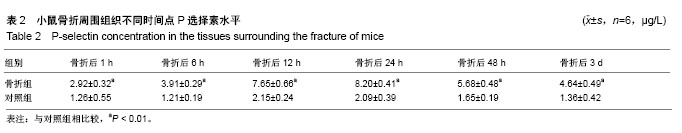
.jpg) 文题释义:
E、P选择素:是一类由糖基化单链跨膜蛋白构成的细胞黏附分子,主要分布于血小板及内皮细胞上,介导细胞间选择性识别、迁移、黏附,并在炎症反应、肿瘤转移及血栓形成等中起重要作用。
酶联免疫吸附法(ELISA):是一类利用抗原抗体结合专一性进行的免疫反应,可定性、定量检测组织中的蛋白含量。ELISA的基础是抗原或抗体的固相化及抗原或抗体的酶标记。由于酶的催化效率很高,间接地放大了免疫反应的结果,使测定方法达到很高的灵敏度。
文题释义:
E、P选择素:是一类由糖基化单链跨膜蛋白构成的细胞黏附分子,主要分布于血小板及内皮细胞上,介导细胞间选择性识别、迁移、黏附,并在炎症反应、肿瘤转移及血栓形成等中起重要作用。
酶联免疫吸附法(ELISA):是一类利用抗原抗体结合专一性进行的免疫反应,可定性、定量检测组织中的蛋白含量。ELISA的基础是抗原或抗体的固相化及抗原或抗体的酶标记。由于酶的催化效率很高,间接地放大了免疫反应的结果,使测定方法达到很高的灵敏度。