| [1] 张建军,史焕昌,杨卫山,等. 亚低温条件下脊髓损伤模型大鼠神经再生微环境及运动功能的变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2015, 19(27):4316-4321.[2] Vipin A, Kortelainen J, Al-Nashash H, et al. Prolonged Local Hypothermia Has No Long-Term Adverse Effect on the Spinal Cord. Ther Hypothermia Temp Manag. 2015;5(3):152-162.[3] 康文博,李晓红,陈翀,等. 亚低温对脊髓损伤后反应性星形胶质细胞增生的影响[J]. 中国应用生理学杂志,2016,32(4): 289-292.[4] Raavé R, de Vries RB, Massuger LF, et al. Drug delivery systems for ovarian cancer treatment: a systematic review and meta-analysis of animal studies. PeerJ. 2015;3:e1489.[5] 姚海燕,李青,梁道臣,等. 甲泼尼龙联合亚低温治疗急性脊髓损伤[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2016,22(5):414-417.[6] 廖烨晖,钟德君,康敏,等. 全反式维甲酸干预鼠胚神经干细胞联合胶质细胞源性神经营养因子及硫酸软骨素酶ABC移植修复大鼠脊髓损伤的研究[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2015,29(8): 1009-1015.[7] Panthee N, Ono M. Spinal cord injury following thoracic and thoracoabdominal aortic repairs. Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann. 2015;23(2):235-246.[8] 王东,付红杰,张建军,等. 亚低温联合高压氧干预对大鼠神经干细胞RhoA/RHOCK通路的影响[J]. 山东医药, 2016, 56(33): 34-36.[9] Tu Y,Miao XM,Yi TL,et al.Neuroprotective effects of bloodletting at Jing points combined with mild induced hypothermia in acute severe traumatic brain injury.Neural Regen Res.2016;11(6): 931-936.[10] Lv HY,Wu SJ,Wang QL,et al.Effect of erythropoietin combined with hypothermia on serum tau protein levels and neurodevelopmental outcome in neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Neural Regen Res.2017; 12 (10): 1655-1663.[11] Chen D, Lee J, Gu X, et al. Intranasal Delivery of Apelin-13 Is Neuroprotective and Promotes Angiogenesis After Ischemic Stroke in Mice. ASN Neuro. 2015;7(5): 1759091415605114.[12] 张梅,王跃新,侯晓华,等. bcl-2基因修饰神经干细胞移植修复大鼠脊髓损伤[J]. 中国比较医学杂志, 2016,26(7):35-41.[13] Jellish WS. Spinal Cord Protection During Thoracoabdominal Aortic Intervention: Now and in the Future--It's Not All About Hypothermia. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2016;30(2): 275-279.[14] Tracy B, Armola R, Micham J. The "cold cord": a review of therapeutic hypothermia for traumatic spinal cord injuries. Am J Crit Care. 2015;24(6):540-543.[15] 秦玲,周铁丽,吴巧萍,等. hTERT基因修饰神经干细胞移植修复大鼠脊髓损伤[J]. 医学研究杂志, 2016,45(2):99-104.[16] Blacker DJ, Musuka T. Management of intracerebral hemorrhage in 2020. Future Neurology. 2015;6(6):745-756.[17] Lee SH, Jin KS, Bang OY, et al. Differential Migration of Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Ischemic Regions after Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion in Rats. PLoS One. 2015;10(8): e0134920.[18] 张雪松. 外胚层间充质来源的神经干细胞-纤维蛋白支架复合体移植修复大鼠脊髓损伤的实验研究[D]. 镇江:江苏大学, 2016.[19] Ashwal S, Hartman RE, Ghosh N, et al. Human neural stem cells reduce penumbral volume and improve motor and cognitive outcomes in neonatal hypoxic ischemic cerebra injury. Eur J Paediatric Neurol. 2015;19:S95.[20] Liu H, Yang M, Pan L, et al. Hyperbaric Oxygen Intervention Modulates Early Brain Injury after Experimental Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Rats: Possible Involvement of TLR4/NF-x03BA; B-Mediated Signaling Pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;38(6):2323-2336.[21] 余永涛,廖烨晖,唐强,等. 硫酸软骨素酶ABC及Nogo-66受体拮抗剂联合鼠胚神经干细胞移植对大鼠脊髓损伤的影响[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2016,26(6):527-536.[22] Ma J, Wang Z, Liu C, et al. Pramipexole-Induced Hypothermia Reduces Early Brain Injury via PI3K/AKT/GSK3β pathway in Subarachnoid Hemorrhage rats. Sci Rep. 2016;6:23817.[23] 王喜良. 神经干细胞移植联合促红细胞生成素对脊髓损伤大鼠神经轴突修复作用的实验研究[D]. 内蒙古:内蒙古医科大学, 2015.[24] Panackel C, Thomas R, Sebastian B, et al. Recent advances in management of acute liver failure. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2015;19(1):27-33. |
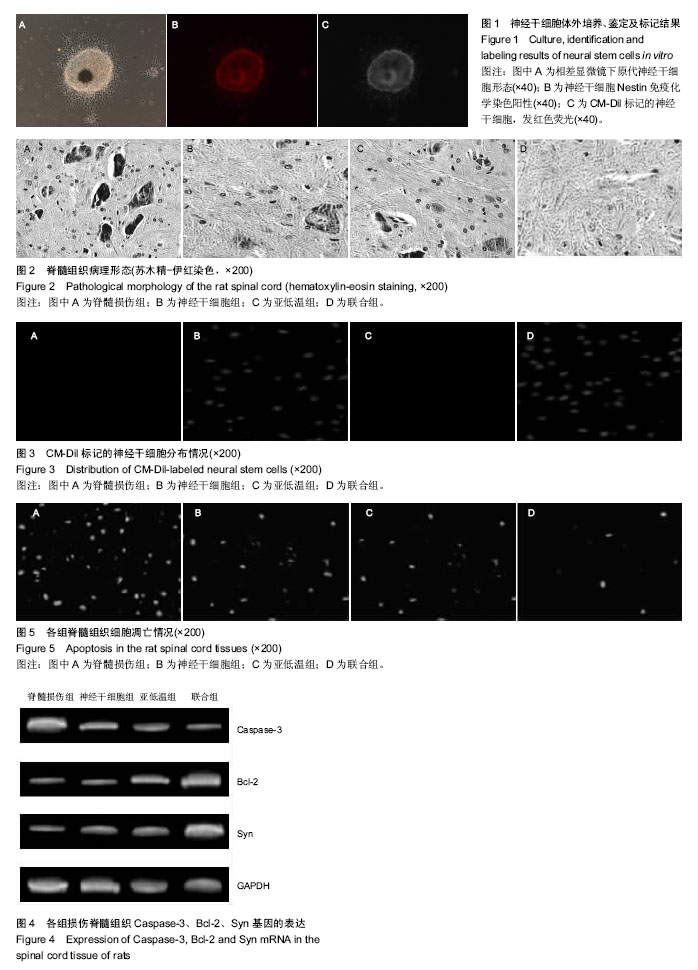
.jpg)
.jpg)