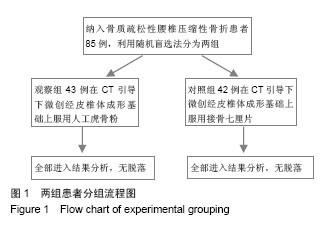
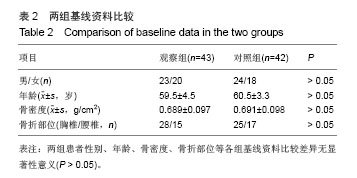
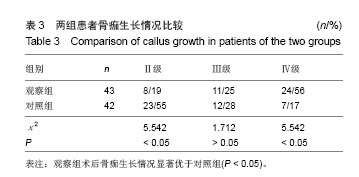
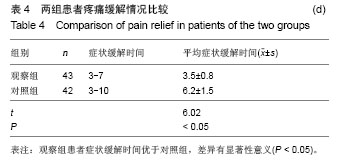
| [1]吕小华,陈科.金天格胶囊治疗骨质疏松症200例[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2009,18(7):788-789.
[2]王晋平,张佳红,王慧娟,等.金天格胶囊治疗骨关节炎临床疗效分析[J].中国医院药学杂志,2011,31(10):848-850.
[3]赵冀伟.金天格胶囊治疗骨质疏松性骨折50例临床研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2012,18(1):63-65.
[4]姜波,闻辉,杨春辉.金天格胶囊治疗原发性骨质疏松症的临床疗效[J].中国社区医师(医学专业),2010,12(35):123.
[5]杨宇君,武晓波,向川.金天格胶囊治疗骨质疏松症的临床研究[J].中国医疗前沿(上半月),2011,6(9):32-33.
[6]Kim KW,Ha KY,Moon MS.Volumetric change of the grit bone after intertransverse fusion.Spine. 1999;8(4):221.
[7]Lied B,Roenning PA,Sundseth J.Anterior cervical discectomy with fusion in patients with cervical disc degeneration:a prospective outcome study of 258 patients (181 fused with autologous bone graft and 77 fused with a PEEK cage).BMC Surg. 2010;8(4):554.
[8]Fraser JF,Hartl R.Anterior approaches to fusion of the cervical spine:a metaanalysis of fusion rates. J Neurosurg Spine. 2007;5(2):189.
[9]Atkins D, Best D, Briss PA, et al. Grading quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ. 2004; 328(7454): 1490.
[10]Zhang B, Dai M, Tang Y. Unilateral versus bilateral kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Adv Mat Res. 2012; 393:1064-1068.
[11]Luo XL, Zheng CK, Kan WS, et al. Unilateral versus bilateral percutaneous kyphoplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic compression fractures. Chin J Tissue Eng Res. 2012; 16(3): 567-570.
[12]Pignatello R, Cenni E, Micieli D, et al. A novel biomaterial for osteotropic drug nanocarriers: synthesis and biocompatibility evaluation of a PLGA-ALE conjugate. Nanomedicine 2009; 4: 161-175.
[13]Ma YL, Dai RC, Sheng ZF, et al. Quantitative association between osteocyte density and biomechanics, microcrack and microstructure in OVX rats vertebral trabeculae. J Biomech. 2008; 41:1324-1332.
[14]Teo JC, Si-Hoe KM, Keh JE, et al. Correlation of cancellou bone microarchitectural parameter from microCT to CT number and bone mechanical properties. Mater Sci Eng C. 2007; 27:333-339.
[15]Boyd SK, Davision P, Muller R, et al. Monitoring individual morphological changes overtime in ovariectomized rats by in vivo micro-computed tomography. Bone. 2006;39: 854-862.
[16]Waarsing JH, Day JS, van der Linden JC, et al. Detecting and tracking local changes in the tibiae of individual rats: a novel method to analyse longitudinal in vivo micro-CT data. Bone. 2004; 34:163-169.
[17]Sheng Z, Dai R, Wu X, et al. Regionally-specific compensation for bone loss in the tibial trabeculae of estrogen deficient rats. Acta Radiologica. 2007; 48: 531-539.
[18]Zhang SD, Wang C, Jiang XJ, et al. Experimental research on biomechanics of calcium sulfate cement in thoracolumbar burst fractures. Ortho J Chin. 2009;17:1-5.
[19]Yun MH, Kwon KI. High-performance liquid chromatography method for determining alendronate sodium in human plasma by detecting fluorescence: Application to a pharmacokinetics study in humans. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2006;40:168-172.
[20]Rhim SY, Park JH, Park YS, et al. Bioavailability and bioequivalence of two oral formulations of alendronate sodium 70 mg: an open-label, randomized, two-period crossover comparision in healthy Korean adult male volunteers. Clin Ther. 2009; 31:1037-1045.
[21]Keaveny TM, Hayes WC. A 20-year perspective on the mechanical properties of trabecular bone. J Biomech Eng. 1993; 115:534-542. |