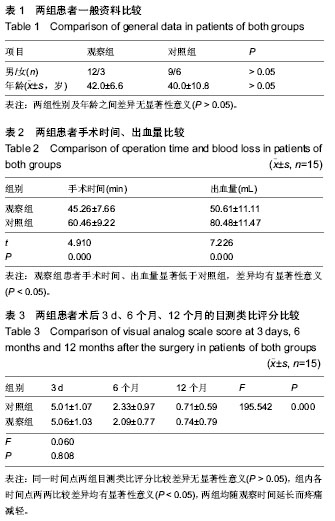
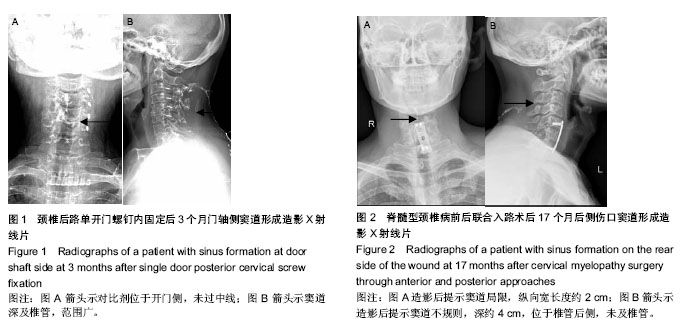
| [1] Wimmer C, Gluch H, Franzreb M,et al. Predisposing fractors for infection in spinal surgury:a survey of 850 spinal procedures. Spinal Disord. 1998;11(2):124-128.
[2] Dubousset J, Shufflebarger HL,Wenger D. Late “infection” with CD instrumentation.Orthop Trans. 1994;118:121.
[3] Richards BS. Delayed infections following posterior spinal instrumentation for the treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995;77:524-529.
[4] Wimmer C, Gluch H. Management of postoperative wound infection in posterior spinal fusion with instrumentation.Spinal Disord. 1996;9(6):505-508.
[5] 仉建国,李书刚,杨新宇,等.脊柱后路矫形融合术术后感染的治疗[J].中华骨科杂志,2001,21(8):453-456.
[6] Ho C, Sucato DJ, Richards BS. Risk fraction for the development of delayed infection posterior spinal fusion and instrumentation in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients. Spine. 2007;32(20):2272-2277.
[7] 林文辉,黄秀萍,林玉媛.碘海醇与泛影葡胺在CT增强扫描中的效果比较[J].海峡医药,1999,11(2):93-95.
[8] 范家栋,谢敬霞.CT诊断学基础[M].2版.北京:北京医科大学出版社,2001.
[9] 吴保杰.现代临床治疗药物大全[M].北京:中国医药科技出版社,1995:655.
[10] 吕志珍,刘利兵.亚甲蓝的外科临床应用[J].张家口医学院学报,2003,20(4):68.
[11] 职良喜.复方亚甲蓝液穴位注射治疗第三腰椎横突综合征30例[J].江苏中医药,2003,24(3):38-39.
[12] 胡红艳,黄秋明,李艳.亚甲蓝在非解毒领域中的应用[J].中国医药导报,2009,6(28):7-9.
[13] Wu H,Xu X,Ying H, et al.Preliminary study of indirect CT lymphography-guided sentinel lymph node biopsy in a tongue VX2 carcinoma model. Int J Oral Maxillof Surg. 2009;38(12): 1268-1272.
[14] Wu H, Ying H,Xi X, et al. Localization of the sentinel lymph node in tongue VX2 carcinoma via indirect CT lymphography combined with methylene blue dye injection. Acta Oto Laryngologica. 2010;130(4):503-510.
[15] Tsuruno A, Shibazaki A,Kanda N, et al. Visualization of the thoracic duct with injections of dyes or contrast media into the testicular parenchyma in the rabbit. J Vet Med Sci. 2009;71(6): 759-762.
[16] Rissanen T, Reinikainen H, Apaja-Sarkkinen M, et al.Breast sonography in localizing the cause of nipple discharge: comparison with galactography in 52 patients. J Ultr Med. 2007; 26(8):1031-1039.
[17] Gofeld M. Development and validation of a new technique for ultrasound-guided stellate ganglion block. Reg Anesthesia Pain Med. 2009;34(5):475-479.
[18] 徐秀寅,石芳,陈晓平,等.碘海醇复合染料定位兔舌癌前哨淋巴结. 中国眼耳鼻喉科杂志,2013,13(4):243-246.
[19] 胡小兵,熊鸿燕,宋建勇,等.亚甲蓝在光敏效应对血液中细菌的灭活效果研究[J].预防医学情报杂志,2003,19(6):491.
[20] Thalgot JS, Cotler HB, Sasso RC,et al. Postoperaive infections in spinal implants, classification and analysis. A multi center study. Spine. 1991;16:981-984.
[21] 贾连顺.颈椎术后感染的危险因素与其他[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2008,16(23):1802-1804.
[22] Randall W, Howard A, Sarah M. Delayed infection after elective spinal instrumentation and fusion. Spine. 1997; 22: 2444-2451.
[23] Cynthia E, Clark RN, Harry L. Late-developing infection in instrumented idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 1999;24:1909-1912.
[24] Gristina AG, Kolkin J. Current concepts review :total joint replacement and sepsis. J Bone Joint Surg(Am). 1985;67:264-270. |