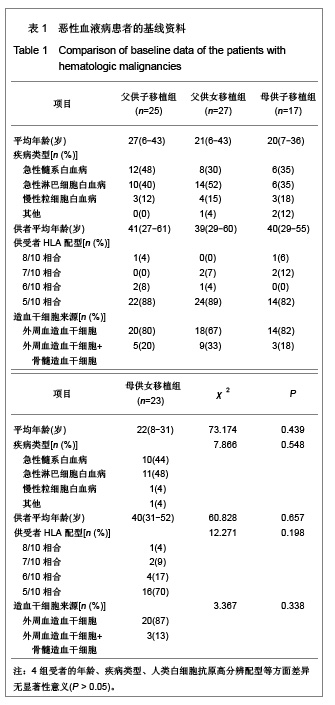
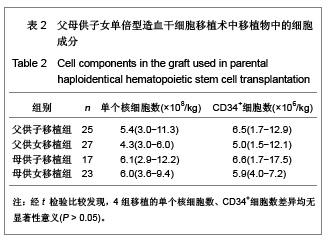
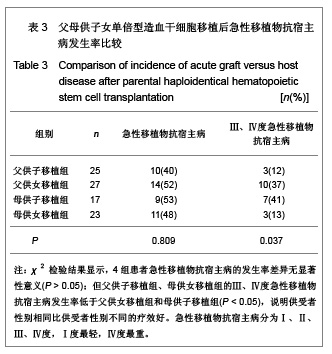
| [1] Hart DP, Peggs KS. Current status of allogeneic stem cell transplantation for treatment of hematologic malignancies. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2007;82(3):325-329.[2] Laughlin MJ, Barker J, Bambach B, et al. Hematopoietic engraftment and survival in adult recipients of umbilical-cord blood from unrelated donors. N Engl J Med. 2001;344(24): 1815-1822.[3] Lu DP. Blood and marrow transplantation in mainland China. Hong Kong Med J. 2009;15(3 Suppl 3):9-12.[4] Yuan HL, Jiang M, Wen BZ, et al. Zhonghua Qiguan Yizhi Zazhi. 2010;31(2):79-83. 袁海龙,江明,温丙昭,等.HLA单倍体相合与全相合外周血造血干细胞移植治疗恶性血液病的疗效比较[J].中华器官移植杂志, 2010,31(2):79-83.[5] Huang XJ. Current status of haploidentical stem cell transplantation for leukemia. J Hematol Oncol. 2008;1:27.[6] Wan DM, Zhang C, Xie XS, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(19): 3485-3488. 万鼎铭,张诚,谢新生,等.单倍型相合造血干细胞移植治疗高危白血病[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(19):3485- 3488.[7] Ruggeri L, Mancusi A, Burchielli E, et al. NK cell alloreactivity and allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2008;40(1):84-90.[8] Zhang ZN, Shen T. Beijing: Science Press. 2008. 张之南,沈悌.血液病诊断及疗效标准[M]. 3版.北京:科学出版社, 2008.[9] Ji SQ, Chen HR, Wang HX, et al. G-CSF-primed haploidentical marrow transplantation without ex vivo T cell depletion: an excellent alternative for high-risk leukemia. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2002;30(12):861-866.[10] Chang YJ, Huang XJ. Use of G-CSF-stimulated marrow in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation settings: a comprehensive review. Clin Transplant. 2011;25(1):13-23.[11] Wan DM, Kang YQ, Sun H, et al. Zhongguo Shiyong Neike Zazhi. 2009;29(7):648-649. 万鼎铭,康轶青,孙慧,等.改良BU/CY预处理方案行异基因造血干细胞移植治疗恶性血液病的临床研究[J].中国实用内科杂志, 2009,29(7):648-649.[12] Wan DM, Shao YL, Qin T, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2012;16(32):6076-6080. 万鼎铭,邵运丽,秦童,等. HLA单倍体与全相合异基因造血干细胞移植治疗恶性血液病[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(32): 6076-6080.[13] Wang Y, Liu DH, Xu LP, et al. Superior graft-versus-leukemia effect associated with transplantation of haploidentical compared with HLA-identical sibling donor grafts for high-risk acute leukemia: an historic comparison. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2011;17(6):821-830.[14] Laughlin MJ, Barker J, Bambach B, et al. Hematopoietic engraftment and survival in adult recipients of umbilical-cord blood from unrelated donors. N Engl J Med. 2001;344(24): 1815-1822.[15] Kang Y, Chao NJ, Aversa F. Unmanipulated or CD34 selected haplotype mismatched transplants. Curr Opin Hematol. 2008; 15(6):561-567.[16] Chang YJ, Zhao XY, Huo MR, et al. Influence of lymphocyte recovery on outcome of haploidentical transplantation for hematologic malignancies. Medicine (Baltimore). 2009;88(6): 322-330.[17] Gyurkocza B, Rezvani A, Storb RF. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: the state of the art. Expert Rev Hematol. 2010;3(3):285-299.[18] Henslee-Downey PJ, Abhyankar SH, Parrish RS, et al. Use of partially mismatched related donors extends access to allogeneic marrow transplant. Blood. 1997;89(10):3864-3872.[19] Rizzieri DA, Koh LP, Long GD, et al. Partially matched, nonmyeloablative allogeneic transplantation: clinical outcomes and immune reconstitution. J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25(6): 690-697.[20] Aversa F, Tabilio A, Velardi A, et al. Treatment of high-risk acute leukemia with T-cell-depleted stem cells from related donors with one fully mismatched HLA haplotype. N Engl J Med. 1998;339(17):1186-1193.[21] Ochiai N, Shimazaki C, Fuchida S, et al. Successful non-T cell-depleted HLA haplo-identical three-loci mismatched hematopoietic stem cell transplantation from mother to son based on the feto-maternal microchimerism in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2002; 30(11): 793-796.[22] Wang Y, Wu DP, Sun AN, et al. Zhonghua Xueyexue Zazhi. 2006;27(12):842-844. 王荧,吴德沛,孙爱宁,等.母体内微量子代细胞嵌合体在HLA半相合造血干细胞移植中的意义[J].中华血液学杂志,2006,27(12): 842-844. [23] Tamaki S, Ichinohe T, Matsuo K, et al. Superior survival of blood and marrow stem cell recipients given maternal grafts over recipients given paternal grafts. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2001;28(4):375-380.[24] van Rood JJ, Loberiza FR Jr, Zhang MJ, et al. Effect of tolerance to noninherited maternal antigens on the occurrence of graft-versus-host disease after bone marrow transplantation from a parent or an HLA-haploidentical sibling. Blood. 2002;99(5):1572-1577.[25] Aversa F. Haploidentical haematopoietic stem cell transplantation for acute leukaemia in adults: experience in Europe and the United States. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2008; 41(5):473-481. [26] Huang XJ, Xu LP, Liu KY, et al. Partially matched related donor transplantation can achieve outcomes comparable with unrelated donor transplantation for patients with hematologic malignancies. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15(14):4777-4783.[27] Xiang QQ, Kong PY, Li JP, et al. Jiefangjun Yixue Zazhi.2012; 37(2):121-125. 向茜茜,孔佩艳,李杰平,等.亲代间单倍体相合造血干细胞移植治疗血液病45例临床分析[J].解放军医学杂志,2012,37(2):121- 125.[28] Qu JH, Wen BZ. Linchuang Xueyexue Zazhi. 2008;21(11): 621-624. 曲建华,温丙昭.诱导造血干细胞胞移植免疫耐受的研究进展[J].临床血液学杂志, 2008,21(11):621-624.[29] Tong J. Guoji Mianyixue Zazhi.2007;30(1):23-27. 童娟.NK细胞在异基因造血干细胞移植中对移植物抗白血病效应及移植物抗宿主病作用的影响[J].国际免疫学杂志,2007, 30(1): 23-27.[30] Ruggeri L, Mancusi A, Capanni M, et al. Donor natural killer cell allorecognition of missing self in haploidentical hematopoietic transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia: challenging its predictive value. Blood. 2007;110(1):433-440.[31] Symons HJ, Leffell MS, Rossiter ND, et al. Improved survival with inhibitory killer immunoglobulin receptor (KIR) gene mismatches and KIR haplotype B donors after nonmyeloablative, HLA-haploidentical bone marrow transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2010;16(4): 533-542. |