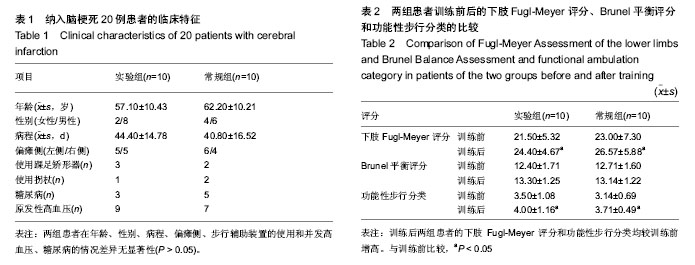
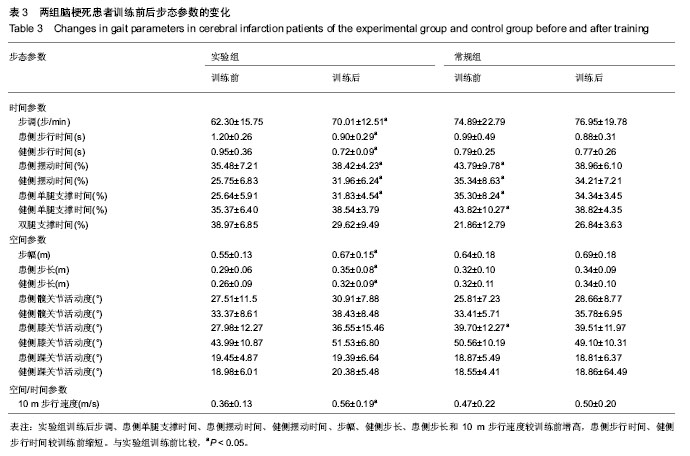
| [1] Nilsson L, Carlsson J, Danielsson A, et al. Walking training of patients with hemiparesis at an early stage after stroke: a comparison of walking training on a treadmill with body weight support and walking training on the ground. Clin Rehabil. 2001; 15(5):515-527.[2] Alptekin N, Gok H, Geler-Kulcu D, et al. Efficacy of treatment with a kinaesthetic ability training device on balance and mobility after stroke: a randomized controlled study. Clin Rehabil. 2008;22(10-11):922-930.[3] French B, Thomas L, Leathley M, et al. Does repetitive task training improve functional activity after stroke? A Cochrane systematic review and meta-analysis. J Rehabil Med. 2010; 42(1):9-14.[4] Daly JJ, Ruff RL. Construction of efficacious gait and upper limb functional interventions based on brain plasticity evidence and model-based measures for stroke patients. ScientificWorldJournal. 2007;7:2031-2045.[5] Prado-Medeiros CL, Sousa CO, Souza AS, et al. Effects of the addition of functional electrical stimulation to ground level gait training with body weight support after chronic stroke. Rev Bras Fisioter. 2011;15(6):436-444. [6] 张大威,叶祥明,林坚,等.下肢任务导向性训练对慢性期脑卒中患者步行能力的影响[J]. 中国康复医学杂志,2011,26(8): 768-770. [7] Chen G, Patten C, Kothari DH, et al. Gait differences between individuals with post-stroke hemiparesis and non-disabled controls at matched speeds. Gait Posture. 2005;22(1):51-56.[8] Goldie PA, Matyas TA, Evans OM. Gait after stroke: initial deficit and changes in temporal patterns for each gait phase. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2001;82(8):1057- 1065. [9] Sudarsky L. Geriatrics: gait disorders in the elderly. N Engl J Med. 1990;17; 322(20):1441-1446.[10] Globas C, Becker C, Cerny J, et al. Chronic stroke survivors benefit from high-intensity aerobic treadmill exercise: a randomized control trial. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2012; 26(1):85-95.[11] Gjellesvik TI, Brurok B, Hoff J, et al. Effect of high aerobic intensity interval treadmill walking in people with chronic stroke: a pilot study with one year follow-up. Top Stroke Rehabi. 2012;19(4):353-360.[12] Visintin M, Barbeau H, Korner-Bitensky N, et al. A new approach to retrain gait in stroke patients through body weight support and treadmill stimulation. Stroke. 1998;29(6):1122- 1128.[13] Walker ML, Ringleb SI, Maihafer GC, et al. Virtual reality–enhanced partial body weight–supported treadmill training poststroke: feasibility and effectiveness in 6 subjects. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2010;91(1):115-122.[14] 肖湘,毛玉瑢,李乐,等. 虚拟现实同步减重训练对脑卒中患者步态影响的对照研究[J].中国康复医学杂志, 2012,27(6):533-537.[15] 毛玉珞,李乐,肖湘,等. 减重平板训练对早期脑卒中患者下肢运动力矩峰值的影响[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2013,35(1): 21-24.[16] 中华医学会神经病学分会脑血管病学组. 急性缺血性脑卒中诊治指南2010. 中华神经科杂志,2010,43(2):146-152.[17] Wade DT, Wood VA, Heller A, et al. Walking after stroke. Measurement and recovery over the first 3 months. Scand J Rehabil Med. 1987;19(1):25-30.[18] 杨雅琴,王拥军,冯涛,等. 平衡评价量表在临床中的应用[J]. 中国康复理论与实践,2011,17(8):709-712.[19] 肖灵君,廖丽贞,燕铁斌,等. Brunel平衡量表中文版的开发及信度研究[J]. 中国康复医学杂志,2009,25(2):145-148.[20] 孟殿怀,伊文超,顾昭华,等. 功能性电刺激辅助步行设备对脑卒中足下垂患者步态时空参数的影响[J]. 中国康复医学杂志, 2013,28(10):923-928.[21] 瓮长水,王军,潘小燕,等.强制性使用运动疗法对慢性期脑卒中患者上肢运动功能的康复疗效[J].中国康复理论与实践,2006, 12(10):890-892.[22] Burgess JK, Weibel GC, Brown DA. Overground walking speed changes when subjected to body weight support conditions for nonimpaired and post stroke individuals. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2010;7:6.[23] Sousa CO, Barela JA, Prado-Medeiros CL, et al. The use of body weight support on ground level: an alternative strategy for gait training of individuals with stroke. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2009;1;6:43.[24] 李卫东,李红桃. 急性脑梗死患者偏瘫早期康复的介入对上下肢运动功能恢复的疗效观察[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2001,5(23):63-67.[25] Leddy AL, Crowner BE, Earhart GM. Functional gait assessment and balance evaluation system test: reliability, validity, sensitivity, and specificity for identifying individuals with Parkinson disease who fall. Phys Ther. 2011;91(1): 102-113. [26] 马超,麦明泉,许俭兴,等. 脑梗死急性期下肢运动功能恢复与体感诱发电位变化的关系[J]. 中国康复理论与实践,2004,10(2): 88-89.[27] Patterson SL, Rodgers MM, Macko RF, et al. Effect of treadmill exercise training on spatial and temporal gait parameters in subjects with chronic stroke: a preliminary report. J Rehabil Res. 2008;45(2):221-228.[28] Balasubramanian CK, Bowden MG, Neptune RR, et al. Relationship between step length asymmetry and walking performance in subjects with chronic hemiparesis. Arch Phys Med Rehabi. 2007;88(1):43-49. [29] 黄怡,陈瑞林,万新炉,等. 减重步行训练对脑梗死偏瘫患者下肢运动能力的影响[J]. 实用医学杂志,2009,37(14):2270-2272.[30] 李海峰,王俊华,徐远红,等.减重步行训练对脑源性步态异常患者步行能力的影响[J].中国临床康复,2004,8(28):6046.[31] 刘晓冬,董继革,孙丽,等. 减重平板步行训练对脑卒中偏瘫患者下肢运动功能的影响[J]. 中国现代医学杂志,2013,23(21): 85-88.[32] Lamontagne A, Fung J. Faster is better: implications for speed-intensive gait training after stroke. Stroke. 2004;35(11): 2543-2548.[33] Mirelman A, Patritti BL, Bonato P, et al. Effects of virtual reality training on gait biomechanics of individuals post-stroke. Gait Posture. 2010;31(4):433-437.[34] 杨雨洁,岳雨珊,郭佳宝,等. 虚拟现实技术对脑卒中患者上下肢运动功能康复效果的系统评价[J]. 中国康复理论与实践,2013, 19(8):710-721.[35] Kim JH, Jang SH, Kim CS, et al. Use of virtual reality to enhance balance and ambulation in chronic stroke: a double-blind, randomized controlled study. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2009;88(9):693-701. [36] Westlake KP, Patten C. Pilot study of Lokomat versus manual-assisted treadmill training for locomotor recovery post-stroke. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2009;12;6:18.[37] Yang S, Hwang WH, Tsai YC, et al. Improving balance skills in patients who had stroke through virtual reality treadmill training. Am J Phys Med Rehabi. 2011;90(12): 969-978.[38] Peurala S H, Airaksinen O, Jäkälä P, et al. Effects of intensive gait-oriented physiotherapy during early acute phase of stroke. J Rehabil Res Dev. 2007;44(5):637-648.[39] Deutsch JE. Using virtual reality to improve walking post-stroke: translation to individuals with diabetes. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2011;1;5(2):309-314.[40] 丁德权,谭峰,张明霞,等. Bobath技术加功能性电刺激对急性脑梗死患者下肢运动功能的影响[J].按摩与康复医学,2012,3(18): 3-4.[41] 李红颖,单晶丽,王凤军.肢体智能反馈训练系统在脑梗死后患者肢体康复中的应用[J].中国伤残医学,2013,21(8):44-46.[42] Galen S, Wiggins L, McWilliam R, et al. A combination of Botulinum Toxin A therapy and Functional Electrical Stimu- lation in children with cerebral palsy- A pilot study. Technol Health Care. 2012;20(1):1-9. |
.jpg)