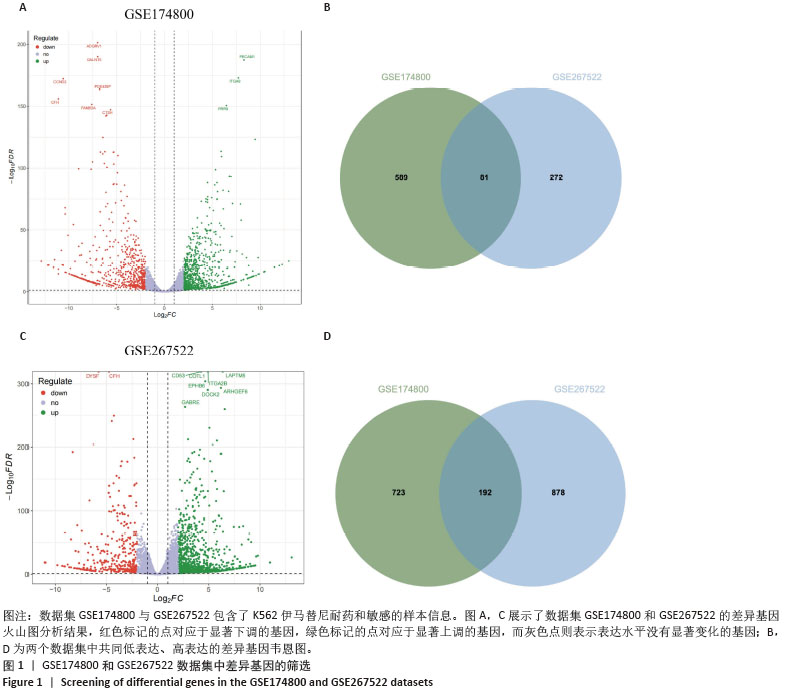
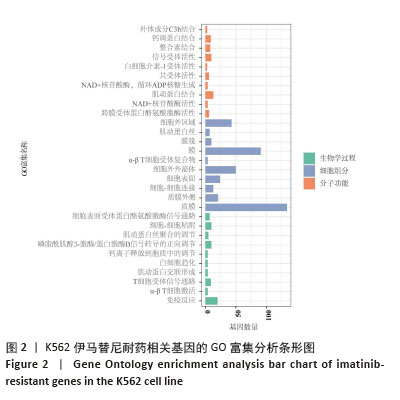
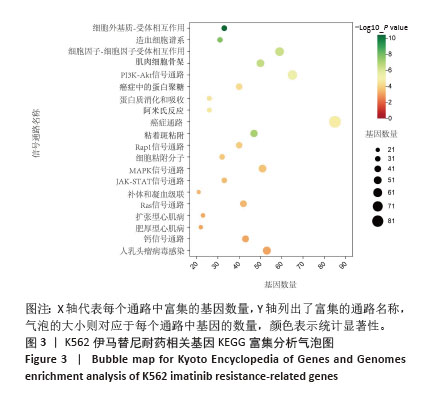
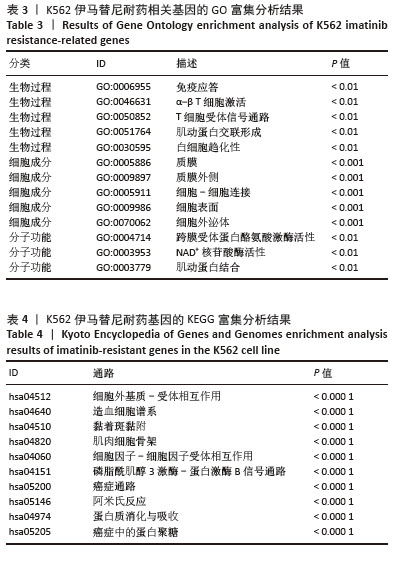
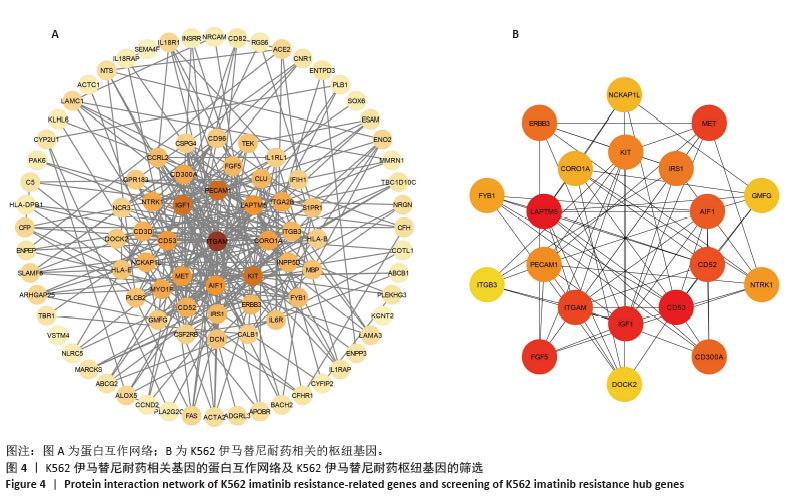
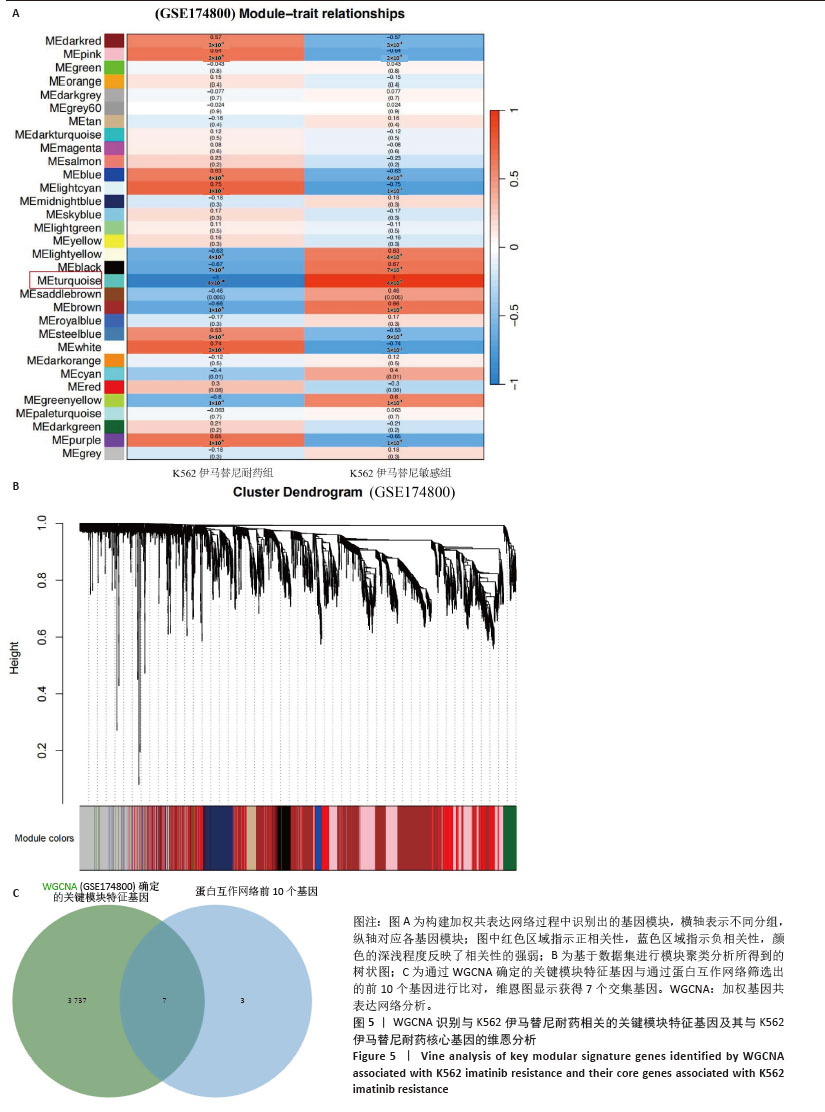
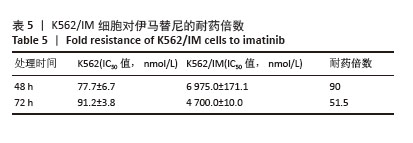
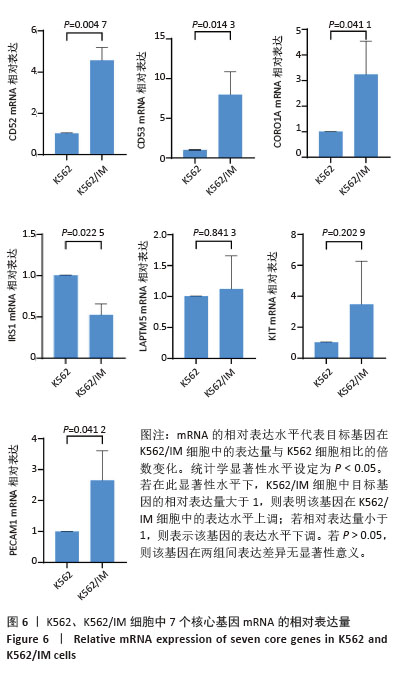
[1] CORTES J, PAVLOVSKY C, SAUßELE S. Chronic myeloid leukaemia. Lancet. 2021;398(10314):1914-1926.
[2] MINCIACCHI VR, KUMAR R, KRAUSE DS. Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Model Disease of the Past, Present and Future. Cells. 2021;10(1):117.
[3] L’ABBATE A, MORETTI V, PUNGOLINO E, et al. Occurrence of L1M Elements in Chromosomal Rearrangements Associated to Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML): Insights from Patient-Specific Breakpoints Characterization. Genes (Basel). 2023;14(7):1351.
[4] BRAUN TP, EIDE CA, DRUKER BJ. Response and Resistance to BCR-ABL1-Targeted Therapies. Cancer Cell. 2020;37(4):530-542.
[5] HADDAD FG, KANTARJIAN H. Navigating the Management of Chronic Phase CML in the Era of Generic BCR::ABL1 Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2024;22(1):e237116.
[6] DEREME J, SÉGOT A, FRIEDRICH N, et al. Recognizing and managing side effects of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in chronic myeloid leukemia. Rev Med Suisse. 2023;19(850):2175-2181.
[7] SRINIVASAN N, OLIVIER T, HASLAM A, et al. Imatinib remains the best frontline therapy in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia: Critical analysis of the ASC4FIRST trial. Am J Hematol. 2024;99(12):2392-2394.
[8] LAGANÀ A, SCALZULLI E, BISEGNA ML, et al. Understanding and overcoming resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). Expert Rev Hematol. 2025;18(1):65-79.
[9] SUN J, HU R, HAN M, et al. Mechanisms underlying therapeutic resistance of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in chronic myeloid leukemia. Int J Biol Sci. 2024;20(1):175-181.
[10] KAEHLER M, VON BUBNOFF N, CASCORBI I, et al. Molecular biomarkers of leukemia: convergence-based drug resistance mechanisms in chronic myeloid leukemia and myeloproliferative neoplasms. Front Pharmacol. 2024;15:1422565.
[11] HASANOVA A, ASADOV C, SHIRINOVA A, et al. Role of genetic factors in imatinib resistance of chronic myeloid leukemia: P53, RB1, ASS1 gene deletions, and chromosome 8 hyperdiploidy. Pathol Res Pract. 2025;269:155943.
[12] XU XL, CAO YJ, ZHANG W, et al. Research Status, Synthesis and Clinical Application of Recently Marketed and Clinical BCR-ABL Inhibitors. Curr Med Chem. 2022;29(17):3050-3078.
[13] LAGANÀ A, SCALZULLI E, BISEGNA ML, et al. Treatment free remission (TFR) after second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors (2G-TKIs) treatment in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML): from feasibility to safety. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2024;23(8):969-979.
[14] VELTMAAT L, CORTES J. Tyrosine kinase inhibitor for CML: all the same? Blood Adv. 2024;8(20):5339-5341.
[15] LIPTON JH, CORTES JE. Bosutinib for the Treatment of CML-Using it Safely: a Podcast. Target Oncol. 2025;20(2):183-189.
[16] GEORGE B, CHAN KH, RIOS A. Therapeutic options for chronic myeloid leukemia following the failure of second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy. Front Oncol. 2024;14:1446517.
[17] YUDA J, DOKI N, MATSUOKA H, et al. Asciminib vs bosutinib in CML patients pretreated with ≥2 tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Results from the Japanese subgroup analysis of ASCEMBL study. Cancer Med. 2023;12(3):2990-2998.
[18] JABBOUR E, KANTARJIAN H. Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Review. JAMA. 2025;333(18):1618-1629.
[19] MALKAN UY, HAZNEDAROGLU IC. Chronic myeloid leukemia, tyrosine kinase inhibitors and cardiovascular system. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2023;27(12):5493-5506.
[20] RÉA D. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors for chronic myeloid leukemia. Rev Prat. 2023;73(10):1051-1055.
[21] BAI J, FENG Z, CHEN Y, et al. Lycorine attenuated proliferation and induced apoptosis on imatinib-resistant K562 cell by inhibiting autophagy. Discov Oncol. 2024;15(1):217.
[22] PETTINELLA F, MARIOTTI B, LATTANZI C, et al. Surface CD52, CD84, and PTGER2 mark mature PMN-MDSCs from cancer patients and G-CSF-treated donors. Cell Rep Med. 2024;5(2):101380.
[23] KARNAN S, HANAMURA I, OTA A, et al. CD52 is a novel target for the treatment of FLT3-ITD-mutated myeloid leukemia. Cell Death Discov. 2021;7(1):121.
[24] AN N, BIAN K, LI C. Alemtuzumab for haematological malignancies. Ann Hematol. 2025;104(5):2593-2603.
[25] FUHR V, HEIDENREICH S, SRIVASTAVA M, et al. CD52 and OXPHOS-potential targets in ibrutinib-treated mantle cell lymphoma. Cell Death Discov. 2022;8(1):505.
[26] OEHLER VG, WALTER RB, CUMMINGS C, et al. CD52 Expression In Leukemic Stem/Progenitor Cells. Blood. 2010;116(21):2743.
[27] BALISE VD, SAITO-REIS CA, GILLETTE JM. Tetraspanin Scaffold Proteins Function as Key Regulators of Hematopoietic Stem Cells. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:598.
[28] DUNLOCK VE. Tetraspanin CD53: an overlooked regulator of immune cell function. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2020;209(4):545-552.
[29] GREENBERG ZJ, PARACATU LC, MONLISH DA, et al. The tetraspanin CD53 protects stressed hematopoietic stem cells via promotion of DREAM complex-mediated quiescence. Blood. 2023;141(10):1180-1193.
[30] DUNLOCK VE, ARP AB, SINGH SP, et al. Tetraspanin CD53 controls T cell immunity through regulation of CD45RO stability, mobility, and function. Cell Rep. 2022;39(13):111006.
[31] KARABACZ N, CABEZAS-WALLSCHEID N. CD53 sends HSCs to sweet DREAMs. Blood. 2023;141(10):1100-1101.
[32] HE Y, DING J, LIU L, et al. Investigation of TSRP reverses imatinib resistance through the PI3K / Akt pathway in chronic myeloid leukemia. Ann Hematol. 2024;103(12):5285-5296.
[33] QIU Q, SUN Y, YANG L, et al. TSPAN32 suppresses chronic myeloid leukemia pathogenesis and progression by stabilizing PTEN. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8(1):90.
[34] AFIFY SM, OO AKK, HASSAN G, et al. How can we turn the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway down? Insights into inhibition and treatment of cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2021;21(6):605-619.
[35] FILIK Y, BAUER K, PETER B, et al. Deciphering the Mechanisms of Osteoblast-Induced Resistance of Leukemic Stem Cell (LSC) in Ph+ CML: Role of PI3-Kinase, BRD4 and MYC and Development of Strategies to Overcome Osteoblast-Induced Resistance. Blood. 2021; 138(Supplement 1):1481-1482.
[36] GU WJ, LIU XX, SHEN YW, et al. TRIM4 enhances small-molecule-induced neddylated-degradation of CORO1A for triple negative breast cancer therapy. Theranostics. 2024;14(18):7023-7041.
[37] KROS JM, ZENEYEDPOUR L, PEDROSA RMSM, et al. T cell induced expression of Coronin-1A facilitates blood-brain barrier transmigration of breast cancer cells. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):31516.
[38] STOCKER TJ, PIRCHER J, SKENDERI A, et al. The Actin Regulator Coronin-1A Modulates Platelet Shape Change and Consolidates Arterial Thrombosis. Thromb Haemost. 2018;118(12):2098-2111.
[39] SIEGMUND K, THUILLE N, POSCH N, et al. Novel protein kinase C θ: coronin 1A complex in T lymphocytes. Cell Commun Signal. 2015; 13:22.
[40] GAUR P, SAINI S, RAY K, et al. Temporal transcriptome analysis suggest modulation of multiple pathways and gene network involved in cell-cell interaction during early phase of high altitude exposure. PLoS One. 2020;15(9):e0238117.
[41] PAMUK GE, CHOW ECY, IONAN AC, et al. FDA Approval Summary: Asciminib for Ph+ CML in Chronic Phase Treated with Two or More Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors and for the T315I Mutation. Clin Cancer Res. 2024;30(19):4266-4271.
[42] DWYER AR, TRUONG TH, KERKVLIET CP, et al. Insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) mediates progesterone receptor-driven stemness and endocrine resistance in oestrogen receptor+ breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 2021;124(1):217-227.
[43] LEI Y, JAMAL M, ZENG X, et al. Insulin receptor substrate 1(IRS1) is related with lymph node metastases and prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Gene. 2022;835:146651.
[44] POUDEL G, TOLLAND MG, HUGHES TP, et al. Mechanisms of Resistance and Implications for Treatment Strategies in Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia. Cancers (Basel). 2022;14(14):3300.
[45] VOCKOVA P, MOLINSKY J, KLANOVA M, et al. CD31/PECAM-1 impacts engraftment, growth and spread of mantle cell lymphoma cells and positively correlates with extramedullary involvement. Leuk Lymphoma. 2021;62(4):861-867.
[46] LERTKIATMONGKOL P, LIAO D, MEI H, et al. Endothelial functions of platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (CD31). Curr Opin Hematol. 2016;23(3):253-259.
[47] YAN Y, SUN D, HU J, et al. Multi-omic profiling highlights factors associated with resistance to immuno-chemotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat Genet. 2025;57(1):126-139. |