[1] GBD Spinal Cord Injuries Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of spinal cord injury, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 2023;22(11):1026-1047.
[2] AHUJA CS, WILSON JR, NORI S, et al. Traumatic spinal cord injury. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17018.
[3] ALIZADEH A, DYCK SM, KARIMI-ABDOLREZAEE S. Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury: An Overview of Pathophysiology, Models and Acute Injury Mechanisms. Front Neurol. 2019;10:282.
[4] 汪晶,李伦兰,丁杨,等.脊髓损伤患者住院医疗费用及其影响因素分析[J].中国病案,2021,22(4):50-54.
[5] 王超宇,亢毅,娄永富,等.多中心创伤性颈脊髓损伤流行病学分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2023,33(5):408-416.
[6] ALLISON DJ, DITOR DS. Immune dysfunction and chronic inflammation following spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord. 2015;53(1): 14-18.
[7] MILICH LM, RYAN CB, LEE JK. The origin, fate, and contribution of macrophages to spinal cord injury pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2019;137(5):785-797.
[8] ORR MB, GENSEL JC. Spinal Cord Injury Scarring and Inflammation: Therapies Targeting Glial and Inflammatory Responses. Neurotherapeutics. 2018;15(3):541-553.
[9] SHECHTER R, SCHWARTZ M. Harnessing monocyte-derived macrophages to control central nervous system pathologies: no longer ‘if’ but ‘how’. J Pathol. 2013;229(2):332-346.
[10] 樊保佑,冯世庆,陈琳,等.脊髓损伤神经修复临床治疗指南(IANR/CANR 2019年版)[J].西部医学,2020,32(6):790-802.
[11] HORVATH CM, STARK GR, KERR IM, et al. Interactions between STAT and non-STAT proteins in the interferon-stimulated gene factor 3 transcription complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1996;16(12):6957-6964.
[12] MARTINEZ-MOCZYGEMBA M, GUTCH MJ, FRENCH DL, et al. Distinct STAT structure promotes interaction of STAT2 with the p48 subunit of the interferon-alpha-stimulated transcription factor ISGF3. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(32):20070-20076.
[13] VEALS SA, SCHINDLER C, LEONARD D, et al. Subunit of an alpha-interferon-responsive transcription factor is related to interferon regulatory factor and Myb families of DNA-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1992;12(8):3315-3324.
[14] PAUL A, TANG TH, NG SK. Interferon Regulatory Factor 9 Structure and Regulation. Front Immunol. 2018;9:1831.
[15] RENGACHARI S, GROISS S, DEVOS JM, et al. Structural basis of STAT2 recognition by IRF9 reveals molecular insights into ISGF3 function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115(4):E601-609.
[16] ZENG C, ZHU X, LI H, et al. The Role of Interferon Regulatory Factors in Liver Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(13):6874.
[17] GANTA VC, CHOI MH, KUTATELADZE A, et al. A MicroRNA93-Interferon Regulatory Factor-9-Immunoresponsive Gene-1-Itaconic Acid Pathway Modulates M2-Like Macrophage Polarization to Revascularize Ischemic Muscle. Circulation. 2017;135(24):2403-2025.
[18] ZHANG Y, LIU X, SHE ZG, et al. Interferon regulatory factor 9 is an essential mediator of heart dysfunction and cell death following myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Basic Res Cardiol. 2014; 109(5):434.
[19] ZHANG SM, ZHU LH, CHEN HZ, et al. Interferon regulatory factor 9 is critical for neointima formation following vascular injury. Nat Commun. 2014;5:5160.
[20] CHEN HZ, GUO S, LI ZZ, et al. A critical role for interferon regulatory factor 9 in cerebral ischemic stroke. J Neurosci. 2014;34(36):11897-11912.
[21] LEI J, ZHOU MH, ZHANG FC, et al. Interferon regulatory factor transcript levels correlate with clinical outcomes in human glioma. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(8):12086-12098.
[22] DAS A, CHAI JC, KIM SH, et al. Transcriptome sequencing of microglial cells stimulated with TLR3 and TLR4 ligands. BMC Genomics. 2015; 16(1):517.
[23] CHAMANKHAH M, EFTEKHARPOUR E, KARIMI-ABDOLREZAEE S, et al. Genome-wide gene expression profiling of stress response in a spinal cord clip compression injury model. BMC Genomics. 2013; 14:583.
[24] TURNER SMF, SUNSHINE MD, CHANDRAN V, et al. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy after Mid-Cervical Spinal Contusion Injury. J Neurotrauma. 2022;39(9-10):715-723.
[25] LI X, YANG Z, ZHANG A. The effect of neurotrophin-3/chitosan carriers on the proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells. Biomaterials. 2009;30(28):4978-4985.
[26] JOHNSON WE, LI C, RABINOVIC A. Adjusting batch effects in microarray expression data using empirical Bayes methods. Biostatistics. 2007; 8(1):118-127.
[27] PEDREGOSA F, VAROQUAUX G, GRAMFORT A, et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J Mach Learn Res. 2011;12:2825-2830.
[28] SMYTH GK. Linear models and empirical bayes methods for assessing differential expression in microarray experiments. Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol. 2004;3:Article3.
[29] HUNTER JD. Matplotlib: A 2D Graphics Environment. Comput Sci Eng. 2007;9(3):90-95.
[30] ASHBURNER M, BALL CA, BLAKE JA, et al. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet. 2000;25(1):25-29.
[31] OGATA H, GOTO S, SATO K, et al. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999;27(1):29-34.
[32] YU G, WANG LG, HAN Y, et al. clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. Omics. 2012;16(5): 284-287.
[33] SUBRAMANIAN A, TAMAYO P, MOOTHA VK, et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2005;102(43): 15545-15550.
[34] LIBERZON A, SUBRAMANIAN A, PINCHBACK R, et al. Molecular signatures database (MSigDB) 3.0. Bioinformatics. 2011;27(12):1739-1740.
[35] HÄNZELMANN S, CASTELO R, GUINNEY J. GSVA: gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-seq data. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013;14:7.
[36] SZKLARCZYK D, GABLE AL, LYON D, et al. STRING v11: protein-protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(D1):D607-D613.
[37] SHANNON P, MARKIEL A, OZIER O, et al. Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003;13(11):2498-2504.
[38] CHIN CH, CHEN SH, WU HH, et al. cytoHubba: identifying hub objects and sub-networks from complex interactome. BMC Syst Biol. 2014;8 Suppl 4(Suppl 4):S11.
[39] BREIMAN L. Random Forests. Machine Learning. 2001;45(1):5-32.
[40] LIAW A, WIENER MC. Classification and Regression by randomForest. R News. 2002;2(3):18-22.
[41] SCHNEIDER CA, RASBAND WS, ELICEIRI KW. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods. 2012;9(7):671-675.
[42] 戴静雯,周萍萍,李素,等.抗病毒免疫中干扰素与炎症信号通路的交互调控:防御反应与维持稳态 [J].微生物学报,2022, 62(10):3709-3721.
[43] THIBAULT DL, CHU AD, GRAHAM KL, et al. IRF9 and STAT1 are required for IgG autoantibody production and B cell expression of TLR7 in mice. J Clin Invest. 2008;118(4):1417-1426.
[44] 单佳铃,程虹毓,文乐,等.TLR/MyD 88/NF-κB信号通路参与不同疾病作用机制研究进展[J].中国药理学通报,2019,35(4):451-455.
[45] MEZZASOMA L, ANTOGNELLI C, TALESA VN. A Novel Role for Brain Natriuretic Peptide: Inhibition of IL-1β Secretion via Downregulation of NF-kB/Erk 1/2 and NALP3/ASC/Caspase-1 Activation in Human THP-1 Monocyte. Mediators Inflamm. 2017;2017:5858315.
[46] ZAMBRANO-ZARAGOZA JF, GUTIÉRREZ-FRANCO J, DURÁN-AVELAR MJ, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps and inflammatory response: Implications for the immunopathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis. Int J Rheum Dis. 2021;24(3):426-433.
[47] TAO X, FINKBEINER S, ARNOLD DB, et al. Ca2+ influx regulates BDNF transcription by a CREB family transcription factor-dependent mechanism. Neuron. 1998;20(4):709-726.
[48] LI X, WANG G, LI W, et al. Histone deacetylase 9 plays a role in sevoflurane-induced neuronal differentiation inhibition by inactivating cAMP-response element binding protein transcription and inhibiting the expression of neurotrophin-3. FASEB J. 2023;37(10):e23164.
[49] ARUHAN, GONG Q, TUO YJ, et al. Syringa oblata Lindl Extract Alleviated Corticosterone-Induced Depression via the cAMP/PKA-CREB-BDNF Pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025;341:119274.
[50] YOUNG M, BOOTH DM, SMITH D, et al. Transcriptional regulation in the absence of inositol trisphosphate receptor calcium signaling. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024;12:1473210.
[51] NASSRALLAH WB, CHENG J, MACKAY JP, et al. Mechanisms of synapse-to-nucleus calcium signalling in striatal neurons and impairments in Huntington’s disease. J Neurochem. 2024;168(9):2671-2689.
[52] LIANG CW, CHEN TC. Anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis presenting as fever with undetermined cause. Int J Infect Dis. 2022;122:365-367.
[53] CHEN Q, LIANG Z, YUE Q, et al. A Neuropeptide Y/F-like Polypeptide Derived from the Transcriptome of Turbinaria peltata Suppresses LPS-Induced Astrocytic Inflammation. J Nat Prod. 2022;85(6):1569-1580.
[54] HARLAND M, TORRES S, LIU J, et al. Neuronal Mitochondria Modulation of LPS-Induced Neuroinflammation. J Neurosci. 2020;40(8):1756-1765.
[55] KIM J, LEE HJ, PARK JH, et al. Nilotinib modulates LPS-induced cognitive impairment and neuroinflammatory responses by regulating P38/STAT3 signaling. J Neuroinflammation. 2022;19(1):187.
[56] SKRZYPCZAK-WIERCIOCH A, SAŁAT K. Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Model of Neuroinflammation: Mechanisms of Action, Research Application and Future Directions for Its Use. Molecules. 2022; 27(17):5481.
[57] 吴军,丁单华,李倩倩,等.脂多糖刺激小胶质细胞激活分化的机制研究[J].中华神经医学杂志,2018,17(12):1195-1202.
[58] LI C, WU Z, ZHOU L, et al. Temporal and spatial cellular and molecular pathological alterations with single-cell resolution in the adult spinal cord after injury. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):65.
[59] BALON K, WIATRAK B. PC12 and THP-1 Cell Lines as Neuronal and Microglia Model in Neurobiological Research. Appl Sci. 2021; 11(9):3729.
[60] OPREA D, SANZ CG, BARSAN MM, et al. PC-12 Cell Line as a Neuronal Cell Model for Biosensing Applications. Biosensors (Basel). 2022;12(7):500.
[61] 周涛,许百男,陈德蕙,等.PC12细胞分化的神经元与离体培养的大鼠原代皮质神经元之间功能性突触的形成[J].中华神经科杂志, 2005,38(3):183-186.
[62] BIBER K, OWENS T, BODDEKE E. What is microglia neurotoxicity (Not)? Glia. 2014;62(6):841-854.
[63] DAVID S, KRONER A. Repertoire of microglial and macrophage responses after spinal cord injury. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2011;12(7):388-399.
[64] OLAH M, AMOR S, BROUWER N, et al. Identification of a microglia phenotype supportive of remyelination. Glia. 2012;60(2):306-321.
[65] BROCKIE S, ZHOU C, FEHLINGS MG. Resident immune responses to spinal cord injury: role of astrocytes and microglia. Neural Regen Res. 2024;19(8):1678-1685.
[66] PERRY VH, NICOLL JA, HOLMES C. Microglia in neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 2010;6(4):193-201.
[67] YU H, CHANG Q, SUN T, et al. Metabolic reprogramming and polarization of microglia in Parkinson’s disease: Role of inflammasome and iron. Ageing Res Rev. 2023;90:102032.
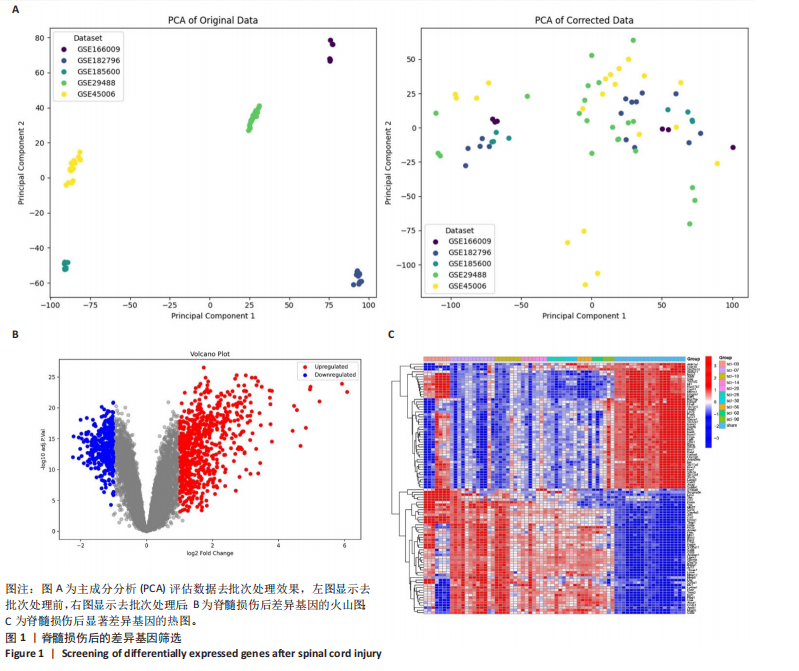
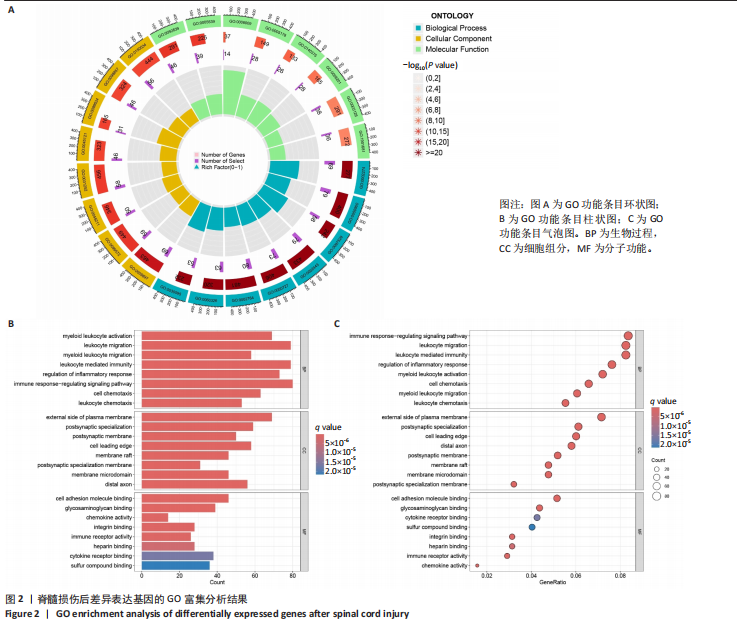
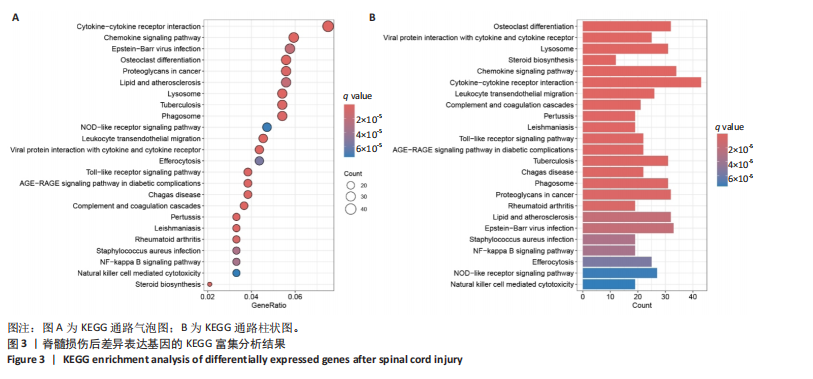
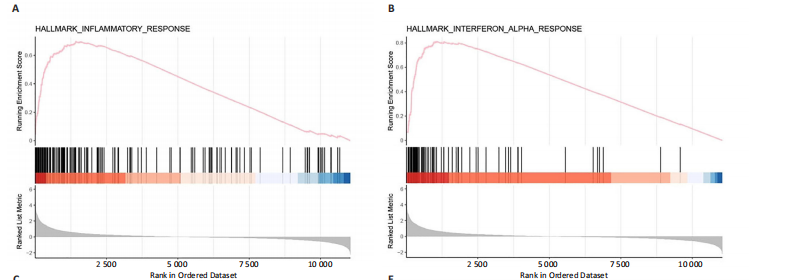
|