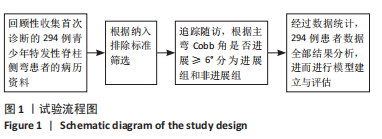
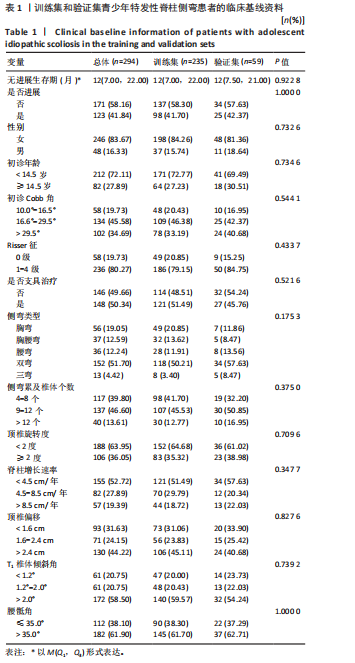
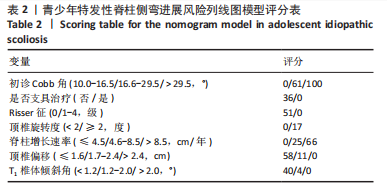
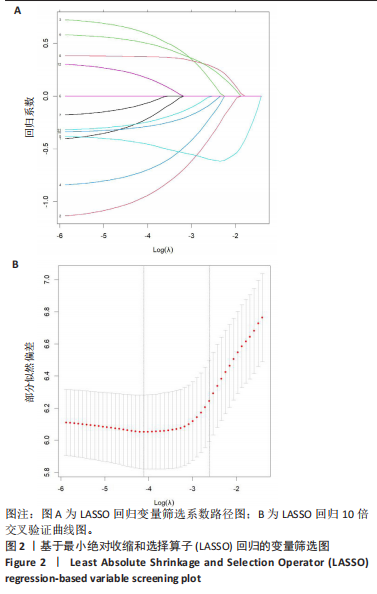
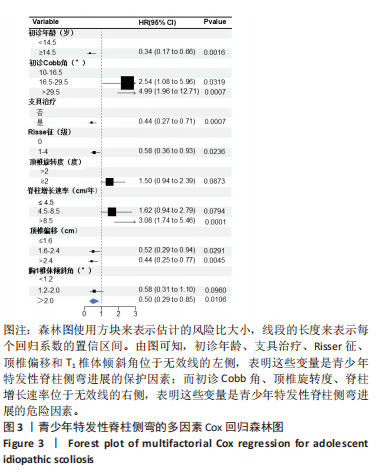
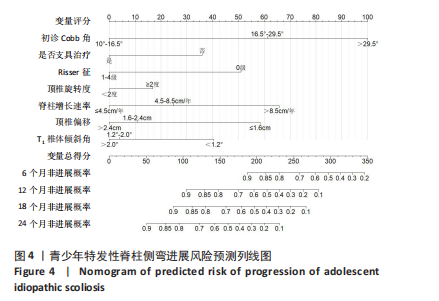
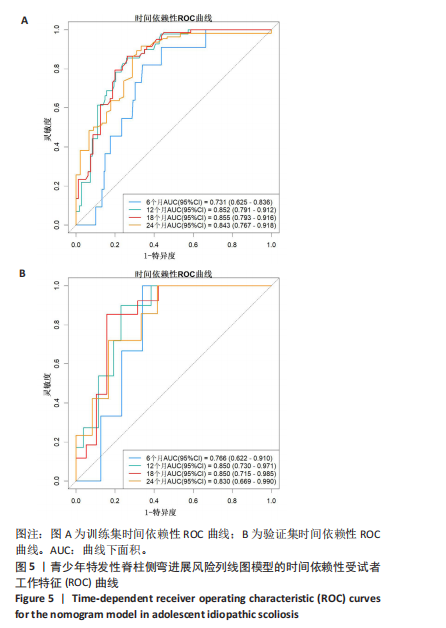
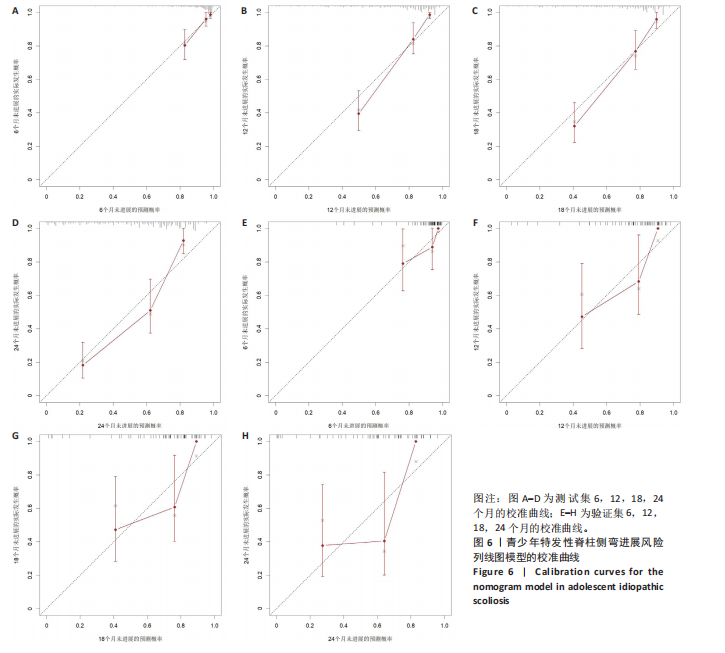
[1] NEGRINI S, DONZELLI S, AULISA AG, et al. 2016 SOSORT guidelines: orthopaedic and rehabilitation treatment of idiopathic scoliosis during growth. Scoliosis Spinal Disord. 2018;13:3.
[2] SUNG S, CHAE HW, LEE HS, et al. Incidence and Surgery Rate of Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Nationwide Database Study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(15):8152.
[3] SELEVICIENE V, CESNAVICIUTE A, STRUKCINSKIENE B, et al. Physiotherapeutic Scoliosis-Specific Exercise Methodologies Used for Conservative Treatment of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis, and Their Effectiveness: An Extended Literature Review of Current Research and Practice. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(15):9240.
[4] LI M, NIE Q, LIU J, et al. Prevalence of scoliosis in children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Pediatr. 2024;12:1399049.
[5] MITSIAKI I, THIRIOS A, PANAGOULI E, et al. Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis and Mental Health Disorders: A Narrative Review of the Literature. Children (Basel). 2022;9(5):597.
[6] GROSSMAN DC, CURRY SJ, OWENS DK, et al. Screening for Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 2018;319(2):165-172.
[7] SARKOVICH S, LEONARDI C, DARLOW M, et al. Back pain in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: frequency and risk factors. Spine Deform. 2024; 12(5):1319-1327.
[8] 徐帅, 苏永佳, 王振波, 等. 中国大陆中小学生脊柱侧凸的患病特点:关于72项研究的Meta分析[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2021, 31(10):901-910.
[9] 儿童青少年脊柱弯曲异常防控技术指南编写组, 马军. 《儿童青少年脊柱弯曲异常防控技术指南》解读[J]. 中国学校卫生,2022, 43(2):165-170+175.
[10] 马钰, 汪南, 罗进玉, 等. 宁夏地区9-24岁学生脊柱认知现状与行为生活方式的相关性[J]. 宁夏医科大学学报,2024,46(1):60-63+70.
[11] DI FELICE F, ZAINA F, DONZELLI S, et al. The Natural History of Idiopathic Scoliosis During Growth: A Meta-Analysis. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2018;97(5):346-356.
[12] 沈洁. 女性特发性脊柱侧弯进展影响因素分析及预测模型研究[D]. 上海:上海体育学院,2021:1-73.
[13] 康晓霞, 肖斌, 刘名名. 青少年特发性脊柱侧凸患者支具治疗后功能性动作特征及疗效影响因素列线图预测模型的建立[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2024,34(1):20-30.
[14] KOLIN DA, THOMPSON GH, BLUMENSCHEIN LA, et al. Providence Bracing: Predicting the Progression to Surgery in Patients With Braced Idiopathic Scoliosis. J Pediatr Orthop. 2023;43(8):e643-e648.
[15] LI L, WONG MS. The application of machine learning methods for predicting the progression of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a systematic review. Biomed Eng Online. 2024;23(1):80.
[16] WANG H, ZHANG T, ZHANG C, et al. An intelligent composite model incorporating global / regional X-rays and clinical parameters to predict progressive adolescent idiopathic scoliosis curvatures and facilitate population screening. EBioMedicine. 2023;95:104768.
[17] DUFVENBERG M, CHARALAMPIDIS A, DIARBAKERLI E, et al. Prognostic model development for risk of curve progression in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a prospective cohort study of 127 patients. Acta Orthop. 2024;95:536-544.
[18] 罗林威, 储振涛, 沈树锋, 等. 青少年特发性脊柱侧弯曲线进展相关危险因素的研究进展 [J]. 浙江医学,2024,46(13):1438-1442.
[19] LENZ M, OIKONOMIDIS S, HARLAND A, et al. Scoliosis and Prognosis-a systematic review regarding patient-specific and radiological predictive factors for curve progression. Eur Spine J. 2021;30(7):1813-1822.
[20] HUNG VWY, QIN L, CHEUNG CSK, et al. Osteopenia: a new prognostic factor of curve progression in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(12):2709-2716.
[21] DAVIES E, NORVELL D, HERMSMEYER J. Efficacy of bracing versus observation in the treatment of idiopathic scoliosis. Evid Based Spine Care J. 2011;2(2):25-34.
[22] KARAVIDAS N. Bracing In The Treatment Of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: Evidence To Date. Adolesc Health Med Ther. 2019;10:153-172.
[23] WONG C, ANDERSEN TB. Evaluation of Brace Treatment Using the Soft Brace Spinaposture: A Four-Years Follow-Up. J Clin Med. 2022;11(1):264.
[24] CHARALAMPIDIS A, DIARBAKERLI E, DUFVENBERG M, et al. Night time Bracing or Exercise in Moderate-Grade Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7(1):e2352492.
[25] TANG S, CHEUNG JPY, CHEUNG PWH. Effectiveness of bracing to achieve curve regression in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Bone Joint J. 2024;106-B(3):286-292.
[26] 张臻, 张迦琅, 冯铭哲, 等. 支具治疗青少年特发性脊柱侧凸的研究进展[J]. 骨科,2023,14(1):87-91.
[27] DEL PRETE CM, TARANTINO D, VIVA MG, et al. Spinal Orthosis in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: An Overview of the Braces Provided by the National Health Service in Italy. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023;60(1):3.
[28] MODI HN, SUH SW, YANG JH, et al. Spontaneous regression of curve in immature idiopathic scoliosis - does spinal column play a role to balance? An observation with literature review. J Orthop Surg Res. 2010;5:80.
[29] WONG LPK, CHEUNG PWH, CHEUNG JPY. Curve type, flexibility, correction, and rotation are predictors of curve progression in patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis undergoing conservative treatment: a systematic review. Bone Joint J. 2022;104-B(4):424-432.
[30] RAJASEKARAN S, ANAND K, SHETTY A. Etiology and natural history of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A review. Indian Spine J. 2020;3:131.
[31] YOO YJ, PARK JG, JO L, et al. Factors Influencing the Progression and Direction of Scoliosis in Children with Neurological Disorders. Children (Basel). 2022;9(1):81.
[32] CHAZONO M, TANAKA T, MARUMO K, et al. Significance of peak height velocity as a predictive factor for curve progression in patients with idiopathic scoliosis. Scoliosis. 2015;10(Suppl 2):S5.
[33] 李富丽, 张书豪, 王帅, 等. 青少年特发性脊柱侧凸患者病情进展影响因素的研究进展[J]. 广西医学,2022,44(17):2031-2035.
[34] LARA T, ASTUR N, JONES TL, et al. The Risk of Curve Progression and Surgery in African Americans With Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Spine Deform. 2017;5(4):250-254.
[35] DOLAN LA, WEINSTEIN SL, ABEL MF, et al. Bracing in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Trial (BrAIST): Development and Validation of a Prognostic Model in Untreated Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Using the Simplified Skeletal Maturity System. Spine Deform. 2019;7(6):890-898 e894.
[36] AULIA TN, DJUFRI D, GATAM L, et al. Etiopathogenesis of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS): Role of genetic and environmental factors. Narra J. 2023;3(3):e217.
[37] 刘小梅, 王艳洋, 刘敏, 等. 青少年特发性脊柱侧凸进展风险的表观遗传学因素研究进展 [J]. 重庆医学,2024,53(9):1401-1405,1411.
[38] LUO CL, MA CZH, ZOU YY, et al. Associations between spinal flexibility and bracing outcomes in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a literature review. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):955.
[39] CHEUNG JPY, CHEUNG PWH. Supine flexibility predicts curve progression for patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis undergoing underarm bracing. Bone Joint J. 2020;102-B(2):254-260.
|