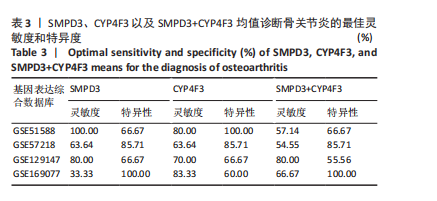
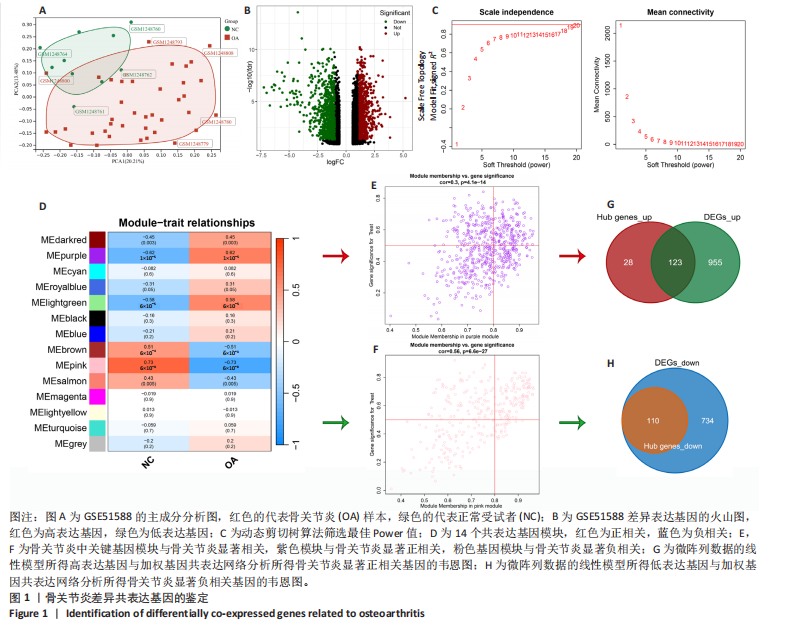
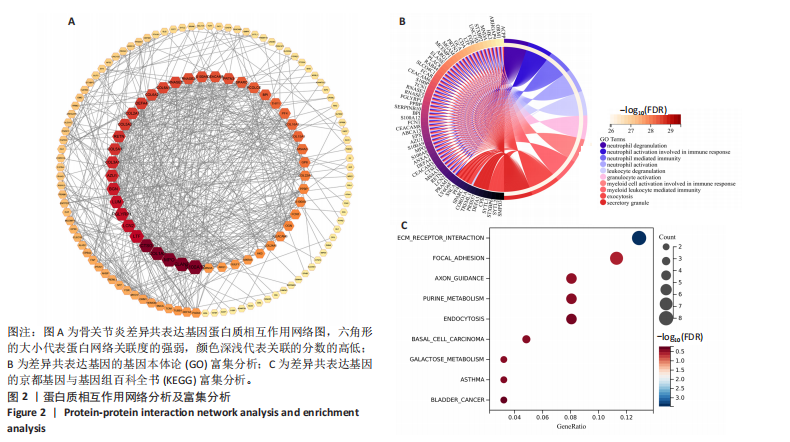
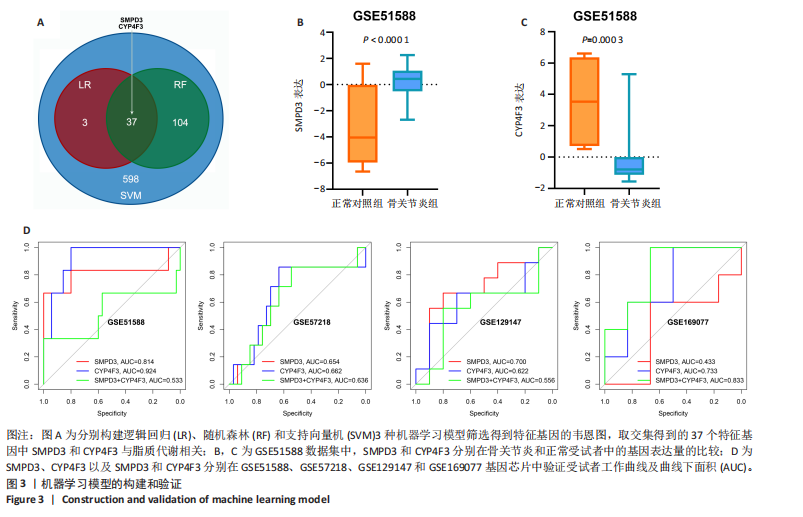
[1] CISTERNAS MG, MURPHY L, SACKS JJ, et al. Alternative Methods for Defining Osteoarthritis and the Impact on Estimating Prevalence in a US Population-Based Survey. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2016;68(5):574-580.
[2] JIANG Y. Osteoarthritis year in review 2021: biology. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(2):207-215.
[3] ALLEN KD, THOMA LM, GOLIGHTLY YM. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(2):184-195.
[4] 王成岩,安静楠,刘畅,等.1990至2019年中国不同部位骨关节炎疾病负担的年龄-时期-队列分析[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2024,13(8):614-620.
[5] GIORGINO R, ALBANO D, FUSCO S, et al. Knee Osteoarthritis: Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Mesenchymal Stem Cells: What Else Is New? An Update. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(7):6405.
[6] 刘勇,蒋联建,梁功强,等.关节腔内注射药物治疗膝骨关节炎的研究进展[J].牡丹江医学院学报,2023,44(4):146-149.
[7] 陈志安,段培押,普进兵,等.骨关节炎基因组学研究进展[J].武警医学,2024,35(5):443-447.
[8] ROOS EM, ARDEN NK. Strategies for the prevention of knee osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12(2):92-101.
[9] ABRAMOFF B, CALDERA FE. Osteoarthritis: Pathology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(2):293-311.
[10] CHIRICHELLA PS, JOW S, IACONO S, et al. Treatment of Knee Meniscus Pathology: Rehabilitation, Surgery, and Orthobiologics. PM R. 2019;11(3):292-308.
[11] GELBER AC. Knee Osteoarthritis. Ann Intern Med. 2024;177(9):ITC129-ITC144.
[12] FRANCISCO V, PÉREZ T, PINO J, et al. Biomechanics, obesity, and osteoarthritis. The role of adipokines: when the levee breaks. J Orthop Res. 2018;36(2):594-604.
[13] XIONG J, LONG J, CHEN X, et al. Dyslipidemia Might Be Associated with an Increased Risk of Osteoarthritis. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:3105248.
[14] BAKER KR, MATTHAN NR, LICHTENSTEIN AH, et al. Association of plasma n-6 and n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids with synovitis in the knee: the MOST study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2012;20(5):382-387.
[15] EBRAHIM HA, ALZAMIL NM, AL-ANI B, et al. Suppression of knee joint osteoarthritis induced secondary to type 2 diabetes mellitus in rats by resveratrol: role of glycated haemoglobin and hyperlipidaemia and biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2022;128(5):1375-1382.
[16] CHOU CH, WU CC, SONG IW, et al. Genome-wide expression profiles of subchondral bone in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15(6):R190.
[17] AŞıK MD, GÜRSOY S, AKKAYA M, et al. Microarray analysis of cartilage: comparison between damaged and non-weight-bearing healthy cartilage. Connect Tissue Res. 2020;61(5):456-464.
[18] RAMOS YF, DEN HOLLANDER W, BOVÉE JV, et al. Genes involved in the osteoarthritis process identified through genome wide expression analysis in articular cartilage; the RAAK study. PLoS One. 2014;9(7):e103056.
[19] DEN HOLLANDER W, RAMOS YF, BOS SD, et al. Knee and hip articular cartilage have distinct epigenomic landscapes: implications for future cartilage regeneration approaches. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(12):2208-2212.
[20] LANGFELDER P, HORVATH S. WGCNA: an R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008;9:559.
[21] WANG J, PENG X, PENG W, et al. Dynamic protein interaction network construction and applications. Proteomics. 2014;14(4-5):338-352.
[22] HU X, NI S, ZHAO K, et al. Bioinformatics-Led Discovery of Osteoarthritis Biomarkers and Inflammatory Infiltrates. Front Immunol. 2022;13:871008.
[23] NEWMAN AM, LIU CL, GREEN MR, et al. Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat Methods. 2015;12(5):453-457.
[24] SCHOBER P, VETTER TR. Logistic Regression in Medical Research. Anesth Analg. 2021;132(2):365-366.
[25] HU J, SZYMCZAK S. A review on longitudinal data analysis with random forest. Brief Bioinform. 2023;24(2):bbad002.
[26] VALKENBORG D, ROUSSEAU AJ, GEUBBELMANS M, et al. Support vector machines. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2023;164(5):754-757.
[27] WANG XG, GAO LX, ZHAO MW, et al. Relationship between quantitative magnetic resonance imaging and clinical symptoms in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Chin Med J (Engl). 2020;133(14):1741-1743.
[28] WEINHAGE T, KÖLSCHE T, RIEGER-FACKELDEY E, et al. Cord Blood Low-Density Granulocytes Correspond to an Immature Granulocytic Subset with Low Expression of S100A12. J Immunol. 2020;205(1):56-66.
[29] 孙思东,黄群.右归丸联合中药熏蒸治疗肾阳虚型老年膝骨关节炎及其对关节液中OPN、S100A12及MMP-3的影响研究[J].辽宁中医杂志, 2023,50(11):113-116.
[30] XU M, TU J, YANG Y, et al. Study on the relationship between the expression of S100A12, CaSR, and IL-7R in the synovium of knee osteoarthritis and angiogenesis. Ann Palliat Med. 2021;10(12):12775-12781.
[31] 代凤雷,尹宏,张斌,等.大鼠滑膜组织中S100A12、IL-1β、Galectin-3与早期膝骨关节炎相关性研究[J].四川医学,2020,41(6):570-574.
[32] 康麟,曹磊,赵秋鹤,等.过表达骨形态发生蛋白2对骨折大鼠的骨愈合和成骨能力的影响及其可能机制[J].广西医学,2021,43(8):966-971.
[33] STOFFEL W, HAMMELS I, JENKE B, et al. Neutral sphingomyelinase (SMPD3) deficiency disrupts the Golgi secretory pathway and causes growth inhibition. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7(11):e2488.
[34] LUAN T, YANG X, KUANG G, et al. Identification and Analysis of Neutrophil Extracellular Trap-Related Genes in Osteoarthritis by Bioinformatics and Experimental Verification. J Inflamm Res. 2023;16:3837-3852.
[35] KANEVA MK. Neutrophil elastase and its inhibitors-overlooked players in osteoarthritis. FEBS J. 2022;289(1):113-116.
[36] LUO Y, WANG L, PENG A, et al. Metabolic profiling of human plasma reveals the activation of 5-lipoxygenase in the acute attack of gouty arthritis. Rheumatology(Oxford). 2019;58(2):345-351.
[37] NI KD, LIU JY. The Functions of Cytochrome P450 ω-hydroxylases and the Associated Eicosanoids in Inflammation-Related Diseases. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:716801.
[38] MONTFORT A, BERTRAND F, ROCHOTTE J, et al. Neutral Sphingomyelinase 2 Heightens Anti-Melanoma Immune Responses and Anti-PD-1 Therapy Efficacy. Cancer Immunol Res. 2021;9(5):568-582.
[39] XU Z, XU C, LU J, et al. Cytochrome P450 F3 promotes colorectal cancer via inhibiting NRF2-mediated ferroptosis. Transl Oncol. 2024;48:102077.
[40] TANG XL, XU ZY, GUAN J, et al. Establishment of a neutrophil extracellular trap-related prognostic signature for colorectal cancer liver metastasis and expression validation of CYP4F3. Clin Exp Med. 2024;24(1):112.
[41] ZHAO Z, HE X, BI Y, et al. Induction of CYP4F3 by benzene metabolites in human white blood cells in vivo in human promyelocytic leukemic cell lines and ex vivo in human blood neutrophils. Drug Metab Dispos. 2009;37(2):282-291.
[42] KIKUTA Y, YAMASHITA Y, KASHIWAGI S, et al. Expression and induction of CYP4F subfamily in human leukocytes and HL60 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004;1683(1-3):7-15.
|