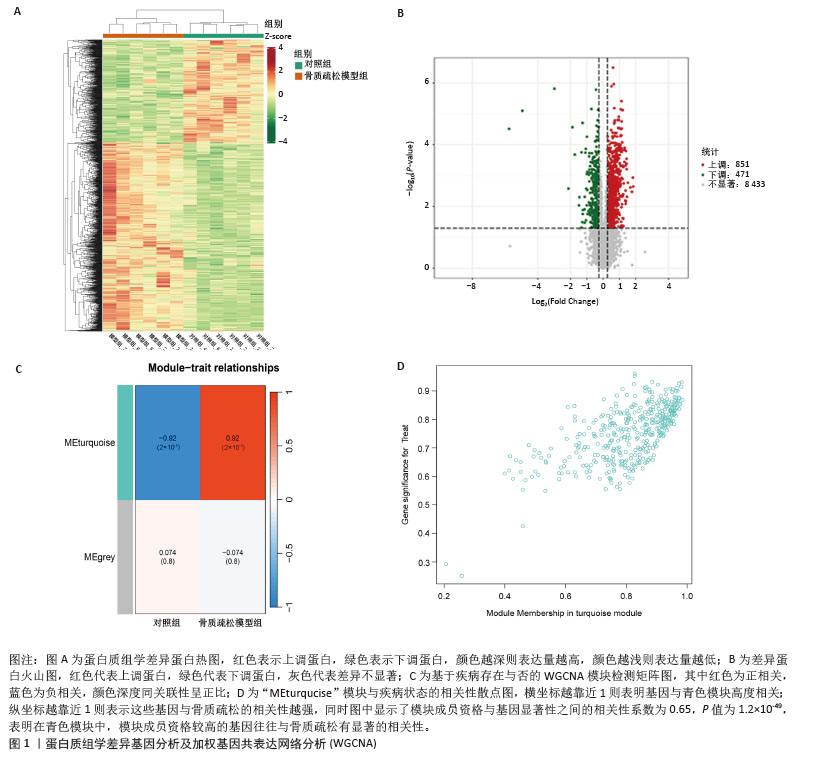
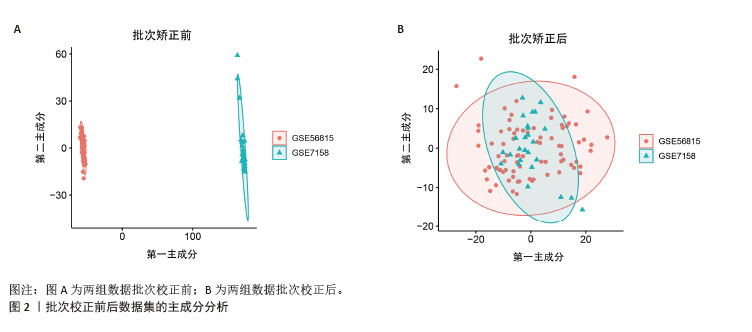
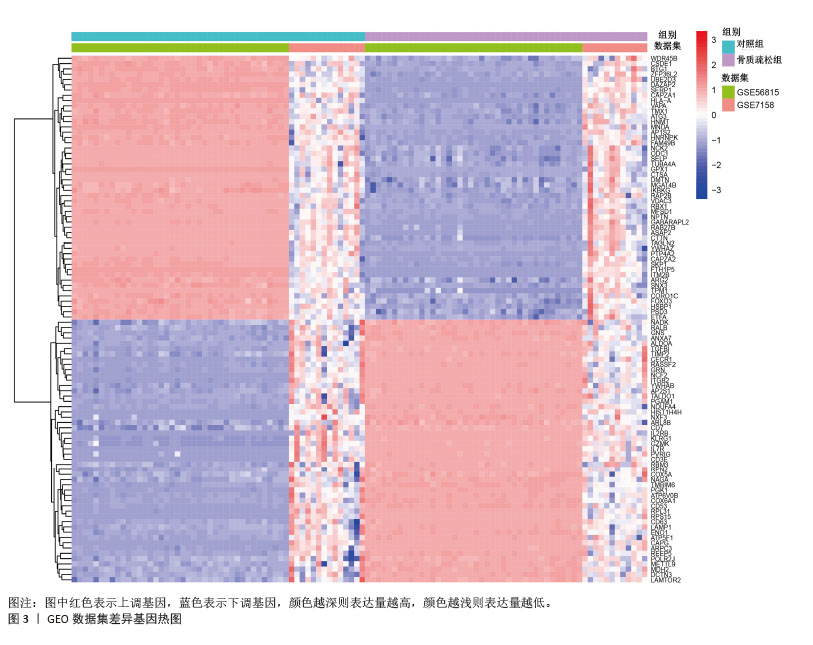
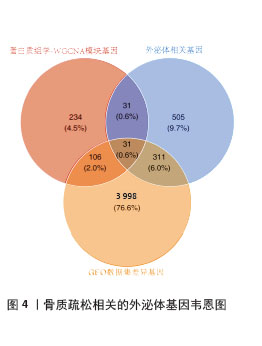
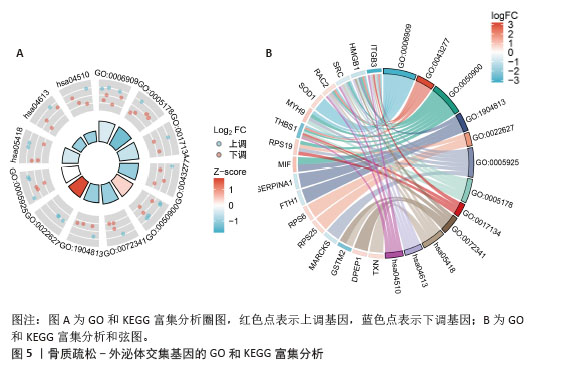
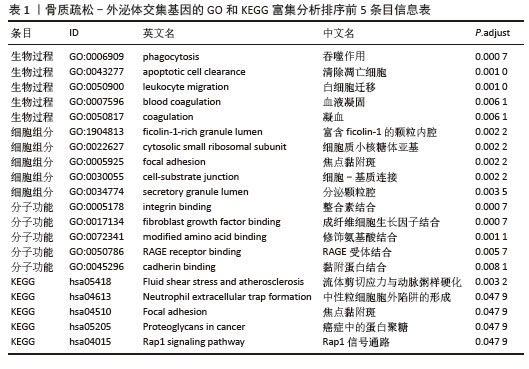
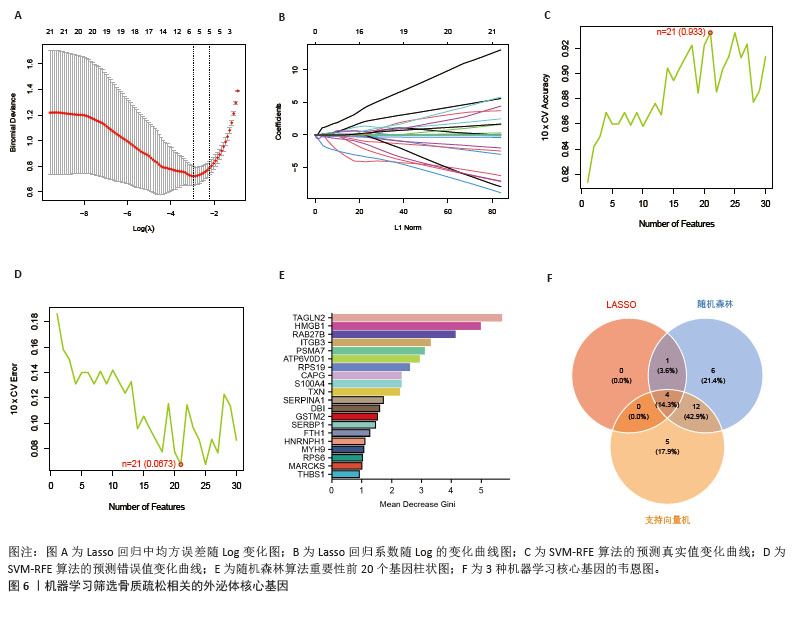
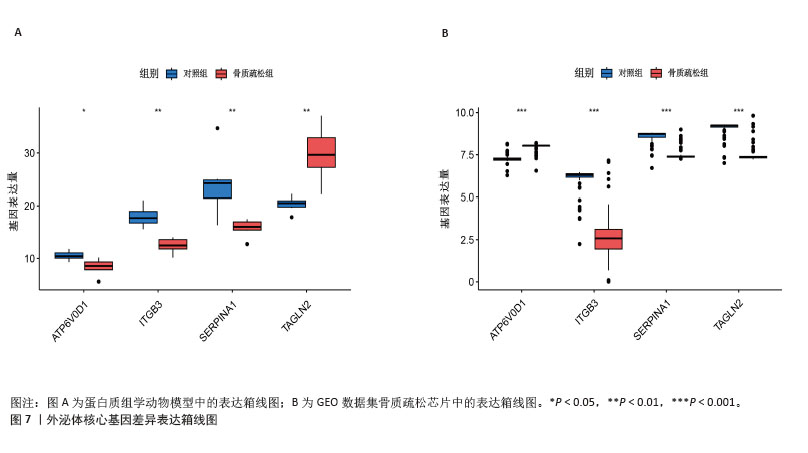
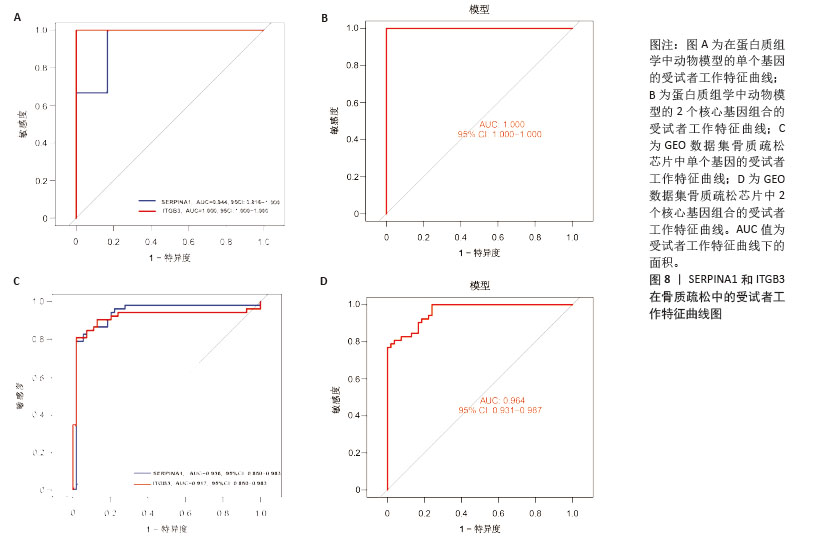
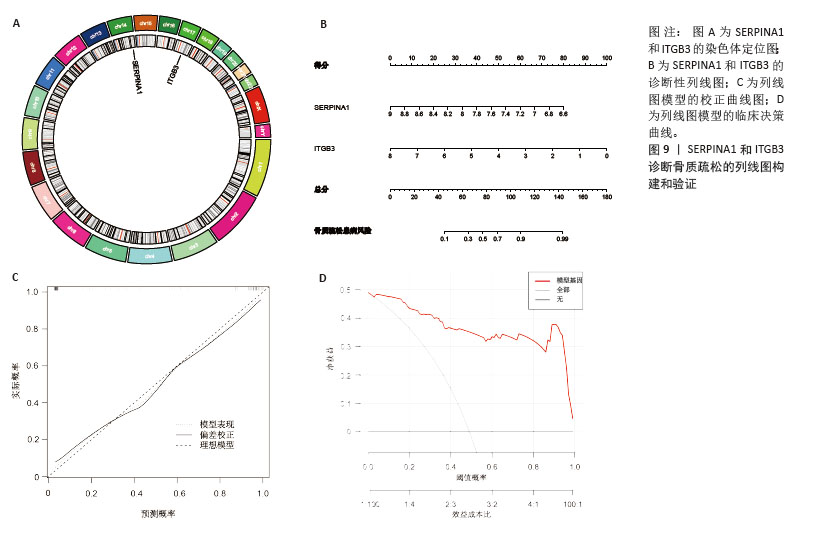
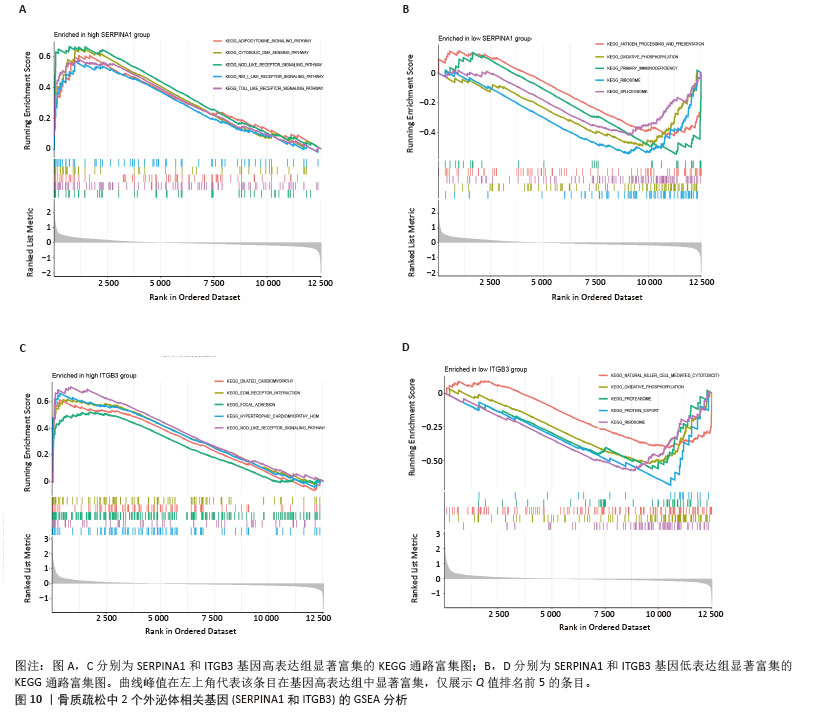
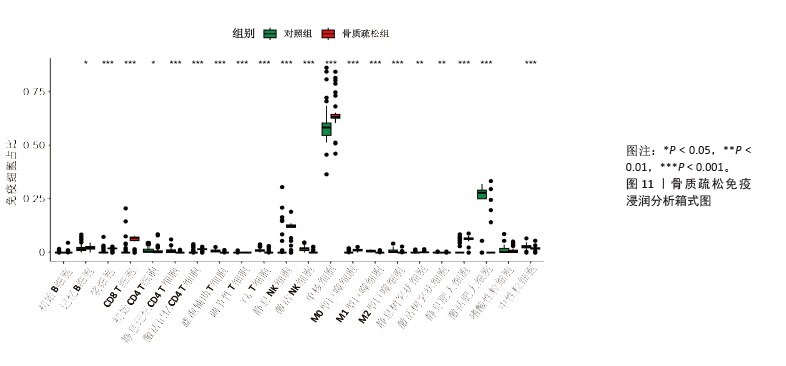
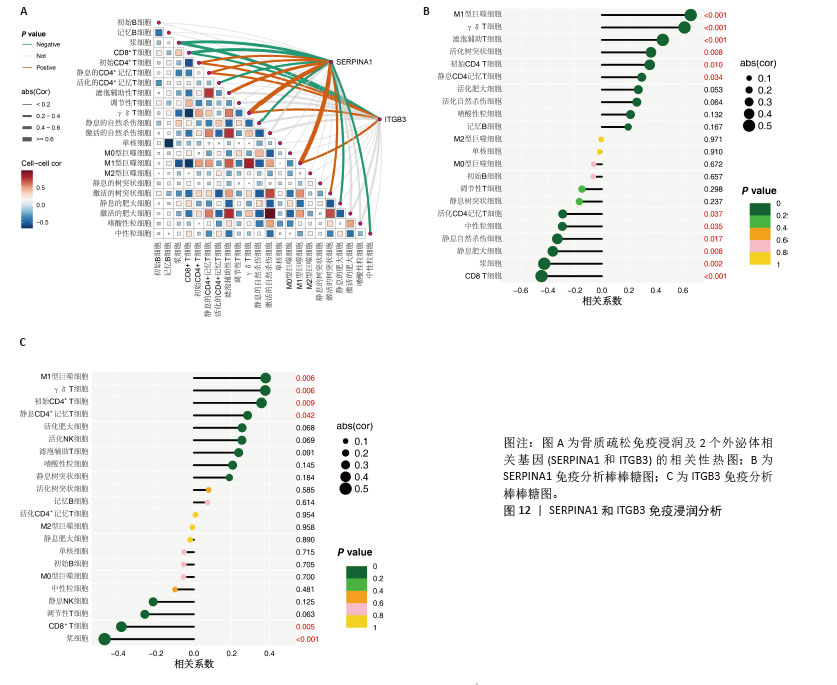
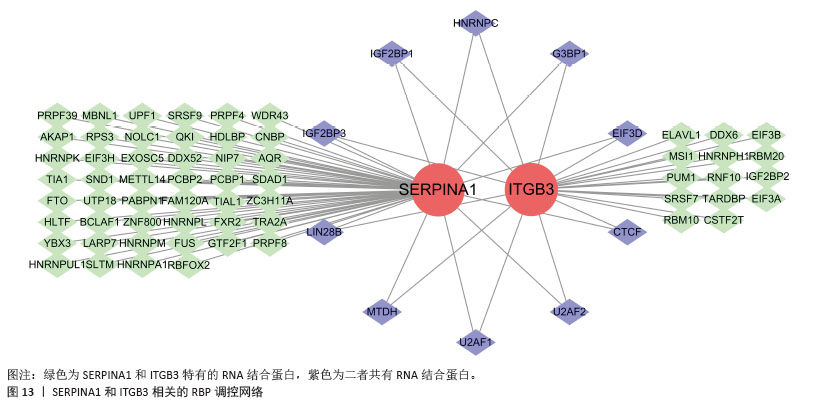
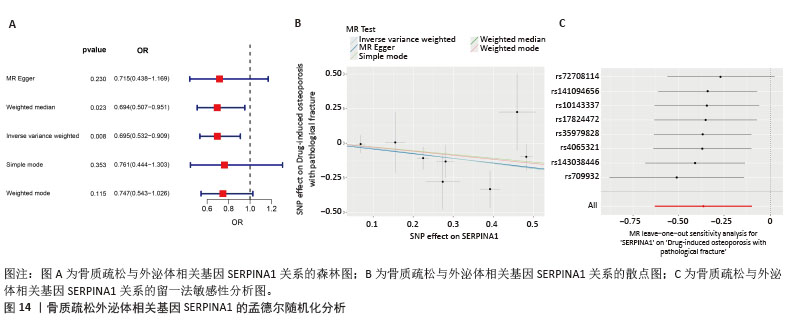
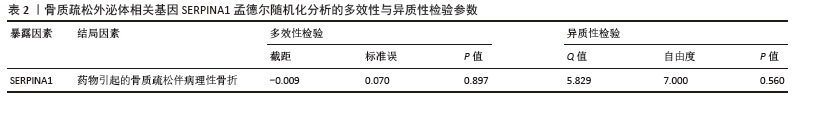
[1] ZHENG XQ, XU L, HUANG J, et al. Incidence and cost of vertebral fracture in urban China: a 5-year population-based cohort study. Int J Surg. 2023;109(7):1910-1918.
[2] ZHU K, LIU K, HUANG J, et al. Toxoplasma gondii infection as a risk factor for osteoporosis: a case-control study. Parasit Vectors. 2022;15(1):151.
[3] ZHANG W, ZHOU X, HOU W, et al. Reversing the imbalance in bone homeostasis via sustained release of SIRT-1 agonist to promote bone healing under osteoporotic condition. Bioact Mater. 2022;19:429-443.
[4] ZHANG J, XIA L, ZHANG X, et al. Development and validation of a predictive model for vertebral fracture risk in osteoporosis patients. Eur Spine J. 2024;33(8):3242-3260.
[5] PISANI P, RENNA MD, CONVERSANO F, et al. Major osteoporotic fragility fractures: Risk factor updates and societal impact. World J Orthop. 2016;7(3):171-181.
[6] ZHAO Y, ZHANG Y, LIU X, et al. Comparative proteomic analysis of plasma exosomes reveals the functional contribution of N-acetyl-alpha-glucosaminidase to Parkinson’s disease. Neural Regen Res. 2025;20(10):2998-3012.
[7] LIU J, WANG B, CHEN H, et al. Osteoclast-derived exosomes influence osteoblast differentiation in osteoporosis progression via the lncRNA AW011738/ miR-24-2-5p/ TREM1 axis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024;178:117231.
[8] HE Y, CHEN Y. The Potential of Exosomes for Osteoporosis Treatment: A Review. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024;18:979-989.
[9] QIU M, ZHAI S, FU Q, et al. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Exosomal MicroRNA-150-3p Promotes Osteoblast Proliferation and Differentiation in Osteoporosis. Hum Gene Ther. 2021; 32(13-14):717-729.
[10] WANG L, TIAN W, WANG S, et al. Serum proteomics identifies biomarkers for predicting non-survivors in elderly COVID-19 patients. J Proteomics. 2025;311:105356.
[11] CAO B, LI M, LI X, et al. Innovative biomarkers TCN2 and LY6E can significantly inhibit respiratory syncytial virus infection. J Transl Med. 2024;22(1):854.
[12] QIU X, YANG Z, ZHANG C, et al. Integration of eQTL and multi-omics comprehensive analysis of triacylglycerol synthase 1 (TGS1) as a prognostic and immunotherapeutic biomarker across pan-cancer. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025;284(Pt 1):137862.
[13] JI J, WU S, BAO X, et al. Mediating oxidative stress through the Palbociclib/miR-141-3p/STAT4 axis in osteoporosis: a bioinformatics and experimental validation study. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):19560.
[14] 梁周,张驰,潘成镇,等.基于肠道菌群和广泛靶向代谢组学的山柰酚抗骨质疏松的作用机制[J].中国组织工程研究, 2025,29(20):4190-4204.
[15] PAN C, ZHANG C, LIN Z, et al. Disulfidptosis-related Protein RPN1 may be a Novel Anti-osteoporosis Target of Kaempferol. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024;27(11):1611-1628.
[16] WÁNG YXJ, CHAN WP, YU W, et al. Quantitative CT lumbar spine BMD cutpoint value for classifying osteoporosis among older Chinese men can be the same as that of older Chinese women, both much lower than the value for Caucasians. Skeletal Radiol. 2025;54(2):193-198.
[17] HUANG X, LI S, LU W, et al. Metformin activates Wnt/β-catenin for the treatment of diabetic osteoporosis. BMC Endocr Disord. 2022;22(1):189.
[18] ZHANG Y, BAI J, XIAO B, et al. BMSC-derived exosomes promote osteoporosis alleviation via M2 macrophage polarization. Mol Med. 2024;30(1):220.
[19] YAO C, SUN J, LUO W, et al. Down-expression of miR-494-3p in senescent osteocyte-derived exosomes inhibits osteogenesis and accelerates age-related bone loss via PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway. Bone Joint Res. 2024;13(2):52-65.
[20] BEHERA J, TYAGI N. Exosomes: mediators of bone diseases, protection, and therapeutics potential. Oncoscience. 2018;5(5-6): 181-195.
[21] LIU J, SUN Z, YOU Y, et al. M2 macrophage-derived exosomal miR-486-5p influences the differentiation potential of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and osteoporosis. Aging (Albany NY). 2023;15(18):9499-9520.
[22] HAN M, LIU Y, CAO Y, et al. The Imbalance of Homeostasis in Neutrophil Extracellular Traps is Associated with Portal Vein Thrombosis in Patients with Decompensated Cirrhosis. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2024;12(12):1009-1019.
[23] YANG W, WANG Y, MO K, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals multiple immune cell subpopulations promote the formation of abnormal bone microenvironment in osteoporosis. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):29493.
[24] YANG P, LIU X, LYU J, et al. Down-regulation of TAGLN2 associated with the development of preeclampsia by effecting the Rap1 signaling pathway. Placenta. 2025;159: 20-31.
[25] HU L, XIE X, XUE H, et al. MiR-1224-5p modulates osteogenesis by coordinating osteoblast/osteoclast differentiation via the Rap1 signaling target ADCY2. Exp Mol Med. 2022;54(7):961-972.
[26] HAN J, WAN M, MA Z, et al. Prediction of Targets of Curculigoside A in Osteoporosis and Rheumatoid Arthritis Using Network Pharmacology and Experimental Verification. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020;14:5235-5250.
[27] ZINTZARAS E, DOXANI C, KOUFAKIS T, et al. Synopsis and meta-analysis of genetic association studies in osteoporosis for the focal adhesion family genes: the CUMAGAS-OSTEOporosis information system. BMC Med. 2011;9:9.
[28] BAGI CM, ROBERTS GW, ANDRESEN CJ. Dual focal adhesion kinase/Pyk2 inhibitor has positive effects on bone tumors: implications for bone metastases. Cancer. 2008;112(10):2313-2321.
[29] LOPES HB, FREITAS GP, ELIAS CN, et al. Participation of integrin β3 in osteoblast differentiation induced by titanium with nano or microtopography. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2019;107(6):1303-1313.
[30] YAMADA S, YOSHIZAWA Y, KAWAKUBO A, et al. Early gene and protein expression associated with osteoblast differentiation in response to fish collagen peptides powder. Dent Mater J. 2013;32(2):233-240.
[31] ZOU Z, LIU R, WANG Y, et al. IL1RN promotes osteoblastic differentiation via interacting with ITGB3 in osteoporosis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2021;53(3):294-303.
[32] YU D, LI Z, CAO J, et al. microRNA-25-3p suppresses osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs in patients with osteoporosis by targeting ITGB3. Acta Histochem. 2022; 124(6):151926.
[33] MURUGANANDAN S, DRANSE HJ, ROURKE JL, et al. Chemerin neutralization blocks hematopoietic stem cell osteoclastogenesis. Stem Cells. 2013;31(10):2172-2182.
[34] QIU Z, LI L, HUANG Y, et al. Puerarin specifically disrupts osteoclast activation via blocking integrin-β3 Pyk2/Src/Cbl signaling pathway. J Orthop Translat. 2022;33:55-69.
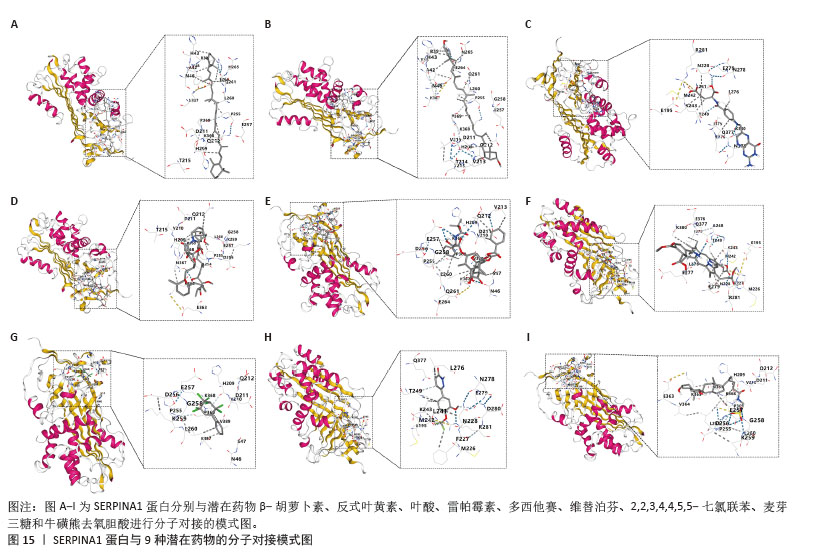
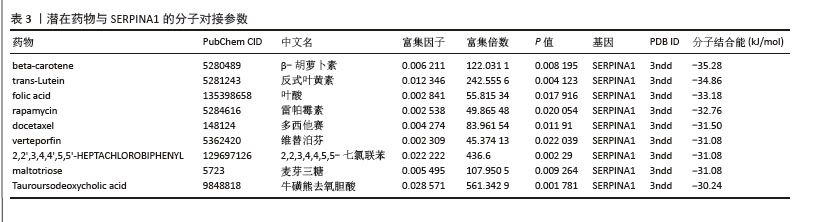
[35] LI L, SONG X, CHEN G, et al. Plasma exosomal protein PLG and SERPINA1 in colorectal cancer diagnosis and coagulation abnormalities. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023;149(11):8507-8519.
[36] MASLAKOVA AA, GOLYSHEV SA, POTASHNIKOVA DM, et al. SERPINA1 long transcripts produce non-secretory alpha1-antitrypsin isoform: In vitro translation in living cells. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023; 241:124433.
[37] AKBAR MA, LU Y, ELSHIKHA AS, et al. Transplantation of Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell (ATMSC) Expressing Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Reduces Bone Loss in Ovariectomized Osteoporosis Mice. Hum Gene Ther. 2017;28(2): 179-189.
[38] CAO JJ, GREGOIRE BR, SUN L, et al. Alpha-1 antitrypsin reduces ovariectomy-induced bone loss in mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011; 1240:E31-35.
[39] BABUTA M, MOREL C, DE CARVALHO RIBEIRO M, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps activate hepatic stellate cells and monocytes via NLRP3 sensing in alcohol-induced acceleration of MASH fibrosis. Gut. 2024;73(11):1854-1869.
[40] LI Y, ZHU X, ZHANG M, et al. Heatstroke-induced hepatocyte exosomes promote liver injury by activating the NOD-like receptor signaling pathway in mice. PeerJ. 2019;7:e8216.
[41] YU T, XIONG Y, LUU S, et al. The shared KEGG pathways between icariin-targeted genes and osteoporosis. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(9):8191-8201.
[42] ZHAI X, YAN Z, ZHAO J, et al. Muscone Ameliorates Ovariectomy-Induced Bone Loss and Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor-κb Ligand-Induced Osteoclastogenesis by Suppressing TNF Receptor-Associated Factor 6-Mediated Signaling Pathways. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:348.
[43] EBRAHIMI T, RUST M, KAISER SN, et al. α1-antitrypsin mitigates NLRP3-inflammasome activation in amyloid β1-42-stimulated murine astrocytes. J Neuroinflammation. 2018;15(1):282.
[44] KE K, SUL OJ, CHUNG SW, et al. Lack of NOD2 attenuates ovariectomy-induced bone loss via inhibition of osteoclasts. J Endocrinol. 2017;235(2):85-96.
[45] SUN D, LU J, TIAN H, et al. The impact of POSTN on tumor cell behavior and the tumor microenvironment in lung adenocarcinoma. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025;145:113713.
[46] QIU P, LIU L, FANG J, et al. Identification of Pharmacological Autophagy Regulators of Active Ulcerative Colitis. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:769718.
[47] CLARK D, BRAZINA S, YANG F, et al. Age-related changes to macrophages are detrimental to fracture healing in mice. Aging Cell. 2020;19(3):e13112.
[48] XU Y, YAN H, ZHANG X, et al. Roles of Altered Macrophages and Cytokines: Implications for Pathological Mechanisms of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, and Alzheimer’s Disease. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:876269.
[49] GENIN M, CLEMENT F, FATTACCIOLI A, et al. M1 and M2 macrophages derived from THP-1 cells differentially modulate the response of cancer cells to etoposide. BMC Cancer. 2015;15:577.
[50] MARTÍNEZ FAJARDO C, MOROTE L, MORENO-GIMÉNEZ E, et al. Exosome-like nanoparticles from Arbutus unedo L. mitigate LPS-induced inflammation via JAK-STAT inactivation. Food Funct. 2024; 15(22):11280-11290.
[51] CHEN X, BAI Z, LI J. The Mantle Exosome and MicroRNAs of Hyriopsis cumingii Involved in Nacre Color Formation. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2019;21(5):634-642.
[52] GAO SS, ZHAO Y. The effects of β-carotene on osteoporosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Osteoporos Int. 2023;34(4):627-639.
[53] KAN B, GUO D, YUAN B, et al. Dietary carotenoid intake and osteoporosis: the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2005-2018. Arch Osteoporos. 2021;17(1):2. |