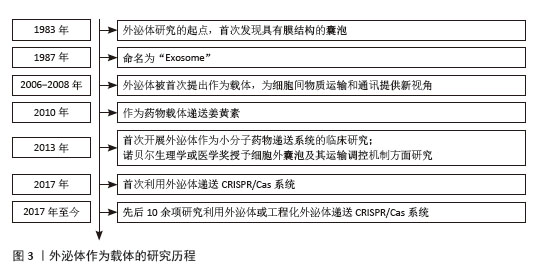
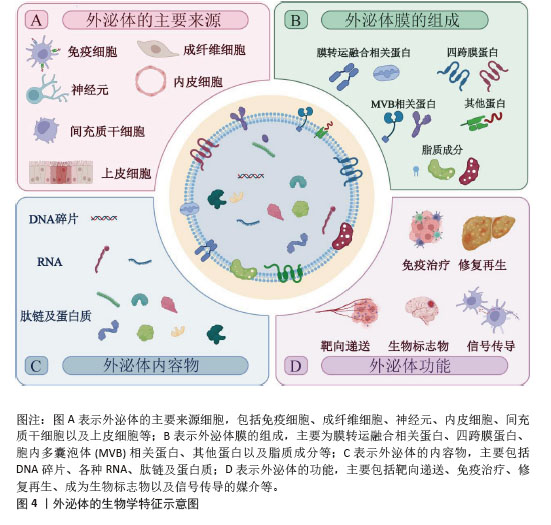
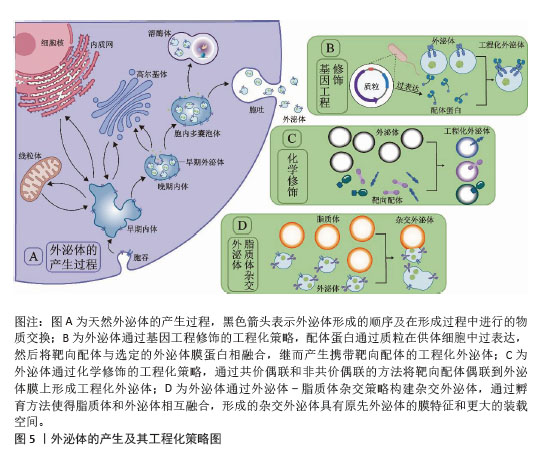
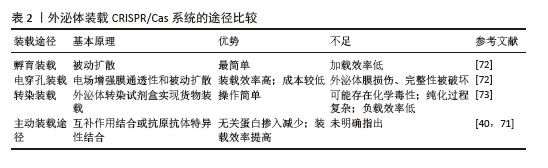
[1] LI L, SHEN G, WU M, et al. CRISPR-Cas-mediated diagnostics. Trends Biotechnol. 2022;40(11):1326-1345.
[2] BHOKISHAM N, LAUDERMILCH E, TRAEGER LL, et al. CRISPR-Cas System: The Current and Emerging Translational Landscape. Cells. 2023;12(8):1103.
[3] TAHA EA, LEE J, HOTTA A. Delivery of CRISPR-Cas tools for in vivo genome editing therapy: Trends and challenges. J Control Release. 2022;342:345-361.
[4] BOUCHER P, CUI X, CURIEL DT. Adenoviral vectors for in vivo delivery of CRISPR-Cas gene editors. J Control Release. 2020; 327:788-800.
[5] SADEGHI S, TEHRANI FR, TAHMASEBI S, et al. Exosome engineering in cell therapy and drug delivery. Inflammopharmacology. 2023;31(1):145-169.
[6] 代月优,郭丹丹,王茜茜,等.工程化外泌体靶向递送药物的抗肿瘤效应[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(31):6753-6764.
[7] TIAN J, HAN Z, SONG D, et al. Engineered Exosome for Drug Delivery: Recent Development and Clinical Applications. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023;18:7923-7940.
[8] TAN D, LI G, FU W, et al. Exosomes: the next frontier in vaccine development and delivery. Front Immunol. 2024;15:1435426.
[9] ZHANG Y, LUO J, GUI X, et al. Bioengineered nanotechnology for nucleic acid delivery. J Control Release. 2023;364:124-141.
[10] JOHNSTONE RM, MATHEW A, MASON AB, et al. Exosome formation during maturation of mammalian and avian reticulocytes: evidence that exosome release is a major route for externalization of obsolete membrane proteins. J Cell Physiol. 1991; 147(1):27-36.
[11] AL-MADHAGI H. The Landscape of Exosomes Biogenesis to Clinical Applications. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024;19:3657-3675.
[12] VALADI H, EKSTRÖM K, BOSSIOS A, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(6):654-659.
[13] BAJ-KRZYWORZEKA M, SZATANEK R, WEGLARCZYK K, et al. Tumour-derived microvesicles carry several surface determinants and mRNA of tumour cells and transfer some of these determinants to monocytes. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2006;55(7):808-818.
[14] SKOG J, WÜRDINGER T, VAN RIJN S, et al. Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10(12):1470-1476.
[15] SUN D, ZHUANG X, XIANG X, et al. A novel nanoparticle drug delivery system: the anti-inflammatory activity of curcumin is enhanced when encapsulated in exosomes. Mol Ther. 2010;18(9):1606-1614.
[16] TENCHOV R, SASSO JM, WANG X, et al. Exosomes─Nature’s Lipid Nanoparticles, a Rising Star in Drug Delivery and Diagnostics. ACS Nano. 2022;16(11):17802-17846.
[17] KIM SM, YANG Y, OH SJ, et al. Cancer-derived exosomes as a delivery platform of CRISPR/Cas9 confer cancer cell tropism-dependent targeting. J Control Release. 2017;266:8-16.
[18] LIN Y, WU J, GU W, et al. Exosome-Liposome Hybrid Nanoparticles Deliver CRISPR/Cas9 System in MSCs. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2018; 5(4):1700611.
[19] SINGH S, PAUL D, NATH V, et al. Exosomes: current knowledge and future perspectives. Tissue Barriers. 2024;12(2):2232248.
[20] HAN QF, LI WJ, HU KS, et al. Exosome biogenesis: machinery, regulation, and therapeutic implications in cancer. Mol Cancer. 2022;21(1):207.
[21] RÄDLER J, GUPTA D, ZICKLER A, et al. Exploiting the biogenesis of extracellular vesicles for bioengineering and therapeutic cargo loading. Mol Ther. 2023;31(5):1231-1250.
[22] WANG C, LI Z, LIU Y, et al. Exosomes in atherosclerosis: performers, bystanders, biomarkers, and therapeutic targets. Theranostics. 2021;11(8):3996-4010.
[23] GURUNG S, PEROCHEAU D, TOURAMANIDOU L, et al. The exosome journey: from biogenesis to uptake and intracellular signalling. Cell Commun Signal. 2021;19(1):47.
[24] YANG W, DING N, LUO R, et al. Exosomes from young healthy human plasma promote functional recovery from intracerebral hemorrhage via counteracting ferroptotic injury. Bioact Mater. 2023;27:1-14.
[25] ZHAO Y, LIU L, SUN R, et al. Exosomes in cancer immunoediting and immunotherapy. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2022;17(2):193-205.
[26] CHENG H, YANG Q, WANG R, et al. Emerging Advances of Detection Strategies for Tumor-Derived Exosomes. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(2):868.
[27] LI J, ZHANG Y, LUO B. Effects of Exosomal Viral Components on the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancers (Basel). 2022; 14(14):3552.
[28] LIANG G, ZHU Y, ALI DJ, et al. Engineered exosomes for targeted co-delivery of miR-21 inhibitor and chemotherapeutics to reverse drug resistance in colon cancer. J Nanobiotechnology. 2020;18(1):10.
[29] LI J, LI J, PENG Y, et al. Dendritic cell derived exosomes loaded neoantigens for personalized cancer immunotherapies. J Control Release. 2023;353:423-433.
[30] MENG X, WU TG, LOU QY, et al. Optimization of CRISPR-Cas system for clinical cancer therapy. Bioeng Transl Med. 2022;8(2):e10474.
[31] FENG S, XIE X, LIU J, et al. A potential paradigm in CRISPR/Cas systems delivery: at the crossroad of microalgal gene editing and algal-mediated nanoparticles. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023;21(1):370.
[32] BAIRQDAR A, KARITSKAYA PE, STEPANOV GA. Expanding Horizons of CRISPR/Cas Technology: Clinical Advancements, Therapeutic Applications, and Challenges in Gene Therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(24): 13321.
[33] ALLEMAILEM KS, ALMATROUDI A, ALRUMAIHI F, et al. Current Updates of CRISPR/Cas System and Anti-CRISPR Proteins: Innovative Applications to Improve the Genome Editing Strategies. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024;19:10185-10212.
[34] WANG SW, GAO C, ZHENG YM, et al. Current applications and future perspective of CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing in cancer. Mol Cancer. 2022;21(1):57.
[35] AZEEZ SS, HAMAD RS, HAMAD BK, et al. Advances in CRISPR-Cas technology and its applications: revolutionising precision medicine. Front Genome Ed. 2024;6: 1509924.
[36] HORODECKA K, DÜCHLER M. CRISPR/Cas9: Principle, Applications, and Delivery through Extracellular Vesicles. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(11):6072.
[37] KHOSHANDAM M, SOLTANINEJAD H, MOUSAZADEH M, et al. Clinical applications of the CRISPR/Cas9 genome-editing system: Delivery options and challenges in precision medicine. Genes Dis. 2023;11(1):268-282.
[38] SONG X, LIU C, WANG N, et al. Delivery of CRISPR/Cas systems for cancer gene therapy and immunotherapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021;168:158-180.
[39] LESMANA H, KIM SY, CORADO AM, et al. Casgevy (exagamglogene autotemcel) and Lyfgenia (lovotibeglogene autotemcel) for individuals 12 years and older with sickle cell disease (SCD) and recurrent vaso-occlusive crises (VOC): A therapeutics bulletin of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG). Genet Med Open. 2024;2:101875.
[40] YE Y, ZHANG X, XIE F, et al. An engineered exosome for delivering sgRNA:Cas9 ribonucleoprotein complex and genome editing in recipient cells. Biomater Sci. 2020;8(10):2966-2976.
[41] KO WC, WANG SJ, HSIAO CY, et al. Pharmacological Role of Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles in Disease Applications. Molecules. 2022;27(5):1551.
[42] HUANG J, ZHOU Y, LI J, et al. CRISPR/Cas systems: Delivery and application in gene therapy. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:942325.
[43] SHAO J, ZARO J, SHEN Y. Advances in Exosome-Based Drug Delivery and Tumor Targeting: From Tissue Distribution to Intracellular Fate. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:9355-9371.
[44] CHEN R, HUANG H, LIU H, et al. Friend or Foe? Evidence Indicates Endogenous Exosomes Can Deliver Functional gRNA and Cas9 Protein. Small. 2019;15(38):e1902686.
[45] HA D, YANG N, NADITHE V. Exosomes as therapeutic drug carriers and delivery vehicles across biological membranes: current perspectives and future challenges. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2016;6(4):287-296.
[46] HE ZY, MEN K, QIN Z, et al. Non-viral and viral delivery systems for CRISPR-Cas9 technology in the biomedical field. Sci China Life Sci. 2017;60(5):458-467.
[47] KANTOR B, O’DONOVAN B, RITTINER J, et al. The therapeutic implications of all-in-one AAV-delivered epigenome-editing platform in neurodegenerative disorders. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):7259.
[48] DEGTEV D, BRAVO J, EMMANOUILIDI A, et al. Engineered PsCas9 enables therapeutic genome editing in mouse liver with lipid nanoparticles. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):9173.
[49] HU X, ENBAR T, TANG L. Delivery approaches of immunomodulatory nucleic acids for cancer therapy. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2024; 89:103182.
[50] KAUPBAYEVA B, TSOY A, SAFAROVA YANTSEN Y, et al. Unlocking Genome Editing: Advances and Obstacles in CRISPR/Cas Delivery Technologies. J Funct Biomater. 2024;15(11):324.
[51] MOLAEI Z, JABBARPOUR Z, OMIDKHODA A, et al. Exploring non-viral methods for the delivery of CRISPR-Cas ribonucleoprotein to hematopoietic stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024;15(1):233.
[52] XU W, ZHANG S, QIN H, et al. From bench to bedside: cutting-edge applications of base editing and prime editing in precision medicine. J Transl Med. 2024;22(1):1133.
[53] MCANDREWS KM, XIAO F, CHRONOPOULOS A, et al. Exosome-mediated delivery of CRISPR/Cas9 for targeting of oncogenic KrasG12D in pancreatic cancer. Life Sci Alliance. 2021;4(9):e202000875.
[54] 罗年安.基于CRISPR/dCas9靶向递送系统的HSCs重编程策略及其在肝纤维化治疗中的应用[D].西安:中国人民解放军空军军医大学,2023.
[55] WAN T, ZHONG J, PAN Q, et al. Exosome-mediated delivery of Cas9 ribonucleoprotein complexes for tissue-specific gene therapy of liver diseases. Sci Adv. 2022;8(37):eabp9435.
[56] LIANG Y, XU X, XU L, et al. Chondrocyte-specific genomic editing enabled by hybrid exosomes for osteoarthritis treatment. Theranostics. 2022;12(11):4866-4878.
[57] YAGHOOBI A, NAZERIAN Y, MEYMAND AZ, et al. Hypoxia-sensitive miRNA regulation via CRISPR/dCas9 loaded in hybrid exosomes: A novel strategy to improve embryo implantation and prevent placental insufficiency during pregnancy. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023;10:1082657.
[58] LIN W, CHEN L, ZHANG H, et al. Tumor-intrinsic YTHDF1 drives immune evasion and resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors via promoting MHC-I degradation. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):265.
[59] GULEI D, BERINDAN-NEAGOE I. Activation of Necroptosis by Engineered Self Tumor-Derived Exosomes Loaded with CRISPR/Cas9. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019;17:448-451.
[60] BAHADORANI M, NASIRI M, DELLINGER K, et al. Engineering Exosomes for Therapeutic Applications: Decoding Biogenesis, Content Modification, and Cargo Loading Strategies. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024;19:7137-7164.
[61] LI YJ, WU JY, LIU J, et al. Artificial exosomes for translational nanomedicine. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021;19(1):242.
[62] ZHANG L, LIN Y, LI S, et al. In Situ Reprogramming of Tumor-Associated Macrophages with Internally and Externally Engineered Exosomes. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2023;62(11):e202217089.
[63] 黄春满,李丽薇,黄勇彬,等.外泌体靶向修饰的研究进展[J].科学通报,2023, 68(33):4532-4543.
[64] LIANG Y, IQBAL Z, LU J, et al. Cell-derived nanovesicle-mediated drug delivery to the brain: Principles and strategies for vesicle engineering. Mol Ther. 2023;31(5):1207-1224.
[65] AKBARI A, NAZARI-KHANAMIRI F, AHMADI M, et al. Engineered Exosomes for Tumor-Targeted Drug Delivery: A Focus on Genetic and Chemical Functionalization. Pharmaceutics. 2022;15(1):66.
[66] ZHANG M, LU X, LUO L, et al. Targeting glutamine synthetase with AS1411-modified exosome-liposome hybrid nanoparticles for inhibition of choroidal neovascularization. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024;22(1):703.
[67] JIA G, HAN Y, AN Y, et al. NRP-1 targeted and cargo-loaded exosomes facilitate simultaneous imaging and therapy of glioma in vitro and in vivo. Biomaterials. 2018;178:302-316.
[68] KIM MS, HANEY MJ, ZHAO Y, et al. Engineering macrophage-derived exosomes for targeted paclitaxel delivery to pulmonary metastases: in vitro and in vivo evaluations. Nanomedicine. 2018;14(1):195-204.
[69] SONG Z, TAO Y, LIU Y, et al. Advances in delivery systems for CRISPR/Cas-mediated cancer treatment: a focus on viral vectors and extracellular vesicles. Front Immunol. 2024;15:1444437.
[70] YOSHIDA Y, AOKI M, NAGASE K, et al. Plasmid DNA Delivery into the Skin via Electroporation with a Depot-Type Electrode. Pharmaceutics. 2024;16(9):1219.
[71] ZHANG X, XU Q, ZI Z, et al. Programmable Extracellular Vesicles for Macromolecule Delivery and Genome Modifications. Dev Cell. 2020;55(6):784-801.e9.
[72] PALAKURTHI SS, SHAH B, KAPRE S, et al. A comprehensive review of challenges and advances in exosome-based drug delivery systems. Nanoscale Adv. 2024;6(23): 5803-5826.
[73] HUYAN T, LI H, PENG H, et al. Extracellular Vesicles - Advanced Nanocarriers in Cancer Therapy: Progress and Achievements. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:6485-6502.
[74] DU Y, LIU Y, HU J, et al. CRISPR/Cas9 systems: Delivery technologies and biomedical applications. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2023;18(6):100854.
[75] KAZEMIAN P, YU SY, THOMSON SB, et al. Lipid-Nanoparticle-Based Delivery of CRISPR/Cas9 Genome-Editing Components. Mol Pharm. 2022;19(6):1669-1686.
[76] ROSENBLUM D, GUTKIN A, DAMMES N, et al. Progress and challenges towards CRISPR/Cas clinical translation. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2020;154-155:176-186.
[77] HUANG X, LI A, XU P, et al. Current and prospective strategies for advancing the targeted delivery of CRISPR/Cas system via extracellular vesicles. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023;21(1):184.
[78] LIN Y, WAGNER E, LÄCHELT U. Non-viral delivery of the CRISPR/Cas system: DNA versus RNA versus RNP. Biomater Sci. 2022; 10(5):1166-1192. |