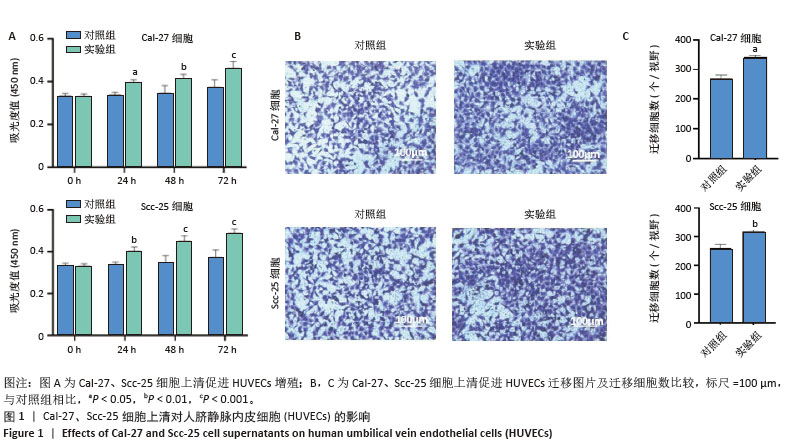
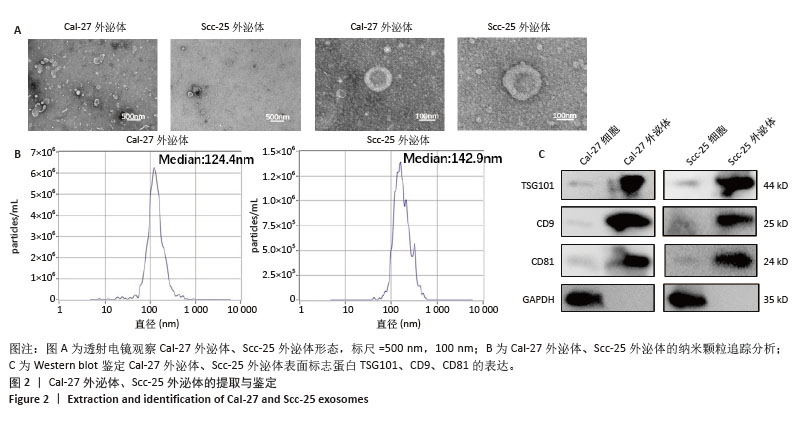
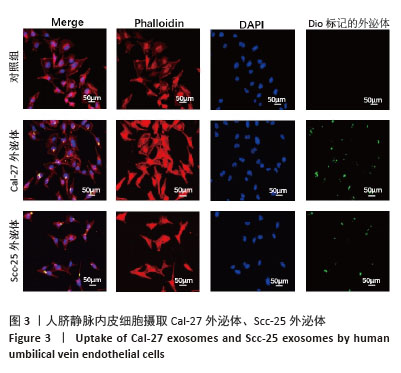
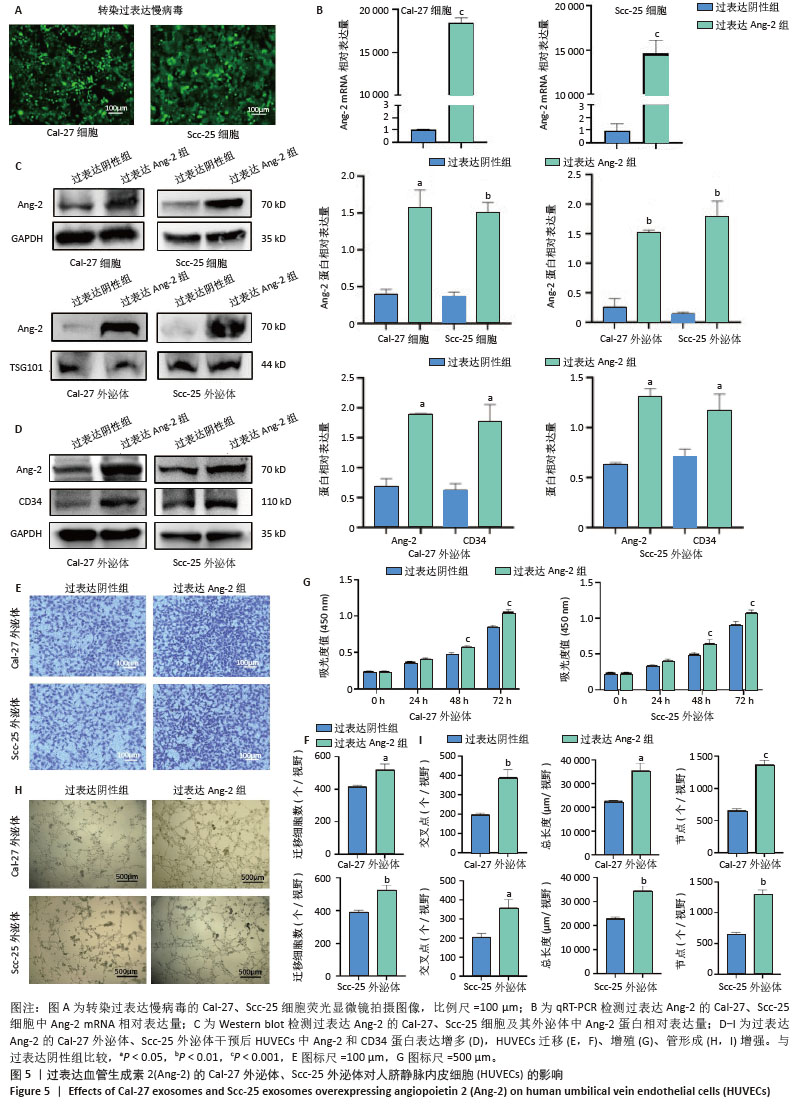
[1] STASIEWICZ M, KARPIŃSKI TM. The oral microbiota and its role in carcinogenesis. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022;86(Pt 3):633-642.
[2] YANG M, LUO Q, CHEN X, et al. Bitter melon derived extracellular vesicles enhance the therapeutic effects and reduce the drug resistance of 5-fluorouracil on oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021;19(1):259.
[3] SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL RL, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209-249.
[4] LIU H, HUANG Y, HUANG M, et al. Current Status, Opportunities, and Challenges of Exosomes in Oral Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022;17:2679-2705.
[5] XIA C, DONG X, LI H, et al. Cancer statistics in China and United States, 2022: profiles, trends, and determinants. Chin Med J (Engl). 2022;135(5):584-590.
[6] LIU TPJ, FISHER BM, CHUA B, et al. Survival outcomes following modern multidisciplinary management of oral squamous cell carcinoma in Australia. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2021;131(1): 92-98.
[7] KUGERATSKI FG, KALLURI R. Exosomes as mediators of immune regulation and immunotherapy in cancer. FEBS J. 2021;288(1):10-35.
[8] GUELFI S, HODIVALA-DILKE K, BERGERS G. Targeting the tumour vasculature: from vessel destruction to promotion. Nat Rev Cancer. 2024;24(10):655-675.
[9] BATISTELLA EA, MIGUEL AFP, NASCIMENTO NL, et al. Microvascular density analysis and histological parameters of oral cancer progression. Oral Dis. 2024;30(4):2110-2121.
[10] MAMILOS A, LEIN A, WINTER L, et al. Immunohistochemical Assessment of Microvessel Density in OSCC: Spatial Heterogeneity of Angiogenesis and Its Impact on Survival. Biomedicines. 2023;11(10):2724.
[11] CHEN YF, LUH F, HO YS, et al. Exosomes: a review of biologic function, diagnostic and targeted therapy applications, and clinical trials. J Biomed Sci. 2024;31(1):67.
[12] LI SR, MAN QW, GAO X, et al. Tissue-derived extracellular vesicles in cancers and non-cancer diseases: Present and future. J Extracell Vesicles. 2021;10(14):e12175.
[13] YU D, LI Y, WANG M, et al. Exosomes as a new frontier of cancer liquid biopsy. Mol Cancer. 2022;21(1):56.
[14] KALLURI R, LEBLEU VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. 2020;367(6478):eaau6977.
[15] MA X, YANG R, LI H, et al. Role of exosomes in the communication and treatment between OSCC and normal cells. Heliyon. 2024;10(7): e28148.
[16] ZHANG X, LI B. Updates of liquid biopsy in oral cancer and multiomics analysis. Oral Dis. 2023;29(1):51-61.
[17] CHEN Y, LI Z, LIANG J, et al. CircRNA has_circ_0069313 induced OSCC immunity escape by miR-325-3p-Foxp3 axes in both OSCC cells and Treg cells. Aging (Albany NY). 2022;14(10):4376-4389.
[18] HE L, PING F, FAN Z, et al. Salivary exosomal miR-24-3p serves as a potential detective biomarker for oral squamous cell carcinoma screening. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;121:109553.
[19] SUN YQ, WANG B, ZHENG LW, et al. Oral cancer cell to endothelial cell communication via exosomal miR-21/RMND5A pathway. BMC Oral Health. 2024;24(1):82.
[20] KINANE DF, GABERT J, XYNOPOULOS G, et al. Strategic approaches in oral squamous cell carcinoma diagnostics using liquid biopsy. Periodontol 2000. 2024;96(1):316-328.
[21] PASQUIER J, GHIABI P, CHOUCHANE L, et al. Angiocrine endothelium: from physiology to cancer. J Transl Med. 2020;18(1):52.
[22] ORIA VO, ERLER JT. Tumor Angiocrine Signaling: Novel Targeting Opportunity in Cancer. Cells. 2023;12(20):2510.
[23] SUN R, KONG X, QIU X, et al. The Emerging Roles of Pericytes in Modulating Tumor Microenvironment. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9: 676342.
[24] SAHARINEN P, LEPPÄNEN VM, ALITALO K. SnapShot: Angiopoietins and Their Functions. Cell. 2017;171(3):724-724.e1.
[25] DAVIS S, ALDRICH TH, JONES PF, et al. Isolation of angiopoietin-1, a ligand for the TIE2 receptor, by secretion-trap expression cloning. Cell. 1996;87(7):1161-1169.
[26] GHALEHBANDI S, YUZUGULEN J, PRANJOL MZI, et al. The role of VEGF in cancer-induced angiogenesis and research progress of drugs targeting VEGF. Eur J Pharmacol. 2023;949:175586.
[27] TEICHERT-KULISZEWSKA K, MAISONPIERRE PC, JONES N, et al. Biological action of angiopoietin-2 in a fibrin matrix model of angiogenesis is associated with activation of Tie2. Cardiovasc Res. 2001;49(3):659-670.
[28] FELCHT M, LUCK R, SCHERING A, et al. Angiopoietin-2 differentially regulates angiogenesis through TIE2 and integrin signaling. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(6):1991-2005.
[29] SCHOLZ A, PLATE KH, REISS Y. Angiopoietin-2: a multifaceted cytokine that functions in both angiogenesis and inflammation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2015;1347:45-51.
[30] XIE JY, WEI JX, LV LH, et al. Angiopoietin-2 induces angiogenesis via exosomes in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Commun Signal. 2020;18(1):46.
[31] TAKAMURA Y, YAMADA Y, MORIOKA M, et al. Turnover of Microaneurysms After Intravitreal Injections of Faricimab for Diabetic Macular Edema. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2023;64(13):31.
[32] MCCORD C, KISS A, MAGALHAES MA, et al. Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Associated with Precursor Lesions. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2021;14(9):873-884.
[33] SHARMA A, NATARAJAN S, MANAKTALA N, et al. Prognostic Nomogram for Lymph-Node Metastasis in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma (OSCC) Using Immunohistochemical Marker D2-40. Cancer Manag Res. 2023; 15:929-936.
[34] HUI L, CHEN Y. Tumor microenvironment: Sanctuary of the devil. Cancer Lett. 2015;368(1):7-13.
[35] HU S, MA J, SU C, et al. Engineered exosome-like nanovesicles suppress tumor growth by reprogramming tumor microenvironment and promoting tumor ferroptosis. Acta Biomater. 2021;135:567-581.
[36] YE D, GONG M, DENG Y, et al. Roles and clinical application of exosomal circRNAs in the diagnosis and treatment of malignant tumors. J Transl Med. 2022;20(1):161.
[37] JAKKULWAR S, VAGHA S, CHAUDHARY M. Tumour Budding in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Narrative Review. Cureus. 2024;16(9): e69624.
[38] HUANG CY, CHOU ST, HSU YM, et al. MEG3-Mediated Oral Squamous-Cell-Carcinoma-Derived Exosomal miR-421 Activates Angiogenesis by Targeting HS2ST1 in Vascular Endothelial Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2024; 25(14):7576.
[39] YAN W, WANG Y, CHEN Y, et al. Exosomal miR-130b-3p Promotes Progression and Tubular Formation Through Targeting PTEN in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:616306.
[40] PAUTA M, RIBERA J, MELGAR-LESMES P, et al. Overexpression of angiopoietin-2 in rats and patients with liver fibrosis. Therapeutic consequences of its inhibition. Liver Int. 2015;35(4):1383-1392.
[41] LI C, SUN CJ, FAN JC, et al. Angiopoietin-2 expression is correlated with angiogenesis and overall survival in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Med Oncol. 2013;30(2):571.
[42] POMELLA S, MELAIU O, DRI M, et al. Effects of Angiogenic Factors on the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Their Impact on the Onset and Progression of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: An Overview. Cells. 2024;13(15):1294.
[43] LIU J, YAN Z, YANG F, et al. Exosomes Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Accelerate Cutaneous Wound Healing by Enhancing Angiogenesis through Delivering Angiopoietin-2. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2021;17(2):305-317.
[44] RUGGERI BA, CAMP F, MIKNYOCZKI S. Animal models of disease: pre-clinical animal models of cancer and their applications and utility in drug discovery. Biochem Pharmacol. 2014;87(1):150-161. |