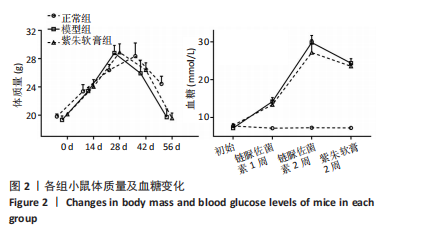
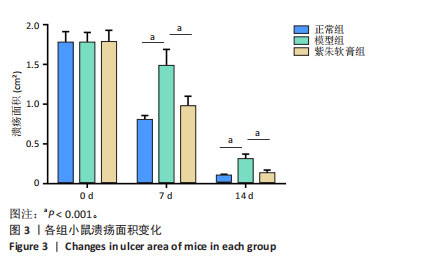
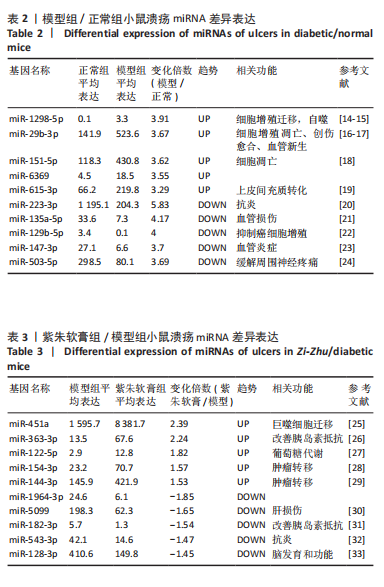
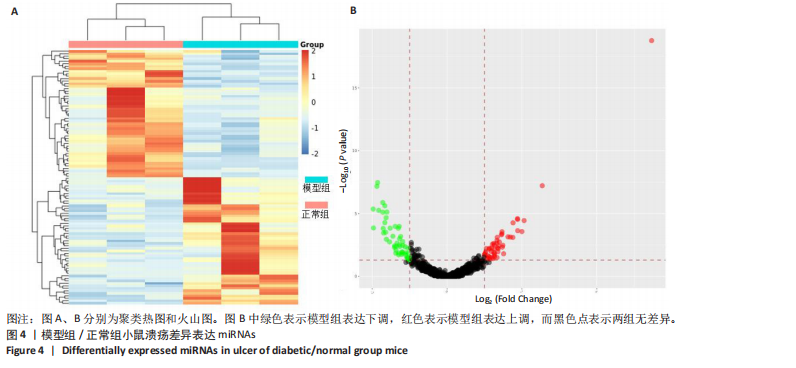
[1] MATIJEVIĆ T, TALAPKO J, MEŠTROVIĆ T, et al. Understanding the multifaceted etiopathogenesis of foot complications in individuals with diabetes. World J Clin Cases. 2023;11(8):1669-1683.
[2] CARUSO P, MAIORINO MI, MACERA M, et al. Antibiotic resistance in diabetic foot infection:how it changed with COVID-19pandemic in a tertiary care center. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2021;175: 108797.
[3] MELONI M, IZZO V, GIURATO L, et al. Prevalence, clinical aspects and outcomes in a large cohort of persons with diabetic foot disease: comparison between neuropathic and ischemic ulcers. J Clin Med. 2020;9(6):1780.
[4] RENNAN MB, HESS TM, BARTLE B, et al. Diabetic foot ulcer severity predicts mortality among veterans with type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Complications. 2017;31(3):556-561.
[5] JIAO Y, CHEN X, NIU Y, et al. Wharton’s jelly mesenchymal stem cells embedded in PF-127 hydrogel plus sodium ascorbyl phosphate combination promote diabetic wound healing in type 2 diabetic rat. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):559.
[6] ANURADHA U, MEHRA NK, KHATRI DK. Understanding molecular mechanisms and miRNA-based targets in diabetes foot ulcers. Mol Biol Rep. 2024;51(1):82.
[7] ZAMPETAKI A, KIECHL S, DROZDOV I, et al. Plasma microRNA profiling reveals loss of endothelial miR-126 and other microRNAs in type 2 diabetes. Circ Res. 2010;107(6):810-817.
[8] XU J, WU W, ZHANG L, et al. The role of microRNA-146a in the pathogenesis of the diabetic wound-healing impairment: correction with mesenchymal stem cell treatment. Diabetes. 2012;61(11):2906-2912.
[9] MADHYASTHA R, MADHYASTHA H, NAKAJIMA Y, et al. MicroRNA signature in diabetic wound healing: promotive role of miR-21 in fibroblast migration. Int Wound J. 2012;9(4):355-361.
[10] CIECHOMSKA M, O’REILLY S, SUWARA M, et al. MiR-29a reduces TIMP-1 production by dermal fibroblasts via targeting TGF-β activated kinase 1 binding protein 1, implications for systemic sclerosis. PLoS One. 2014;9(12):e115596.
[11] MATTICK JS, MAKUNIN IV. Non-coding RNA. Hum Mol Genet. 2006;15: R17-29.
[12] 黄仁燕,王宏飞,王徐红,等.紫朱软膏对糖尿病溃疡小鼠创面炎症反应及上皮-间充质转化的影响[J].陕西中医,2023,44(12): 1673-1677.
[13] 王丽翔,黄仁燕,柳国斌. 清筋术联合紫朱软膏外用治疗糖尿病足筋疽的临床疗效[J]. 辽宁中医杂志,2023,50(7):102-105.
[14] GAO S, GAO T, FENG L, et al. CircPKM2 aggravates the progression of non-small cell lung cancer by regulating MTDH via miR-1298-5p. Thorac Cancer. 2023;14(30):3020-3031.
[15] LI X, ZHU M, ZHAO G, et al. MiR-1298-5p level downregulation induced by Helicobacter pylori infection inhibits autophagy and promotes gastric cancer development by targeting MAP2K6. Cell Signal. 2022; 93:110286.
[16] ZHOU H, YAN Z, ZHU L, et al. miR-29b-3p’s Effects on Prostate Cancer. J Biomater Tiss Eng. 2022;12(4): 681-689.
[17] QIN Z, WANG X, ZHOU Y, et al. Upregulation of miR-29b-3p alleviates coronary microembolization-induced myocardial injury via regulating BMF and GSK-3β. Apoptosis. 2023;28(1-2):210-221.
[18] ZHOU F, CHEN L, XU S , et al. Upregulation of miR-151-5p promotes the apoptosis of intestinal epithelial cells by targeting brain-derived neurotrophic factor in ulcerative colitis mice. Cell Cycle. 2022;21(24): 2615-2626.
[19] LEI B, WANG D, ZHANG M, et al. miR-615-3p promotes the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of breast cancer by targeting PICK1/TGFBRI axis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020;39(1):71.
[20] 邓波,舒远,胡玲. 丹皮酚上调miR-223-3p减轻高糖诱导的小鼠心肌微血管内皮细胞损伤的研究[J].中国糖尿病杂志,2023,31(9): 697-702.
[21] XIE K, LI C, WANG M, et al. miR-135a-5p overexpression in peripheral blood-derived exosomes mediates vascular injury in type 2 diabetes patients. Front Endocrinol. 2023;14:1035029.
[22] ZHENG L, QI Y, LIU S, et al. miR-129b suppresses cell proliferation in the human lung cancer cell lines A549 and H1299. Genet Mol Res. 2016;15(4). doi: 10.4238/gmr15048367.
[23] VLACIL AK, VOLLMEISTER E, BERTRAMS W, et al. Micrornas Mir-147-3p And Mir-298-5p Are Nod-Driven Regulators Of Endothelial Cytokine Expression. Atherosclerosis. 2019;287:e98.
[24] GUO Y, ZENG J, ZHUANG Y, et al. MiR-503-5p alleviates peripheral neuropathy-induced neuropathic pain in T2DM mice by regulating SEPT9 to inhibit astrocyte activation. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):14361.
[25] LIU X, ZHANG D, WANG H, et al. MiR-451a enhances the phagocytosis and affects both M1 and M2 polarization in macrophages. Cell Immunol. 2021:365:104377.
[26] 姚婷婷,李涛,吕红艳,等.运动通过上调肥胖小鼠肝脏miR-363-3p影响AKT/mTOR通路而减轻肝脏胰岛素抵抗[J].中国病理生理杂志,2023,39(2):297-304.
[27] ZHANG J, LI K, GAO L, et al. Glucose metabolism disorder related to follicular fluid exosomal miR-122-5p in cumulus cells of endometriosis patients. Reproduction. 2024;168(4):e240028.
[28] SUN K, LU T, HU C, et al. LINC00115 regulates lung adenocarcinoma progression via sponging miR-154-3p to modulate Sp3 expression. Mol Cell Probes. 2023:68:101909.
[29] XIU C, DENG X, DENG D, et al. miR-144-3p Targets GABRB2 to Suppress Thyroid Cancer Progression In Vitro. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024;82(4):3585-3595.
[30] YANG R, YANG F, HUANG Z, et al. Serum microRNA-122-3p, microRNA-194-5p and microRNA-5099 are potential toxicological biomarkers for the hepatotoxicity induced by Airpotato yam. Toxicol Lett. 2017; 280:125-132.
[31] RAO J, CHEN Y, HUANG J, et al. Inhibiting miR-182-3p Alleviates Gestational Diabetes Mellitus by Improving Insulin Resistance in Skeletal Muscle. Balkan Med J. 2022;39(2):121-129.
[32] NEAMAH WH, SINGH NP, ALGHETAA H, et al. AhR Activation Leads to Massive Mobilization of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells with Immunosuppressive Activity through Regulation of CXCR2 and MicroRNA miR-150-5p and miR-543-3p That Target Anti-Inflammatory Genes. J Immunol. 2019;203(7):1830-1844.
[33] KIEL K, KRÓL SK, BRONISZ A, et al. MiR-128-3p - a gray eminence of the human central nervous system. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024; 35(1):102141.
[34] COFFEY L, MAHON C, GALLAGHER P. Perceptions and experiences of diabetic foot ulceration and foot care in people with diabetes: A qualitative meta-synthesis. Int Wound J. 2019;16(1):183-210.
[35] ASVHNER P, KARURANGA S, JAMES S, et al. The international diabetes federation’s guide for diabetes epidemiological studies. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2021:172(2):108630.
[36] ARMSTRONG DG, TAN TW, BOULTON AJM, et al. Diabetic Foot Ulcers: A Review. JAMA. 2023;330(1):62-75.
[37] EMING SA, MARTIN P, TOMIC-CANIC M. Wound repair and regeneration: mechanisms, signaling, and translation. Sci Transl Med. 2014;6(265):265sr6.
[38] ZIMMET P, ALBERTI KG, MAGLIANO DJ, et al. Diabetes mellitus statistics on prevalence and mortality: facts and fallacies. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2016;12(10):616-622.
[39] 黄仁燕,樊炜静,柳国斌.中药油膏治疗糖尿病足溃疡用药规律研究[J].海南医学院学报,2021,27(4):302-306.
[40] HO PTB, CLARK LM, LE CTT. MicroRNA-Based Diagnosis and Therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(13):7167.
[41] WANG L, WANG C, HUANG C, et al. Role of microRNAs in diabetic foot ulcers: Mechanisms and possible interventions. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2024;217:111858.
[42] ZHAO X, XU M, TANG Y, et al. Changes in miroRNA-103 expression in wound margin tissue are related to wound healing of diabetes foot ulcers. Int Wound J. 2023;20(2):467-483.
[43] AMIN KN, UMAPATHY D, ANANDHARAJ A, et al. miR-23c regulates wound healing by targeting stromal cell-derived factor-1α (SDF-1α/CXCL12) among patients with diabetic foot ulcer. Microvasc Res. 2020;127:103924.
[44] XIONG Y, CHEN L, YU T, et al. Inhibition of circulating exosomal microRNA-15a-3p accelerates diabetic wound repair. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(10):8968-8986.
[45] RODRIGUES BT, VANGAVETI VN, URKUDE R, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of lower limb amputations in patients with diabetic foot ulcers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2022;16(2):102397.
[46] CHEN L, SUN S, GAO Y, et al. Global mortality of diabetic foot ulcer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2023;25(1):36-45.
[47] GUO J, LIN Q, SHAO Y, et al. miR-29b promotes skin wound healing and reduces excessive scar formation by inhibition of the TGF-β1/Smad/CTGF signaling pathway. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2017;95(4):437-442.
[48] LIU X, GUO B, LI Q, et al. mTOR in metabolic homeostasis and disease. Exp Cell Res. 2024;441(2):114173.
[49] SOLINAS G, BECATTINI B. PI3K and AKT at the Interface of Signaling and Metabolism. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2022; 436:311-336.
[50] JIN T. Current understanding on role of the Wnt signaling pathway effector TCF7L2 in glucose homeostasis. Endocr Rev. 2016;37(3):254-277.
|