中国组织工程研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (34): 7405-7414.doi: 10.12307/2025.891
• 生物材料综述 biomaterial review • 上一篇 下一篇
支架材料结合生物因素对牙囊细胞增殖及骨向分化生物学特性的影响
李中正1,2,陈政豪1,2,唐子又1,2,娄凯阳1,2,张 睿1,2,刘 琪1,2,赵 娜1,2,杨 琨1,2
- 1遵义医科大学,贵州省遵义市 563000;2遵义医科大学附属口腔医院牙周科,贵州省遵义市 563000
-
收稿日期:2024-09-12接受日期:2024-11-05出版日期:2025-12-08发布日期:2025-01-17 -
通讯作者:杨琨,博士,副教授,主任医师,遵义医科大学,贵州省遵义市 563000;遵义医科大学附属口腔医院牙周科,贵州省遵义市 563000 -
作者简介:李中正,男,2004年生,江西省赣州市人,汉族。 -
基金资助:遵义市科技计划项目[遵市科合HZ字(2023)79号],项目负责人:杨琨;遵义医科大学“12345”“未来临床名医”未来人才培养计划,项目负责人:杨琨;贵州省科技厅基础研究项目(黔科合基础-ZK[2023]一般535);项目负责人:张睿;遵义医科大学附属医院院基金[院字(2022)02号],项目负责人:刘琪;贵州省卫健委科学技术基金项目(gzwkj2022-423),项目负责人:赵娜
Effects of scaffold materials combined with biological factors on biological characteristics of dental follicle cell proliferation and osteogenic differentiation
Li Zhongzheng1, 2, Chen Zhenghao1, 2, Tang Ziyou1, 2, Lou Kaiyang1, 2, Zhang Rui1, 2, Liu Qi1, 2, Zhao Na1, 2, Yang Kun1, 2
- 1Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China; 2Department of Periodontology, Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2024-09-12Accepted:2024-11-05Online:2025-12-08Published:2025-01-17 -
Contact:Yang Kun, PhD, Associate professor, Chief physician, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China; Department of Periodontology, Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Li Zhongzheng, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China; Department of Periodontology, Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:Zunyi Science and Technology Program, No. Zunshi Kehe HZ Zi (2023) 79 (to YK); Zunyi Medical University “12345” “Future Clinical Doctor” Future Talent Cultivation Program (to YK); Basic Research Project of Guizhou Province Department of Science and Technology, No. ZK[2023]535 (to ZR); Zunyi Medical University Affiliated Hospital Hospital Fund, No. (2022)02 (to LQ); Science and Technology Fund Project of Guizhou Provincial Health and Health Commission, No. gzwkj2022-423 (to ZN)
摘要:
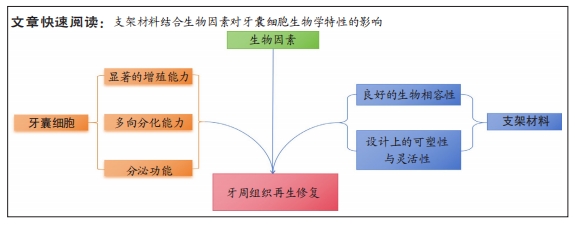
文题释义:
生物因素:分为内源及外源因素,前者是指来自生物体内部的因素,通常与生物体的内部结构、功能或代谢状态相关联;后者则指来自生物体外部环境的因素,通常与生物体与外界环境的相互作用和适应有关。组织再生工程:其要素包括种子细胞、生物材料、细胞与生物材料的整合以及植入物与体内微环境的整合,是无创伤修复的一种重要手段,正积极应用于牙周组织修复研究。
背景:牙囊细胞因优异的特性在牙周组织再生工程中的运用更加广泛,随着生物支架材料研究的发展,牙囊细胞与牙周组织再生技术的关系日益紧密。
目的:综述不同实验对象牙囊细胞在内外源生物因素作用下的表现,并结合支架材料分析其对牙囊细胞生物学特性的影响。方法:以“dental follicle cell,scaffolds,material,periodontal tissue regeneration,tissue engineering,review”及“牙囊细胞,支架,材料,牙周组织再生,组织工程,综述”为关键词,检索PubMed,Sciencedirect和中国知网数据库2013-2023年发表的文献,最后纳入95篇文献进行分析与讨论。
结果与结论:①牙囊细胞起源于牙囊组织,具有一定的干细胞分化潜能,因其优良性能正积极应用于牙周组织再生工程研究。②牙囊细胞的增殖及成骨分化受多种生物因素的影响,内源性因素与外源性因素在一定程度上均对牙囊细胞的增殖以及骨向分化能力具有一定的促进作用。③3D打印技术、纳米技术使研究者们能够制造出更为合适的支架材料。④高分子材料显示了其在牙周组织再生中的灵活性和可塑性,可根据缺损部位的不同,从而制造具有针对性的支架材料,实现高效的组织再生;无机材料因具备良好的生物相容性在牙周组织再生工程中得以广泛使用,通过调整纳米级无机材料的含量或许可改善支架的性能,从而制备生物相容性更好的支架。⑤目前尚有多种新型人工合成(复合)材料,向研究者们展现出优良的特性,但由于支架材料中生物因素对牙囊细胞作用的机制较为复杂,且有关牙囊细胞的研究多集中在体外培养,故如何制作出更适合牙囊细胞生长发育的支架材料,并将其安全有效地应用于临床治疗是未来研究的方向。
https://orcid.org/0009-0007-8722-1429(李中正);https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7720-8681(杨琨)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
李中正, 陈政豪, 唐子又, 娄凯阳, 张 睿, 刘 琪, 赵 娜, 杨 琨. 支架材料结合生物因素对牙囊细胞增殖及骨向分化生物学特性的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(34): 7405-7414.
Li Zhongzheng, Chen Zhenghao, Tang Ziyou, Lou Kaiyang, Zhang Rui, Liu Qi, Zhao Na, Yang Kun. Effects of scaffold materials combined with biological factors on biological characteristics of dental follicle cell proliferation and osteogenic differentiation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7405-7414.
用于体外培养和后续研究的牙囊细胞可以从大鼠或人类的牙囊组织中提取,通常选择因各种原因被拔除的智齿附带组织进行传代培养。通过倒置显微镜及苏木精-伊红染色观察细胞形态与生长状态,并采用免疫组化染色技术检测牙囊细胞的特征,结果显示牙囊细胞呈长梭形、纺锤形及不规则三角形,且表达典型的干细胞标志物[21]。
2.1.1 增殖能力 牙囊细胞具有显著的增殖能力,受到培养时间和传代次数的影响。SHOI等[22]对健康儿童的相同嵌生上颌切牙中的牙髓干细胞与牙囊细胞进行比较,发现牙囊细胞的细胞增殖率和集落形成能力显著高于牙髓干细胞。王贺等[23]使用二次酶消化法对小鼠牙囊细胞进行原代培养,观察到第3代细胞的生长速度最快且状态最佳,适合用于各种后续实验。
2.1.2 多向分化能力 牙囊细胞不仅具备显著的增殖特性,还展现出良好的骨向分化能力,能够向牙周膜、牙骨质和牙槽骨分化[24-27]。相较于牙周膜干细胞[28],牙囊细胞具有更好的分化潜能,并且在多能性和免疫因子表达上优于人牙髓干细胞和人胚胎干细胞[29]。在体外培养条件下,牙囊细胞还可以向脂肪细胞及神经细胞分化[30]。在人肝细胞生长因子的存在下,牙囊细胞能向肝细胞分
化[31],并保持一定的干细胞生物学特性。此外,牙囊细胞在组蛋白脱乙酰酶抑制剂的作用下可分化为心肌细胞,分化后的心肌细胞具有较高的归巢率,显示出牙囊细胞在心肌细胞分化和再生中的潜力[32]。YANG等[33]评估了5种牙源性干细胞在不同的神经细胞分化诱导模式及时间点,结果表明牙囊细胞相比其他细胞具有更高的增殖能力,并在表皮生长因子和碱性成纤维细胞生长因子培养条件下展现出最佳的神经分化潜能,可能成为更优的候选细胞类型。
2.1.3 牙囊细胞的分泌功能 牙囊细胞能够分泌多种细胞因子和基质成分,如生长因子和细胞外基质,参与组织再生与修复。间充质干细胞的活性成分有相当一部分取决于它们的分泌组,分泌组指的是在条件培养基或细胞外囊泡中释放的所有生物活性分子(神经营养因子)[34-35]。外泌体就属于分泌组的一种,其内包括了多种细胞因子和生长因子等,这些物质对组织修复有一定的促进作用,其原理涉及一种由蛋白质介导的“肇事逃逸机制”[36],即免疫细胞或者是缺损组织的细胞通过分泌、摄取细胞外囊泡和免疫介导的吞噬作用,将分泌组内的旁分泌物质转导至细胞内[37-38],并产生一定的生物学效应,见图3。牙囊细胞外泌体对牙囊细胞自身[39]、牙源性以及非牙源性细胞和组织均具有一定的调控作用,可促进牙周组织及其他组织的再生修复[40]。
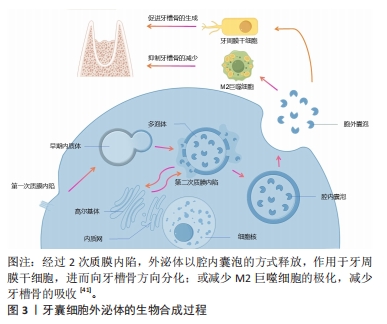
有学者将牙囊细胞外泌体提取分离后与大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞共培养,发现外泌体能够被骨髓间充质干细胞摄取并且可以促进骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖活性以及迁移分化[42]。另有学者将牙囊细胞外泌体与牙周膜干细胞共培养,发现牙周膜干细胞对牙囊细胞外泌体也有摄取情况,并且能够增强牙周膜干细胞的增殖迁移能力[43-44]。
田俊等[45-46]则通过研究发现,牙囊细胞外泌体除了可抑制巨噬细胞炎症反应,还能被牙髓组织摄取,并可能通过抑制牙髓炎症反应促进炎症牙髓组织的修复。
尽管在临床实践转化方面仍存在许多障碍,且尚未有较完善的研究来对牙囊细胞外泌体的临床治疗效果进行评估[47],但不可否认,牙囊细胞衍生的外泌体正在成为一种有前途且实用的组织修复和再生治疗方法。
牙囊细胞以上的良好生物学特性均向研究者们展示了其运用在牙周组织再生当中的潜力,是十分具有潜力的牙周组织再生工程种子细胞。
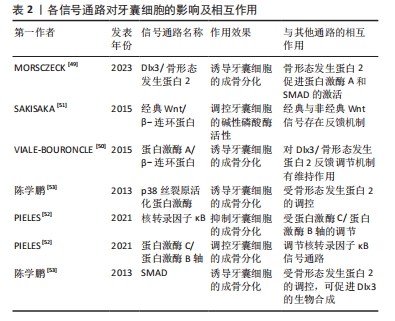
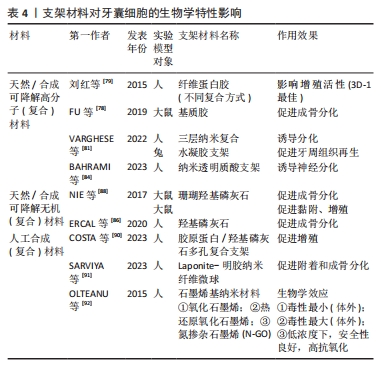
2.2 生物因素对牙囊细胞生物学特性的影响 牙囊细胞的增殖以及成骨分化受多种生物因素影响,见图4。内源性信号以及各微环境是影响干细胞性能的决定性因素[48],为方便区分,文章将生物因素分类为内源性因素和外源性因素,前者主要包括各常见信号通路以及细胞自身的生物代谢途径,后者主要是指为进一步研究牙囊细胞相关生物学特性而人工构建的微环境等。不同的生物因素可以单独作用于牙囊细胞产生生物学效应的变化,也可以由不同生物因素结合起来共同作用于牙囊细胞,从而造成不同的生物学效应,相关研究集中于对牙囊细胞增殖与成骨分化的影响。

2.2.1 内源性因素 Dlx3/骨形态发生蛋白2反馈调节机制在调控牙囊细胞的成骨分化上尤为重要[49],牙囊细胞的成骨分化在一定程度上取决于Dlx3和骨形态发生蛋白的浓度比例,转录因子Dlx3具有能诱导牙囊细胞成骨向分化的作用,具体机制涉及Dlx3对骨形态发生蛋白信号通路的调节:骨形态发生蛋白2促进蛋白激酶A和SMAD的激活,上述生物因子促进Dlx3的合成,Dlx3则对骨形态发生蛋白2和Runt相关转录因子的合成具有诱导作用,值得一提的是,除了通过骨形态发生蛋白2依赖性途径刺激成骨分化,Dlx3也可直接刺激牙囊细胞的成骨分化。除此之外,蛋白激酶A/β-连环蛋白通路对Dlx3/骨形态发生蛋白反馈调节机制有维持作用,蛋白激酶A通过磷酸化β-连环蛋白来增加其活性,而β-连环蛋白则是调控牙囊细胞成骨分化的重要因子,调控Dlx3合成的同时也诱导成骨标志物Runt相关转录因子2[50]。在经典Wnt/β-连环蛋白信号通路中,经典与非经典Wnt信号之间同样存在一定的反馈机制[51],经典信号Wnt3a可以促进牙囊细胞的碱性磷酸酶活性,非经典信号Wnt5a选择性地抑制Wnt3a介导的碱性磷酸酶活性的增加,而Wnt3a亦可以通过增加Wnt5a的表达对碱性磷酸酶表达进行负反馈调节。蛋白激酶C和蛋白激酶B的经典亚型可通过β-连环蛋白和核转录因子κB信号通路对牙囊细胞的成骨分化进行调控,牙囊细胞中的蛋白激酶B活性受经典蛋白激酶C的调节,核转录因子κB通路在牙囊细胞中则受蛋白激酶C/蛋白激酶B轴调节[52]。另有研究表明,骨形态发生蛋白2诱导牙囊细胞内的Runt相关转录因子2等表达可通过p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路、SMAD信号通路等多种信号通路转导机制完成[53]。各信号通路对牙囊细胞的影响及互作见表2。
自噬过程是AMP活化蛋白激酶信号通路的一个重要生物靶点,在牙齿发育过程中具有重要作用[54],研究表明牙囊细胞同其他干细胞一样同样会发生自噬。由于AMP活化蛋白激酶和自噬在牙囊细胞中的作用尚不明确,故有研究使用AMP活化蛋白激酶激活剂AICAR以及AMP活化蛋白激酶抑制剂dosromorphin分别对牙囊细胞进行处理,发现3 d时激活组的碱性磷酸酶活性与相关成骨标志物表达均降低,而抑制组的部分成骨标志物则上升,表明AMP活化蛋白激酶调控牙囊细胞的早期成骨分化[55];进一步研究采用自噬激活剂PI103或自噬抑制剂wortmannin分别处理牙囊细胞,发现牙囊细胞的自噬作用会抑制其分化与矿化,随后采用特异性小干扰RNA敲除AMP活化蛋白激酶α基因,发现自噬相关蛋白表达降低,而相关成骨分化标志物下降,表明AMP活化蛋白激酶还可通过自噬间接影响生物矿化。
2.2.2 外源性因素 由于体外培养与体内培养的条件不同,学者们一直力求通过营造各种微环境和运用各种手段来干预牙囊细胞的生物学特性变化。牙囊细胞在炎症微环境中仍保留较好的牙周组织再生效能[56],且经过脂多糖预处理后的牙囊细胞小细胞外囊泡对牙周炎治疗的疗效增强[57]。研究发现,在大肠杆菌脂多糖模拟的炎症微环境下,牙囊细胞的成骨能力受到了抑制,但低浓度的大肠杆菌脂多糖却对牙囊细胞的增殖迁移有一定的促进作用[58],其机制可能为大肠杆菌脂多糖可以显著上调白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α表达,通过Toll样受体4介导的磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B通路和核转录因子κB通路促进牙囊细胞的增殖,并且可以降低成骨相关基因mRNA相对表达量,从而达到抑制牙囊细胞成骨分化的作用。WEI等[59]研究发现,在炎症微环境中,骨膜蛋白的剔除会导致牙囊细胞的增殖和成骨分化能力减弱;进一步研究表明,骨膜蛋白通过整合素αM/p-ERK/ERK信号通路调节巨噬细胞来介导牙囊细胞促进牙周再生的过程[60]。此外,在体外培养的持续低氧条件下,低氧可能通过触发Nanog,八聚体结合转录因子4(Octamer-bindingtranscriptionfactor-4,Oct-4)和SRY盒-2(SRY related HMG box-2,Sox-2)基因等干细胞标志物表达来保持牙囊细胞的干细胞特性,但具体信号通路仍不明确[61];钙离子浓度也会影响牙囊细胞生物学特性,低钙离子浓度会影响人牙囊细胞增殖与迁移,而高钙离子浓度则通过上调成骨分化相关基因RUNX2和骨桥蛋白的表达来调节牙囊细胞的成骨分化[62-63]。
另有研究发现,短期刺激牙囊细胞可显著增加其白细胞介素6,8的释放[64],这表明牙囊细胞具有一定的免疫特性。介于这些免疫特性,外源性生长因子难以发挥其效用,但通过基因转染生长因子基因片段导入靶细胞内,有利于获得生长因子持续高效发挥作用,对此,冉玲等[65]开展研究,最终发现超声强度为0.5 W/cm2且辐照时间为30 s时转染率明显高于其他超声参数组合以及传统脂质体介导的转染率,且对细胞活力无明显影响,从而为牙周组织工程提供一种较理想的基因转染方法。
长期的天然或者是人为因素(如医疗检查)所导致的低剂量红外线可能会导致DNA的病变,而DNA损伤反应是真核生物进化而来用以保护DNA免受辐射诱导的DNA双链断裂导致的损伤。BELMANS等[66]发现牙囊细胞暴露于低剂量的X射线下,会诱导DNA双链断裂的发生,并且DNA双链断裂的数量随着辐射剂量的增加而线性增加;为深入研究其具体机制,有研究用NU7441来抑制DNA蛋白激酶,DNA蛋白激酶是DNA损伤反应的重要因子,结果发现与对照组相比,β-半乳糖苷酶活性和阳性细胞数量均减少,即细胞衰老减少[67];蛋白激酶B是DNA蛋白激酶的靶蛋白,在加入蛋白激酶B的情况下,发现β-半乳糖苷酶活性和阳性细胞数量有一定程度的回弹,这些结果表明,DNA损伤反应的抑制与细胞衰老的诱导有关,而DNA蛋白激酶则通过诱导蛋白激酶B的上调来实现细胞衰老。
此外,生物提取物/药物也对牙囊细胞的生物学特性产生一定的影响。如淫羊藿苷具有调控人牙囊干细胞旁分泌的作用,从而释放更多调节成骨分化的细胞因子[68];有研究对常见的转录因子p53在牙囊细胞中的作用进行研究,比较了可诱导p53基因表达的E2F-1基因,观察两者在牙囊细胞增殖发育和成骨分化中的作用,结果发现E2F-1对成骨分化的无诱导作用[69];而p53抑制衰老牙囊细胞的成骨分化和细胞增殖,但对衰老诱导没有明显作用,而姜黄素能通过下调p16、p21和上调E2F1、p53以及恢复成骨标志物Runt相关转录因子2和骨桥蛋白来抑制由于细胞传代所导致的牙囊细胞衰老[70]。另有研究表明,牙囊细胞可通过与其他细胞相互作用以提高自身能力,如牙乳头干细胞和牙囊细胞可通过体外交互作用调节体外培养微环境,通过能提高内源性Oct-4、Sox2和C-myc而保持牙囊细胞的干细胞特性[71]。以上研究或许能为牙囊细胞在牙周再生治疗的应用提供理论基础以及新的思路。
2.3 支架材料在牙囊细胞研究中的应用
2.3.1 支架材料在牙科干细胞中运用的现状 支架材料是牙周组织再生的一个必不可少的部分。为了使种子细胞增殖和分化,需要提供一个由生物材料所构成的细胞支架,支架材料相当于人工细胞外基质,支架材料与种子细胞结合,培养成熟后植入生物体内,继而发生再生过程,支架降解,新的组织形成并填补缺损[72];生物打印的出现有别于其他传统支架的制作方法,它使研究者们可以针对不同的缺损定制出能改进或治疗该缺损的生物支架材料[73-75],见图5。研究发现种子细胞和支架之间存在相互作用,支架会影响到细胞的功能,而细胞在再生过程中也会导致支架的形态变化,其机制涉及细胞和支架的反馈回路,即细胞的活动如机械传导、功能调节以及增殖分化迁移等,可以影响支架的重组和收缩力,而支架的重组和收缩力又会反馈地影响上述提及的细胞活动,故或许可以以此为依据设计适合牙囊细胞的支架材料。
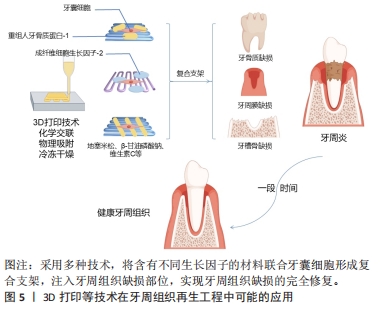
支架材料按其性质主要分为天然/合成可降解高分子材料、天然/合成可降解无机材料;还有其他各种人工合成(复合)材料。合成(复合)材料通常指的是2种或2种以上常见的天然/合成可降解高分子材料或者天然/合成可降解无机材料,通过化学交联、物理吸附、冷冻干燥、3D打印和特异性结合等复合技术,形成具有某种联合作用,该联合作用对牙囊细胞的增殖发育以及成骨分化效应往往要比一种支架单独作用要更为明显。
用于牙周组织工程再生的支架材料要求具有良好的生物相容性[76]。有体外研究表明,细胞与支架之间的微机械相容性与牙囊细胞的机械敏感基因表达标志物和成骨分化标志物显著相关[77],这为寻找更适合牙囊细胞生长增殖分化的支架材料提供了一定的理论基础。事实上,此类研究仍需进一步发展。
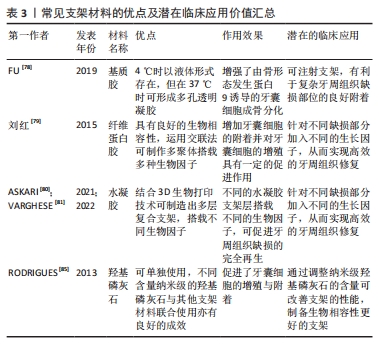
2.3.2 天然/合成可降解高分子(复合)材料 胶原材料因具有优异的生物相容性而被用作组织工程再生的支架材料:FU等[78]的研究评估了可注射基质胶作为支架的潜在用途,该研究采用三维支架材料基质胶,以骨形态发生蛋白9和大鼠牙囊细胞为实验对象,采用皮下植入的方法,6周后进行染色、分析与评估,结果发现骨形态发生蛋白9有效促进了大鼠牙囊细胞的成骨分化,而基质胶则促进了骨形态发生蛋白9诱导的大鼠牙囊干细胞在体内的成骨。
纤维蛋白胶同样因独特的生理学性质而具有良好的生物相容性,其在组织工程内作为支架材料已较为广泛。刘红等[79]评估了纤维蛋白胶作为细胞移植载体的可行性及有效性,该研究以纤维蛋白胶与人牙囊细胞为实验对象,分析了纤维蛋白胶与人牙囊细胞二维及三维结合模式对细胞存活、增殖及凋亡的影响,结果发现纤维蛋白胶的3D-1复合模式下,牙囊细胞具有较高的增殖趋势。
由亲水均聚物、共聚物或大聚体形成的水凝胶,因具有与组织相似特征的三维聚合物网络而在牙科生物材料领域受到了广泛的关注[80]。在3层纳米复合水凝胶支架中[81],支架的每一层均由不同的物质构成,并且都设计用于再生牙周组织的特定部分[82]:骨质层由几丁质-聚(乳酸-乙醇酸)水凝胶支架与纳米生物活性玻璃陶瓷和骨质蛋白1制成;面向骨表面的肺泡骨层由几丁质-聚(乳酸-乙醇酸)水凝胶支架制成,其中含有纳米生物活性玻璃陶瓷和富血小板血浆;试图再生牙周韧带纤维的中间层由相同的几丁质-聚(乳酸-乙醇酸)水凝胶支架制成,其中含有成纤维细胞生长因子。将3层组装在一起形成生物相容性复合支架,诱导人牙囊细胞分化为成骨细胞、成牙骨质细胞和成纤维细胞,将该支架注入兔牙周缺损模型,发现具有促进缺损的骨水泥、牙周膜以及牙槽骨再生的效能[83]。此外,还有关于牙囊细胞诱导的神经分化,研究发现添加了一定量的鼠尾草水提取物以及氯白链球菌提取物的纳米透明质酸支架对牙囊干细胞的神经分化有一定的诱导作用[84]。
因此,高分子材料向研究者们展示了其在牙周组织再生中的灵活性和可塑性,可以根据缺损部位的不同,从而制造具有针对性的支架材料,实现高效的组织再生。
2.3.3 天然/合成可降解无机(复合)材料 羟基磷灰石在骨组织工程中具有优异效果,作为最常用的磷酸钙骨移植材料,不仅可以用作临床支持牙槽骨,纳米羟基磷灰石还可以改善骨再生特性,与其他不同支架结合使用也可取得一定成效[85]。有研究表明,接种了人牙囊细胞 6周的羟基磷灰石支架,细胞的3D组织和细胞簇周围存在致密物质,即表明羟基磷灰石支架能有效促进人牙囊细胞的骨向分化[86]。
在体内,将播种在羟基磷灰石/β-磷酸三钙支架上的Dickkopf相关蛋白3与短发夹RNA复合牙囊细胞移植到重症联合免疫缺陷小鼠的皮下组织,然后进行苏木精-伊红和马森染色,与对照细胞相比,慢病毒介导的Dickkopf相关蛋白3和短发夹RNA在牙囊细胞中的表达促进了钙化结节的形成、碱性磷酸酶活性以及β-连环蛋白、Runt相关转录因子2和骨钙素的表达;在体内,植入部分呈现出大部分新形成的类骨基质和胶原蛋白,结果证实,在大鼠牙囊细胞矿物质诱导过程中,Dickkopf相关蛋白3的表达被下调,而下调Dickkopf相关蛋白3可促进人牙囊细胞的成骨[87]。
此外,NIE等[88]生产了一种新型支架,其中包含可生物降解的珊瑚羟基磷灰石,该支架接种了表达骨形态发生蛋白9转染鼠牙囊细胞的重组腺病毒(Ad-骨形态发生蛋白9转染的鼠牙囊细胞),通过对照实验发现该支架植入物可促进牙槽骨缺损后的牙槽骨再生,而骨形态发生蛋白9对鼠牙囊细胞成骨分化的诱导作用涉及Smad1/5/8信号通路的激活。
无机材料良好的生物相容性使得其在牙周组织再生工程中得以广泛使用,通过调整纳米级无机材料的含量或许可改善支架的性能,从而制备生物相容性更好的支架。
2.3.4 其他各种人工合成(复合)材料 如今的牙周组织再生工程常采用多种支架材料复合的方法,以追求良好的生物相容性与机械性。骨桥蛋白作为一种细胞因子,可以促进成骨过程中的磷酸钙成核,甚至可以调节羟基磷灰石晶体的形态[89]。COSTA等[90]从患者牙囊组织中分离出组织碎片,用一定方法制成干细胞培养物并对此进行研究,结果证明带有骨桥蛋白纤维蛋白仿生水凝胶的3D复合支架胶原蛋白/纳米羟基磷灰石可促进体内外牙囊细胞的增殖,并促进其成骨基因的表达。
除了常见的复合材料,还出现了一类新型支架材料。如纳米纤维微球,它正在成为突出的下一代仿生注射支架系统,其作为聚合物支架显示出宿主体的可接受性更高,免疫反应较小。SARVIYA等[91]系统研究以了解单独使用仿生纳米纤维微球和不同浓度锂皂石的物理化学特性对人牙囊细胞及其细胞附着、增殖和成骨分化的影响,结果发现,锂皂石纳米硅酸盐与仿生纳米纤维可注射支架系统的作用有助于在正常生理条件下增强干细胞分化。
石墨烯基纳米材料常被用于石墨烯基聚合物纳米复合材料,作为组织工程中的支架材料填充,考虑到其研究内容是对牙囊细胞细胞毒性、氧化应激诱导以及细胞和线粒膜改变等的影响[92],故也纳入讨论当中,望其能为更适合的支架材料提供理论实验基础。实际上,在牙科领域中,石墨烯基纳米材料正逐渐成为组织工程的替代品[93]。
目前常用的牙周组织再生工程支架材料见表3。表4总结了各材料对牙囊细胞生物学特性的影响,便于直观反映不同支架材料对牙囊细胞的作用效果,主要涉及其增殖以及成骨分化的影响。
此外,有系统性的关于复合支架搭载间充质干细胞外泌体的研究[94],外泌体注入支架中可在一定程度上解决其体内半衰期短、无法实现局部缓释的局限性,从而用于组织修复和再生,并取得了一定的治疗效果。但目前其在牙周组织修复的运用集中在牙周韧带干细胞中,尚未有牙囊细胞外泌体结合支架材料的研究,故该方法在未来也许能通过实验验证其应用价值。

| [1] VARGHESE J, RAJAGOPAL A, SHANMUGASUNDARAM S. Role of biomaterials used for periodontal tissue regeneration-a concise evidence-based review. Polymers (Basel). 2022;14(15):3038. [2] 陈发明,高丽娜,陈芳.牙周再生治疗现状和进展[J].口腔疾病防治,2019,27(1):9-16. [3] EL-KADIRY AE, RAFEI M, SHAMMAA R. Cell therapy: types, regulation, and clinical benefits. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8: 756029. [4] 王畅,张茜,刘悦,等.牙周组织再生材料应用研究进展[J].化学与生物工程,2022,39(6):18-21. [5] THALAKIRIYAWA DS, DISSANAYAKA WL. Advances in regenerative dentistry approaches: an update. Int Dent J. 2024;74(1):25-34. [6] 郑晓雪.淫羊藿苷诱导的牙囊干细胞条件培养基对MC3T3-E1增殖、迁移及成骨分化的影响[D].长春:吉林大学,2022. [7] YANG C, DU XY, LUO W. Clinical application prospects and transformation value of dental follicle stem cells in oral and neurological diseases. World J Stem Cells. 2023;15(4):136-149. [8] GUO S, GUO W, DING Y, et al. Comparative study of human dental follicle cell sheets and periodontal ligament cell sheets for periodontal tissue regeneration. Cell Transplant. 2013;22(6):1061-1073. [9] 蒙盛子,刘蓉,罗雅馨,等.牙囊干细胞应用于牙及牙周组织再生修复的前景及临床转化价值[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(19): 3095-3099. [10] SANCILIO S, MARSICH E, SCHWEIKL H, et al. Redox control of il-6-mediated dental pulp stem-cell differentiation on alginate/hydroxyapatite biocomposites for bone ingrowth. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2019;9(12):1656. [11] TERRANOVA L, LOUVRIER A, HÉBRAUD A, et al. Highly structured 3D electrospun conical scaffold: a tool for dental pulp regeneration. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2021;7(12):5775-5787. [12] RENAUD M, BOUSQUET P, MACIAS G, et al. Allogenic stem cells carried by porous silicon scaffolds for active bone regeneration in vivo. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023;10(7):852. [13] ZAWADZKA-KNEFEL A, RUSAK A, MROZOWSKA M, et al. Chitin scaffolds derived from the marine demosponge Aplysina fistularis stimulate the differentiation of dental pulp stem cells. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1254506. [14] YU BH, ZHOU Q, WANG ZL. Periodontal ligament versus bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in combination with Bio-Oss scaffolds for ectopic and in situ bone formation: a comparative study in the rat. J Biomater Appl. 2014;29(2):243-253. [15] LIANG C, WANG G, LIANG C, et al. Hierarchically patterned triple-layered gelatin-based electrospun membrane functionalized by cell-specific extracellular matrix for periodontal regeneration. Dent Mater. 2024;40(1):90-101. [16] WANG W, WANG A, HU G, et al. Potential of an aligned porous hydrogel scaffold combined with periodontal ligament stem cells or gingival mesenchymal stem cells to promote tissue regeneration in rat periodontal defects. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2023;9(4):1961-1975. [17] YANG M, GUO Z, LI T, et al. Synergetic effect of chemical and topological signals of gingival regeneration scaffold on the behavior of human gingival fibroblasts. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2019;107(9): 1875-1885. [18] SAKULPAPTONG W, CLAIRMONTE IA, BLACKSTONE BN, et al. 3D engineered human gingiva fabricated with electrospun collagen scaffolds provides a platform for in vitro analysis of gingival seal to abutment materials. PLoS One. 2022;17(2):e0263083. [19] KARABULUT H, ULAG S, DALBAYRAK B, et al. A novel approach for the fabrication of 3d-printed dental membrane scaffolds including antimicrobial pomegranate extract. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15(3):737. [20] MORSCZECK C. Mechanisms during osteogenic differentiation in human dental follicle cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(11):5945. [21] MORSCZECK C. Molecular mechanisms in dental follicle precursor cells during the osteogenic differentiation. Histol. 2015;30(10):1161-1169. [22] SHOI K, AOKI K, OHYA K, et al. Characterization of pulp and follicle stem cells from impacted supernumerary maxillary incisors. Pediatr Dent. 2014;36(3):79-84. [23] 王贺,吴补领,段小红.小鼠牙囊细胞体外培养方法与形态特征探讨[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2015,25(6):370-374. [24] 董正谋,刘锐,刘鲁川,等.种子细胞在牙周组织再生治疗中的研究进展[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2019,46(1):48-54. [25] MOSADDAD SA, RASOOLZADE B, NAMANLOO RA, et al. Stem cells and common biomaterials in dentistry: a review study. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2022;33(7):55. [26] BI R, LYU P, SONG Y, et al. Function of dental follicle progenitor/stem cells and their potential in regenerative medicine: from mechanisms to applications. Biomolecules. 2021;11(7):997. [27] SOWMYA S, CHENNAZHI KP, ARZATE H, et al. Periodontal specific differentiation of dental follicle stem cells into osteoblast, fibroblast, and cementoblast. Tissue Eng. 2015;21:1044-1058. [28] 陶昱,喻金凤,陈军,等.人牙髓细胞条件培养液对人牙囊细胞成骨分化作用的体外研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2017,33(3):339-343. [29] KARAMZADEH R, BAGHABAN ESLAMINEJAD M, SHARIFI-ZARCHI A. Comparative in vitro evaluation of human dental pulp and follicle stem cell commitment. Cell J. 2016;18(4):609-618. [30] 张琳琳,安莹,陈发明,等.牙源性干细胞的研究进展[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2015,31(3):425-431. [31] PATIL R, KUMAR BM, LEE WJ, et al, Multilineage potential and proteomic profiling of human dental stem cells derived from a single donor, Exp Cell Res. 2014;320(1):92-107. [32] SUNG IY, SON HN, ULLAH I, et al. Cardiomyogenic differentiation of human dental follicle-derived stem cells by suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid and their in vivo homing property. Int J Med Sci. 2016;13(11):841-852. [33] YANG C, SUN L, LI X, et al. The potential of dental stem cells differentiating into neurogenic cell lineage after cultivation in different modes in vitro. Cell Reprogram. 2014;16(5):379-391. [34] SANTILLI F, FABRIZI J, SANTACROCE C, et al. Analogies and differences between dental stem cells: focus on secretome in combination with scaffolds in neurological disorders. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2024;20(1):159-174. [35] CAI R, WANG L, ZHANG W, et al. The role of extracellular vesicles in periodontitis: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and therapy. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1151322. [36] LEVY O, KUAI R, SIREN EMJ, et al. Shattering barriers toward clinically meaningful MSC therapies. Sci Adv. 2020;6(30):eaba6884. [37] RIAZIFAR M, PONE EJ, LÖTVALL J, et al. Stem cell extracellular vesicles: extended messages of regeneration. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2017;57:125-154. [38] MULCAHY LA, PINK RC, CARTER DR. Routes and mechanisms of extracellular vesicle uptake. J Extracell Vesicles. 2014. DOI: 10.3402/jev.v3.24641. [39] 朱梦远.LIPUS诱导的hDFSCs外泌体对hDFSCs增殖分化的作用机制研究[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2020. [40] SHI W, GUO S, LIU L, et al. Small extracellular vesicles from lipopolysaccharide-preconditioned dental follicle cells promote periodontal regeneration in an inflammatory microenvironment. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(10):5797-5810. [41] HUANG Y, LIU Q, LIU L, et al. Lipopolysaccharide-preconditioned dental follicle stem cells derived small extracellular vesicles treating periodontitis via reactive oxygen species/mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling-mediated antioxidant effect. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022;17:799-819. [42] 黄少阳.牙囊干细胞来源的外泌体在骨缺损修复中的实验研究[D].昆明:昆明医科大学,2023. [43] 马丽娅.牙囊干细胞源外泌体调控牙周膜干细胞促进牙周组织再生的相关研究[D]. 昆明:昆明医科大学,2021. [44] MA L, RAO N, JIANG H, et al. Small extracellular vesicles from dental follicle stem cells provide biochemical cues for periodontal tissue regeneration. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):92. [45] 田俊,李梦婕,韦曦.大鼠牙囊干细胞来源外泌体免疫调节牙髓炎的体内研究[C]//中华口腔医学会牙体牙髓病学专业委员会.中华口腔医学会牙体牙髓病学专业委员会第十四次全国牙体牙髓病学学术大会论文汇编.中山大学附属口腔医院广东省口腔医学重点实验室;2022:3. doi:10.26914/c.cnkihy.2022.064354. [46] 田俊,李梦婕,于抗抗,等.大鼠牙囊干细胞来源外泌体诱导巨噬细胞向M2型极化的体外研究[C]//中国化学会化学生物学专业委员会.第十一届全国化学生物学学术会议论文摘要(第二卷).中山大学光华口腔医学院·附属口腔医院广东省口腔医学重点实验室;四川大学生命科学学院;绿色化学与技术教育部重点实验室四川大学化学学院;2019:1. doi:10.26914/c.cnkihy.2019.087965. [47] MAI Z, CHEN H, YE Y, et al. Translational and clinical applications of dental stem cell-derived exosomes. Front Genet. 2021;12:750990. [48] LANE SW, WILLIAMS DA, WATT FM. Modulating the stem cell niche for tissue regeneration. Nat Biotechnol. 2014;32(8):795-803. [49] MORSCZECK C, DE PELLEGRIN M, RECK A, et al. Evaluation of current studies to elucidate processes in dental follicle cells driving osteogenic differentiation. Biomedicines. 2023;11(10):2787. [50] VIALE-BOURONCLE S, KLINGELHÖFFER C, ETTL T, et al. A protein kinase A (PKA)/β-catenin pathway sustains the BMP2/DLX3-induced osteogenic differentiation in dental follicle cells (DFCs). Cell Signal. 2015;27(3):598-605. [51] SAKISAKA Y, TSUCHIYA M, NAKAMURA T, et al. Wnt5a attenuates Wnt3a-induced alkaline phosphatase expression in dental follicle cells. Exp Cell Res. 2015;336(1):85-93. [52] PIELES O, REICHERT TE, MORSCZECK C. Classical isoforms of protein kinase C (PKC) and Akt regulate the osteogenic differentiation of human dental follicle cells via both β-catenin and NF-κB. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):242. [53] 陈学鹏,施洁珺,叶青松,等.p38 MAPK信号通路在BMP-2诱导人牙囊细胞成骨分化中的作用[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2013, 35(6):816-823. [54] YANG JW, ZHU LX, YUAN GH, et al. Autophagy appears during the development of the mouse lower first molar. Histochem Cell Biol. 2013;139(1):109-118. [55] MORSCZECK C. Mechanisms during osteogenic differentiation in human dental follicle cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(11):5945. [56] BOUSNAKI M, BEKETOVA A, KONTONASAKI E. A review of in vivo and clinical studies applying scaffolds and cell sheet technology for periodontal ligament regeneration. Biomolecules. 2022;12(3):435. [57] HUANG Y, LIU Q, LIU L, et al. Lipopolysaccharide-preconditioned dental follicle stem cells derived small extracellular vesicles treating periodontitis via reactive oxygen species/mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling-mediated antioxidant effect. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022;17:799-819. [58] 姜震,颜燕宏,韩雪,等.大肠杆菌脂多糖对大鼠牙囊干细胞生物学行为的影响[J].口腔医学研究,2023,39(6):534-540. [59] WEI X, LIU Q, LIU L, et al. Periostin plays a key role in maintaining the osteogenic abilities of dental follicle stem cells in the inflammatory microenvironment. Arch Oral Biol. 2023;153:105737. [60] WEI X, GUO S, LIU Q, et al. Dental follicle stem cells promote periodontal regeneration through periostin-mediated macrophage infiltration and reprogramming in an inflammatory microenvironment. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(7):6353. [61] 梁熙,陈国庆,田卫东.低氧对人DFCs生物学特性的影响[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2017,35(3):245-252. [62] 赵娴,曾锦,左东川,等.钙离子对人牙囊细胞增殖、迁移和成骨分化的影响[J].上海口腔医学,2019,28(6):572-577. [63] 杨晶晶,左东川,谢沂航等.T型钙通道对人牙囊细胞成骨分化的影响[J].口腔医学研究,2021,37(10):900-905. [64] SHANG LL, SHAO JL, GE SH. Immunomodulatory functions of oral mesenchymal stem cells: novel force for tissue regeneration and disease therapy. J Leukoc Biol. 2021;110(3):539-552. [65] 冉玲,李晓倩,蒋欣益,等.超声微泡介导pEGFP-N1转染大鼠牙囊细胞:细胞生物学性质相对稳定[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 18(50):8151-8155. [66] BELMANS N, GILLES L, WELKENHUYSEN J, et al. In vitro assessment of the dna damage response in dental mesenchymal stromal cells following low dose X-ray exposure. Front Public Health. 2021;9: 584484. [67] MORSCZECK C, PIELES O, RECK A, et al. DNA protein kinase promotes cellular senescence in dental follicle cells. Arch Oral Biol. 2023. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2023.105676 [68] 郑晓雪,王乙行,陶天翼,等.淫羊藿苷对人牙囊干细胞旁分泌作用的影响[J].医学研究杂志,2022,51(9):65-70,141. [69] PIELES O, RECK A, REICHERT TE, et al. p53 inhibits the osteogenic differentiation but does not induce senescence in human dental follicle cells. Differentiation. 2020;114:20-26. [70] DASI D, NALLABELLI N, DEVALARAJU R, et al. Curcumin attenuates replicative senescence in human dental follicle cells and restores their osteogenic differentiation. J Oral Biosci. 2023;65(4):371-378. [71] 刘路,彭正军,韦曦等.牙乳头/牙囊细胞交互作用对细胞多能性的作用[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2015,25(2):63-67. [72] 王畅,张茜,刘悦,等.牙周组织再生材料应用研究进展[J].化学与生物工程,2022,39(6):18-21. [73] WANG X, CHEN J, TIAN W. Strategies of cell and cell-free therapies for periodontal regeneration: the state of the art. Stem Cell Res. 2022; 13(1):536. [74] FIGUEIREDO TM, DO AMARAL GCLS, BEZERRA GN, et al. Three-dimensional-printed scaffolds for periodontal regeneration: a systematic review. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2023;27(5):451-460. [75] SHOPOVA D, MIHAYLOVA A, YANEVA A, et al. Advancing dentistry through bioprinting: personalization of oral tissues. J Funct Biomater. 2023;14(10):530. [76] SUI BD, ZHENG CX, ZHAO WM, et al. Mesenchymal condensation in tooth development and regeneration: a focus on translational aspects of organogenesis. Physiological. 2023;103(3):1899-1964. [77] SONG Y, LONG J, DUNKERS JP, et al. Micromechanical compatibility between cells and scaffolds directs the phenotypic transition of stem cells. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(48):58152-58161. [78] FU T, LIANG P, SONG J, et al. Matrigel scaffolding enhances BMP9-induced bone formation in dental follicle stem/precursor cells. Int J Med Sci. 2019;16(4):567-575. [79] 刘红,杨超,陈国庆,等.纤维蛋白胶不同复合方式对牙囊细胞增殖活性的影响[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2015,33(2):135-140. [80] ASKARI M, NANIZ MA, KOUHI M, et al. Recent progress in extrusion 3D bioprinting of hydrogel biomaterials for tissue regeneration: a comprehensive review with focus on advanced fabrication techniques. Biomater Sci. 2021;9(3):535-573. [81] VARGHESE J, RAJAGOPAL A, SHANMUGASUNDARAM S. Role of biomaterials used for periodontal tissue regeneration-a concise evidence-based review. Polymers (Basel). 2022;14(15):3038. [82] ABEDI N, RAJABI N, KHARAZIHA M, et al. Layered scaffolds in periodontal regeneration. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2022;12(6):782-797. [83] SOWMYA S, MONY U, JAYACHANDRAN P, et al. Tri-layered nanocomposite hydrogel scaffold for the concurrent regeneration of cementum, periodontal ligament, and alveolar bone. Adv Healthc Mater. 2017;6:1601251. [84] BAHRAMI N, MANAFI Z, MOHAMMADI F, et al. Neural differentiation of wisdom tooth follicle stem cells on a nano-hydrogel scaffold containing salvia chloroleucat to treat nerve injury in the cancer of nervous system. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023;24(2):649-658. [85] RODRIGUES SC, SALGADO CL, SAHU A, et al. Preparation and characterization of collagen-nanohydroxyapatite biocomposite scaffolds by cryogelation method for bone tissue engineering applications. J Biomed Mater Res. 2013;101A:1080-1094. [86] ERCAL P, PEKOZER GG. A current overview of scaffold-based bone regeneration strategies with dental stem cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020; 1288:61-85. [87] ZHANG X, DU Y, LING J, et al. Dickkopf-related protein 3 negatively regulates the osteogenic differentiation of rat dental follicle cells. Mol Med Rep. 2017;15(4):1673-1681. [88] NIE L, YANG X, DUAN L, et al. The healing of alveolar bone defects with novel bio-implants composed of Ad-BMP9-transfected rDFCs and CHA scaffolds. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):6373. [89] MATLAHOV I, KULPANOVICH A, ILINE-VUL T, et al. Selective excitation with recoupling pulse schemes uncover properties of disordered mineral phases in bone-like apatite grown with bone proteins. Solid State Nucl Magn Reson. 2023;124:101860. [90] COSTA AC, ALVES PM, MONTEIRO FJ, et al. Interactions between dental MSCs and biomimetic composite scaffold during bone remodeling followed by in vivo real-time bioimaging. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(3):1827. [91] SARVIYA N, BASU SM, INDUVAHI V, et al. Laponite-gelatin nanofibrous microsphere promoting human dental follicle stem cells attachment and osteogenic differentiation for noninvasive stem cell transplantation. Macromol Biosci. 2023;23(1):e2200347. [92] OLTEANU D, FILIP A, SOCACI C, et al. Cytotoxicity assessment of graphene-based nanomaterials on human dental follicle stem cells. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2015;136:791-798. [93] NIKNAM Z, HOSSEINZADEH F, SHAMS F, et al. Recent advances and challenges in graphene-based nanocomposite scaffolds for tissue engineering application. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2022;110(10):1695-1721. [94] WANG T, ZHOU Y, ZHANG W, et al. Exosomes and exosome composite scaffolds in periodontal tissue engineering. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024;11:1287714. [95] ZIBANDEH N, GENC D, DURAN Y, et al. Human dental follicle mesenchymal stem cells alleviate T cell response in inflamed tissue of Crohn’s patients. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2020;31(5):400-409. |
| [1] | 王奇飒, 卢雨征, 韩秀峰, 赵文玲, 石海涛, 徐 哲. 3D打印甲基丙烯酰化透明质酸/脱细胞皮肤水凝胶支架的细胞相容性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 1912-1920. |
| [2] | 王菘芃, 刘玉三, 于焕英, 高晓丽, 徐英江, 张晓明, 刘 敏. 沸石基咪唑盐框架8纳米材料的活性氧双向调控:从肿瘤治疗、抗菌到细胞保护[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 2033-2013. |
| [3] | 陈豪杰, 王 黛, 沈 山. 种植体周围炎中的免疫炎症微环境机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 2054-2062. |
| [4] | 刘 洋, 刘东辉, 徐 磊, 展 旭, 孙昊博, 康 凯. 刺激响应型可注射水凝胶在心肌梗死精准化治疗中的作用与趋势[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 2072-2080. |
| [5] | 赖 渝, 陈跃平, 章晓云. 生物活性材料治疗骨感染的研究热点与前沿趋势[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 2132-2144. |
| [6] | 彭志伟, 陈 雷, 佟 磊. 木犀草素促进糖尿病小鼠创面愈合的作用与机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1398-1406. |
| [7] | 朱奎成, 杜春燕, 章金涛. 无毛基因突变促进无毛小鼠白色脂肪组织褐变的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1424-1430. |
| [8] | 李 豪, 陶红成, 曾 平, 刘金富, 丁 强, 牛驰程, 黄 凯, 康宏誉. 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路调控骨关节炎的发生发展:指导中药靶点治疗[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1476-1485. |
| [9] | 陈 驹, 郑锦畅, 梁 振, 黄成硕, 林 颢, 曾 莉. β-石竹烯对小鼠膝骨关节炎的作用及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1341-1347. |
| [10] | 吕国庆, 艾孜麦提江·肉孜, 熊道海. 鸢尾素抑制人关节软骨细胞中铁死亡的作用及其机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1359-1367. |
| [11] | 刘新月, 李春年, 李一卓, 徐世芳. 口腔牙槽骨缺损的再生修复[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1247-1259. |
| [12] | 王明琦, 冯诗雅, 韩银河, 于朋鑫, 郭丽娜, 贾子萱, 王秀丽. 神经化肠黏膜组织工程模型的构建及体外评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(4): 892-900. |
| [13] | 余诗宇, 俞苏桐, 徐 杨, 镇祥燕, 韩凤选. 组织工程治疗策略在口腔黏膜下纤维化中的研究与应用进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(4): 936-948. |
| [14] | 陈伊娴, 陈 晨, 卢立恒, 汤锦鹏, 于晓巍. 雷公藤甲素治疗骨关节炎的网络药理学分析与实验验证[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(4): 805-815. |
| [15] | 许嘉木, 杨 城, 李玮民, 王春庆. 细胞焦亡与炎症因子在骨质疏松症发生中的作用与机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(3): 691-700. |
牙周组织再生修复涉及一种基于干细胞的细胞疗法[3],种子细胞、支架材料和生长因子是其3个基本要素[4],这种方法除了可以通过外源性培养的自体或同种异体干细胞施用到受影响的组织中以介导组织再生之外,亦可以通过吸引干细胞向缺损组织迁移,从而加强其修复作用[5]。
作为牙囊来源的牙周组织再生工程中的种子细胞,牙囊细胞因具有取材方便、易于培养等多种优点,以及其良好的生物学特性[6-7],相较于牙周膜干细胞,牙囊细胞能在牙周组织缺损中表现出更强的牙骨质再生和牙周组织附着能力[8],目前正积极应用于牙周组织及牙槽骨缺损再生修复方面的研究[9]。
支架材料与生物因素结合应用于牙周炎症控制和牙周组织再生是目前乃至未来用以弥补牙周组织再生修复缺陷的手段。目前,支架材料在有关各种牙源性干细胞上如牙髓干细胞、牙周膜干细胞及牙龈成纤维细胞等的研究已较为详尽[10-19],见表1;而关于牙囊细胞还少有论述。对此,文章就牙囊细胞的生物学特性作出阐述,总结了不同种类的支架材料结合生物因素对于牙囊细胞生物学特性产生的影响及其未来可能的研究及临床转化方向。
 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者在2024年9月进行文献检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 检索2013年1月至2023年12月发表的相关文献。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed、Sciencedirect和中国知网数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 以“dental follicle cell,scaffolds,material,periodontal tissue regeneration,tissue engineering,review”为英文检索词,以“牙囊细胞,支架,材料,牙周组织再生,组织工程,综述”为中文检索词。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著,综述和学位论文。
1.1.6 手工检索情况 无手工检索情况。
1.1.7 检索策略 以PubMed数据库检索为例,具体文献检索策略见图1。
1.2 入组标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 同一领域中观点鲜明可靠、依据充分的文献;与文章相关性大的文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 研究内容不公开的文献;与文章相关性不大的文献。
1.3 资料提取与文献质量评价 检索中英文文献,根据纳入标准进行筛选,通过阅读文献摘要及全文,排除内容不公开及相关性不大文献,最终纳入95篇文献进行综述。文献检索筛选流程图见图2。
 目前牙囊细胞及各类支架材料在牙周组织再生工程中的应用存在的问题:第一,牙周炎造成的牙周组织缺损的修复一直是牙科领域需要攻克的难题,牙周治疗成功的一个重要原则是再生牙周缺损中的所有3种类型的组织(牙骨质、牙周膜和牙槽骨)均得到一定程度的修复,而牙囊细胞不仅能够生成牙骨质、牙周膜及牙槽骨,还能在受损组织中促进再生,这一特性使其在牙周炎造成牙周组织缺损等临床问题的修复中具有重要应用价值;牙囊细胞在生物材料结合应用中,能够增强组织愈合、促进新骨生成,极大地提高牙周组织再生的效果,与生物材料结合使用也可在一定程度上解决移植后牙囊细胞可能面临存活率低的问题。第二,牙囊细胞的来源主要是自体细胞,因此其免疫原性较低。然而,在异体细胞应用中,仍需考虑免疫排斥反应的风险,有研究表明牙囊细胞可通过调控T细胞来调节克罗恩病(一种慢性炎症反应)患者发炎组织中的免疫反应[95],或许可以成为牙囊细胞异体移植的应用依据。第三,牙囊细胞的应用往往需要经历分离、培养及纯化等步骤,在这个过程中,可能存在基因组不稳定性和转化为肿瘤细胞的风险,因此,需要定期检测细胞的基因组完整性,确保未出现突变或异常扩增。最后,由于牙囊细胞在组织修复的应用大多还停留在动物以及体外实验中,牙囊细胞在体内的长期安全性尚未得到充分验证,故其用于人类牙周组织修复工程的安全性和有效性的评估需通过后续的临床试验来验证,临床应用前开展长期随访研究,以监测潜在的不良反应也十分必要。
目前牙囊细胞及各类支架材料在牙周组织再生工程中的应用存在的问题:第一,牙周炎造成的牙周组织缺损的修复一直是牙科领域需要攻克的难题,牙周治疗成功的一个重要原则是再生牙周缺损中的所有3种类型的组织(牙骨质、牙周膜和牙槽骨)均得到一定程度的修复,而牙囊细胞不仅能够生成牙骨质、牙周膜及牙槽骨,还能在受损组织中促进再生,这一特性使其在牙周炎造成牙周组织缺损等临床问题的修复中具有重要应用价值;牙囊细胞在生物材料结合应用中,能够增强组织愈合、促进新骨生成,极大地提高牙周组织再生的效果,与生物材料结合使用也可在一定程度上解决移植后牙囊细胞可能面临存活率低的问题。第二,牙囊细胞的来源主要是自体细胞,因此其免疫原性较低。然而,在异体细胞应用中,仍需考虑免疫排斥反应的风险,有研究表明牙囊细胞可通过调控T细胞来调节克罗恩病(一种慢性炎症反应)患者发炎组织中的免疫反应[95],或许可以成为牙囊细胞异体移植的应用依据。第三,牙囊细胞的应用往往需要经历分离、培养及纯化等步骤,在这个过程中,可能存在基因组不稳定性和转化为肿瘤细胞的风险,因此,需要定期检测细胞的基因组完整性,确保未出现突变或异常扩增。最后,由于牙囊细胞在组织修复的应用大多还停留在动物以及体外实验中,牙囊细胞在体内的长期安全性尚未得到充分验证,故其用于人类牙周组织修复工程的安全性和有效性的评估需通过后续的临床试验来验证,临床应用前开展长期随访研究,以监测潜在的不良反应也十分必要。3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 现有文章对牙周膜干细胞、牙髓干细胞等常见牙科干细胞结合支架材料的叙述已较为详尽,但尚未对牙囊细胞结合支架材料的研究进行归纳整理。文章除了介绍牙囊细胞的生物学特性及其受生物因素的影响外,还着重介绍了牙囊细胞在牙周组织工程中的研究进展。
3.3 综述的局限性 由于文献检索过程中检索时间范围的设置,可能导致最新研究进展遗漏而没有被纳入综述当中,因此可能无法及时反映最新的研究成果及进展。由于检索水平有限或其他原因可能导致部分重要文献缺漏,因此结论仅供研究学者参考借鉴。
3.4 综述的重要意义 随着牙囊细胞优良特性的不断发掘,除了作为种子细胞来源不断地应用于牙周组织再生研究中,还有望运用于其他类型的组织修复中。文章综述了牙囊细胞的相关生物学特性受生物因素的影响,并归纳总结目前生物因素、支架材料及牙囊细胞三者结合的研究进展,发现牙囊细胞的增殖发育以及成骨分化受生物因素影响的机制较为复杂,并且各支架材料培育牙囊细胞的研究数量较少。故继续对其机制进行更加深远的研究,如内外源因素间的相互作用,实际上,内源性因素强调不经外界影响,特指牙囊细胞自身的生物代谢等,而外源性因素则强调牙囊细胞与邻近细胞之间的直接相互作用、分泌因子及细胞外基质等微环境,而牙囊细胞的增殖成骨分化是内外源因素相互作用的结果,除此之外,了解支架材料的制作方法和所含生物因子等的不同对牙囊细胞的影响,有助于研究者们培育出更加优良的牙囊细胞,从而用于牙周组织再生修复。
3.5 课题组的专家意见和建议 课题组专家建议未来需要建立牙囊细胞库及前期应用基础、向临床转化应用方向提供牙囊细胞转化应用细节,包括细胞获取,存储,运输,及使用参数方式等。牙周病是人类最常见的口腔疾病之一,其高发病率和难以根治的特性给患者带来了极大的痛苦。传统的手术和药物治疗方法往往难以彻底解决牙周病导致的牙齿松动和脱落问题,随着干细胞技术的不断发展,基于牙囊细胞的牙周组织再生修复技术逐渐成为研究热点。建立牙囊细胞库并推动其向临床转化应用,是解决牙周病治疗难题、推动干细胞技术发展的重要举措。通过明确牙囊细胞的获取、存储、运输及使用参数等关键环节,可以确保干细胞资源的有效利用和临床转化的顺利进行。未来,随着技术的不断进步和临床经验的积累,牙囊细胞将在更多领域展现出其独特的价值。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
 #br#
#br#
文题释义:
生物因素:分为内源及外源因素,前者是指来自生物体内部的因素,通常与生物体的内部结构、功能或代谢状态相关联;后者则指来自生物体外部环境的因素,通常与生物体与外界环境的相互作用和适应有关。组织再生工程:其要素包括种子细胞、生物材料、细胞与生物材料的整合以及植入物与体内微环境的整合,是无创伤修复的一种重要手段,正积极应用于牙周组织修复研究。
文章系统性地针对牙囊细胞优良的生物学特性进行综述,重点介绍其显著的增殖特性、多向分化能力以及分泌功能的潜在应用。从内源性与外源性两个方面阐述生物因素对牙囊细胞的生物学活性影响,详细介绍了信号通路在牙囊细胞中的影响和互作,并提及减少牙囊细胞免疫原性的方法以及医疗检查中可能存在的DNA损伤反应,为之后的临床研究提供指导方法。除了对传统可降解支架材料进行总结,还重点描述有关3D打印技术、纳米颗粒材料等在各新型复合支架材料上的应用,以期制造更适合牙囊细胞的支架。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
