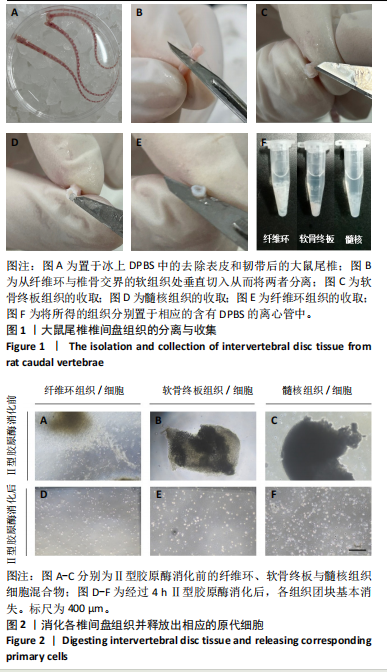
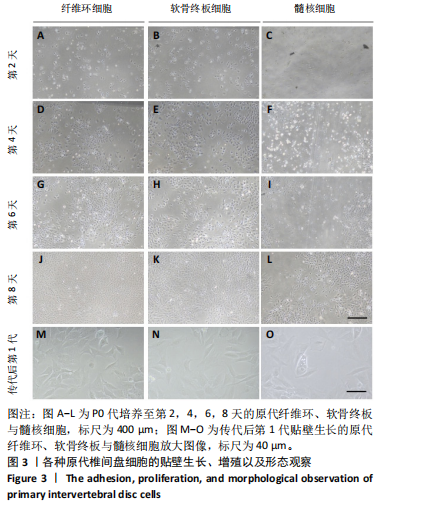
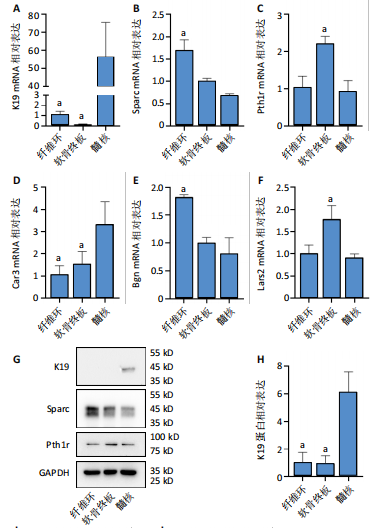
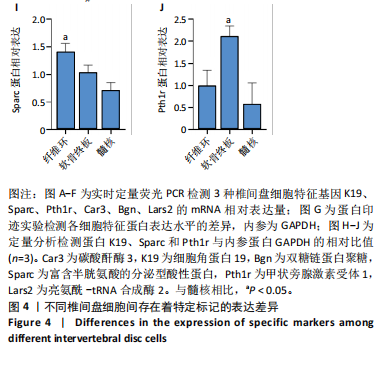
[1] JIN Z, WANG D, ZHANG H, et al. Incidence trend of five common musculoskeletal disorders from 1990 to 2017 at the global, regional and national level: results from the global burden of disease study 2017. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(8):1014-1022.
[2] CHEN S, WU X, LAI Y, et al. Kindlin-2 inhibits Nlrp3 inflammasome activation in nucleus pulposus to maintain homeostasis of the intervertebral disc. Bone Res. 2022;10(1):5.
[3] GENEDY H H, HUMBERT P, LAOULAOU B, et al. MicroRNA-targeting nanomedicines for the treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2024;207:115214.
[4] CHEN F, LEI L, CHEN S, et al. Serglycin secreted by late-stage nucleus pulposus cells is a biomarker of intervertebral disc degeneration. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):47.
[5] ZHANG L, HU S, XIU C, et al. Intervertebral disc-intrinsic Hedgehog signaling maintains disc cell phenotypes and prevents disc degeneration through both cell autonomous and non-autonomous mechanisms. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024;81(1):74.
[6] FRANCISCO V, PINO J, GONZÁLEZ-GAY M, et al. A new immunometabolic perspective of intervertebral disc degeneration. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022; 18(1):47-60.
[7] FRANCISCO V, AIT ELDJOUDI D, GONZáLEZ-RODRíGUEZ M, et al. Metabolomic signature and molecular profile of normal and degenerated human intervertebral disc cells. Spine J. 2023;23(10):1549-1562.
[8] BINCH ALA, FITZGERALD JC, GROWNEY EA, et al. Cell-based strategies for IVD repair: clinical progress and translational obstacles. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021;17(3):158-175.
[9] VAN DEN AKKER GGH, CREMERS A, SURTEL DAM, et al. Isolation of Nucleus Pulposus and Annulus Fibrosus Cells from the Intervertebral Disc. Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2221:41-52.
[10] CHEN Y, ZHANG L, SHI X, et al. Characterization of the Nucleus Pulposus Progenitor Cells via Spatial Transcriptomics. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024;e2303752.
[11] CHERIF H, MANNARINO M, PACIS AS, et al. Single-Cell RNA-Seq Analysis of Cells from Degenerating and Non-Degenerating Intervertebral Discs from the Same Individual Reveals New Biomarkers for Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(7):3993.
[12] REGAN SL, WILLIAMS MT, VORHEES CV. Review of rodent models of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022;132: 621-637.
[13] MANNING WK, BONNER WM JR. Isolation and culture of chondrocytes from human adult articular cartilage. Arthritis Rheum. 1967;10(3):235-239.
[14] 王效, 徐宏光, 肖良, 等. 大鼠腰椎终板软骨干细胞的分离及分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2018,22(13):2093-2097.
[15] 金中行, 徐宏光, 张玙, 等. 大鼠纤维环干细胞的分离与鉴定[J]. 皖南医学院学报,2018,37(4):307-309.
[16] 马东, 陈祁青, 赵继荣, 等. 贴壁法联合纤维连接蛋白差别黏附法分离纯化鉴定大鼠纤维环源干细胞[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2024,28(31): 4980-4986.
[17] HE R, WANG Z, CUI M, et al. HIF1A Alleviates compression-induced apoptosis of nucleus pulposus derived stem cells via upregulating autophagy. Autophagy. 2021;17(11):3338-3360.
[18] HU X, WANG Z, ZHANG H, et al. Single-cell sequencing: New insights for intervertebral disc degeneration. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;165:115224.
[19] WILLIAMS RJ, LAAGLAND LT, BACH FC, et al. Recommendations for intervertebral disc notochordal cell investigation: From isolation to characterization. JOR spine. 2023;6(3):e1272.
[20] DAI Z, XIA C, ZHAO T, et al. Platelet-derived extracellular vesicles ameliorate intervertebral disc degeneration by alleviating mitochondrial dysfunction. Mater Today Bio. 2023;18:100512.
[21] BASATVAT S, BACH FC, BARCELLONA MN, et al. Harmonization and standardization of nucleus pulposus cell extraction and culture methods. JOR spine. 2023;6(1):e1238.
[22] GONG Y, QIU J, JIANG T, et al. Maltol ameliorates intervertebral disc degeneration through inhibiting PI3K/AKT/NF-κB pathway and regulating NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis. Inflammopharmacology. 2023; 31(1):369-384.
[23] TENG Y, HUANG Y, YU H, et al. Nimbolide targeting SIRT1 mitigates intervertebral disc degeneration by reprogramming cholesterol metabolism and inhibiting inflammatory signaling. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023;13(5): 2269-2280.
[24] MA L, ZHANG L, LIAO Z, et al. Pharmacological inhibition of protein S-palmitoylation suppresses osteoclastogenesis and ameliorates ovariectomy-induced bone loss. J Orthop Translat. 2023;42:1-14.
[25] LUO N, ZHANG L, XIU C, et al. Piperlongumine, a Piper longum-derived amide alkaloid, protects mice from ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis by inhibiting osteoclastogenesis via suppression of p38 and JNK signaling. Food Funct. 2024;15(4):2154-2169.
[26] JIANG M, FU X, YANG H, et al. mTORC1 Signaling Promotes Limb Bud Cell Growth and Chondrogenesis. J Cell Biochem.2017;118(4):748-753.
[27] KIM MJ, CHI BH, YOO JJ, et al. Structure establishment of three-dimensional (3D) cell culture printing model for bladder cancer. PloS One. 2019;14(10): e0223689.
[28] HE Q, YANG J, PAN Z, et al. Biochanin A protects against iron overload associated knee osteoarthritis via regulating iron levels and NRF2/System xc-/GPX4 axis. Biomed Pharmacother.2023;157:113915.
[29] 康陈萍, 肖倩倩, 刘青云, 等. 利用体外替代模型评价栀子黄色素的发育毒性[J]. 中国生育健康杂志,2022,33(3):247-253.
[30] CHEN J, YANG X, FENG Y, et al. Targeting Ferroptosis Holds Potential for Intervertebral Disc Degeneration Therapy. Cells. 2022;11(21):3508.
[31] SAMANTA A, LUFKIN T, KRAUS P. Intervertebral disc degeneration-Current therapeutic options and challenges. Front Public Health. 2023;11:1156749.
[32] WANG Y, KANG J, GUO X, et al. Intervertebral Disc Degeneration Models for Pathophysiology and Regenerative Therapy -Benefits and Limitations. J Invest Surg. 2022;35(4):935-952.
[33] LING Z, CRANE J, HU H, et al. Parathyroid hormone treatment partially reverses endplate remodeling and attenuates low back pain in animal models of spine degeneration. Sci Transl Med. 2023;15(722):eadg8982.
[34] LIU L, ZHANG Y, FU J, et al. Gli1 depletion induces oxidative stress and apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells via Fos in intervertebral disc degeneration. J Orthop Translat. 2023;40:116-131.
[35] LU K, WANG Q, JIANG H, et al. Upregulation of β-catenin signaling represents a single common pathway leading to the various phenotypes of spinal degeneration and pain. Bone Res. 2023;11(1):18.
[36] 汪尊冬, 李蔚, 曾臻, 等. 新生SD大鼠心房肌细胞的原代培养及改良[J]. 国际心血管病杂志,2022,49(6):359-362.
[37] HAN F, TU Z, ZHU Z, et al. Targeting Endogenous Reactive Oxygen Species Removal and Regulating Regenerative Microenvironment at Annulus Fibrosus Defects Promote Tissue Repair. ACS Nano. 2023;17(8):7645-7661.
[38] 师雷, 金振晓, 谭延振, 等. 简易灌注装置同时提取成年小鼠心肌细胞和心脏成纤维细胞[J]. 中国体外循环杂志,2023,21(3):172-178.
[39] KIANI AK, PHEBY D, HENEHAN G, et al. Ethical considerations regarding animal experimentation. J Prev Med Hyg. 2022;63(2 Suppl 3):E255-E266.
[40] JIA Z, LIU D, LI X, et al. Cartilage Endplate-Derived Stem Cells for Regeneration of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: An Analytic Study. J Inflamm Res. 2023;16:5791-5806.
[41] 张磊, 修春美, 倪莉, 等. 小鼠髓核特异性标志物的鉴定和表达分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(11):1669-1674.
[42] DU J, QIAN T, LU Y, et al. SPARC-YAP/TAZ inhibition prevents the fibroblasts-myofibroblasts transformation. Exp Cell Res. 2023;429(1):113649.
[43] MARTIN TJ. PTH1R Actions on Bone Using the cAMP/Protein Kinase A Pathway. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;12:833221.
[44] XU H, WANG W, LIU X, et al. Targeting strategies for bone diseases: signaling pathways and clinical studies. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8(1):202.
[45] 鲁燕妮, 龙雯, 常晓峰, 等. 改良全骨髓贴壁法分离及培养大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞[J]. 山西医科大学学报,2023,54(3):364-369.
[46] LI M, YU Y, XUE K, et al. Genistein mitigates senescence of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via ERRα-mediated mitochondrial biogenesis and mitophagy in ovariectomized rats. Redox Biol. 2023;61:102649.
[47] LA MANNO G, GYLLBORG D, CODELUPPI S, et al. Molecular Diversity of Midbrain Development in Mouse, Human, and Stem Cells. Cell. 2016; 167(2):566-580.
[48] ZHENG Y, FU X, LIU Q, et al. Characterization of Cre recombinase mouse lines enabling cell type‐specific targeting of postnatal intervertebral discs. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(9):14422-14431.
[49] CHAN CKF, GULATI GS, SINHA R, et al. Identification of the Human Skeletal Stem Cell. Cell. 2018;175(1):43-56.
[50] 杨春丽, 陆金芝, 刘贝贝, 等. 大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的原代培养及鉴定[J]. 现代生物医学进展,2023,23(18):3425-3430.
[51] MAZOR M, LESPESSAILLES E, BEST TM, et al. Gene Expression and Chondrogenic Potential of Cartilage Cells: Osteoarthritis Grade Differences. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(18):10610. |