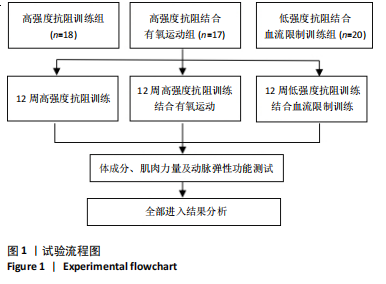
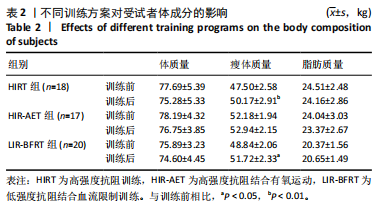
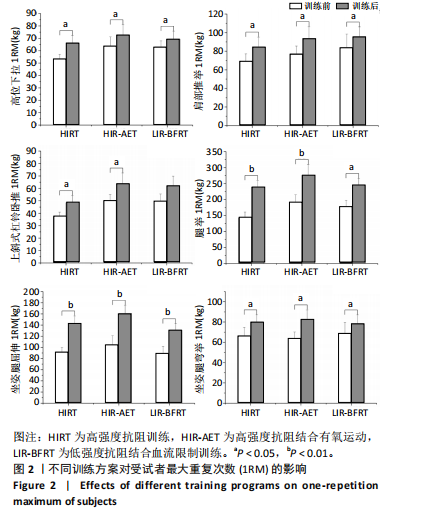
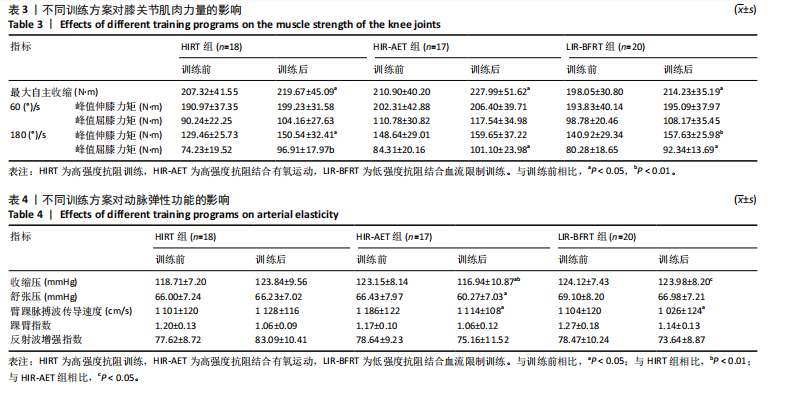
[1] KRAEMER WJ, RATAMESS NA, FLANAGAN SD, et al. Understanding the Science of Resistance Training: An Evolutionary Perspective. Sports Med. 2017;47(12):2415-2435.
[2] NYSTORIAK MA, BHATNAGAR A. Cardiovascular Effects and Benefits of Exercise. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2018;5:135.
[3] VINA J, SANCHIS-GOMAR F, MARTINEZ-BELLO V, et al. Exercise acts as a drug; the pharmacological benefits of exercise. Br J Pharmacol. 2012;167(1):1-12.
[4] MIYACHI M, KAWANO H, SUGAWARA J, et al. Unfavorable effects of resistance training on central arterial compliance: a randomized intervention study. Circulation. 2004;110(18):2858-2863.
[5] SUGA T, OKITA K, TAKADA S, et al. Effect of multiple set on intramuscular metabolic stress during low-intensity resistance exercise with blood flow restriction. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2012;112(11):3915-3920.
[6] OZAKI H, YASUDA T, OGASAWARA R, et al. Effects of high-intensity and blood flow-restricted low-intensity resistance training on carotid arterial compliance: role of blood pressure during training sessions. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2013;113(1):167-174.
[7] ZOUNGAS S, ASMAR RP. Arterial stiffness and cardiovascular outcome. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2007;34(7):647-651.
[8] KAWANO H, TANAKA H, MIYACHI M. Resistance training and arterial compliance: keeping the benefits while minimizing the stiffening. J Hypertens. 2006;24(9):1753-1759.
[9] GARCÍA-RODRÍGUEZ P, PECCI J, VÁZQUEZ-GONZÁLEZ S,et al. Acute and Chronic Effects of Blood Flow Restriction Training in Physically Active Patients With Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: A Systematic Review. Sports Health. 2023;12(1):194-199.
[10] JAVORSKÝ T, SAETERBAKKEN AH, ANDERSEN V, et al. Comparing low volume of blood flow restricted to high-intensity resistance training of the finger flexors to maintain climbing-specific strength and endurance: a crossover study. Front Sports Act Living. 2023;5:1256136.
[11] LOWE TW, TENAN MS, SHAH K, et al. Low-load blood flow restriction reduces time-to-minimum single motor unit discharge rate. Exp Brain Res. 2023;241(11-12):2795-2805.
[12] CURTY VM, MELO AB, CALDAS LC, et al. Blood flow restriction attenuates eccentric exercise-induced muscle damage without perceptual and cardiovascular overload. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2018;38(3):468-476.
[13] VECHIN FC, LIBARDI CA, CONCEIÇÃO MS, et al. Comparisons between low-intensity resistance training with blood flow restriction and high-intensity resistance training on quadriceps muscle mass and strength in elderly. J Strength Cond Res. 2015;29(4):1071-1076.
[14] HUANG PY, JANKAEW A, LIN CF. Effects of Plyometric and Balance Training on Neuromuscular Control of Recreational Athletes with Functional Ankle Instability: A Randomized Controlled Laboratory Study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(10):5269.
[15] DE OLIVEIRA CA, LUCIANO E, MARCONDES MC, et al. Effects of swimming training at the intensity equivalent to aerobic/anaerobic metabolic transition in alloxan diabetic rats. J Diabetes Complications. 2007;21(4):258-264.
[16] AINSWORTH BE, HASKELL WL, HERRMANN SD, et al. 2011 Compendium of Physical Activities: a second update of codes and MET values. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2011;43(8):1575-1581.
[17] HARPER SA, ROBERTS LM, LAYNE AS, et al. Blood-Flow Restriction Resistance Exercise for Older Adults with Knee Osteoarthritis: A Pilot Randomized Clinical Trial. J Clin Med. 2019;8(2):265.
[18] 李嘉玮,陶欣雨,姜荣荣,等.基于InBody的护生人体成分测定与分析[J].医学信息,2020,33(10):143-146.
[19] COBAN O, YILDIRIM NU, YASA ME, et al Determining the number of repetitions to establish isokinetic knee evaluation protocols specific to angular velocities of 60°/second and 180°/second. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2021;25:255-260.
[20] ESGIN T, JOHNSTON N, ROWLEY K, et al. Effect of 12 weeks combined aerobic and resistance training on fitness, arterial stiffness and body composition in Indigenous Australian men and women. J Sci Med Sport. 2017; 20(3): 43-51.
[21] SCHOENFELD BJ. The mechanisms of muscle hypertrophy and their application to resistance training. J Strength Cond Res. 2010;24(10): 2857-2872.
[22] TAKADA S, OKITA K, SUGA T, et al. Low-intensity exercise can increase muscle mass and strength proportionally to enhanced metabolic stress under ischemic conditions. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2012;113(2):199-205.
[23] SLYSZ J, STULTZ J, BURR JF. The efficacy of blood flow restricted exercise: A systematic review & meta-analysis. J Sci Med Sport. 2016;19(8):669-675.
[24] FARUP J, DE PAOLI F, BJERG K, et al. Blood flow restricted and traditional resistance training performed to fatigue produce equal muscle hypertrophy. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2015;25(6):754-763.
[25] DOCHERTY D, SPORER B. A proposed model for examining the interference phenomenon between concurrent aerobic and strength training. Sports Med. 2000;30(6):385-394.
[26] LUNDBERG TR, FEUERBACHER JF, SÜNKELER M, et al. The Effects of Concurrent Aerobic and Strength Training on Muscle Fiber Hypertrophy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2022;52(10):2391-2403.
[27] KISHTON RJ, BARNES CE, NICHOLS AG, et al. AMPK Is Essential to Balance Glycolysis and Mitochondrial Metabolism to Control T-ALL Cell Stress and Survival. Cell Metab. 2016;23(4):649-662.
[28] RICHTER EA, RUDERMAN NB. AMPK and the biochemistry of exercise: implications for human health and disease. Biochem J. 2009;418(2): 261-275.
[29] WEWEGE MA, DESAI I, HONEY C, et al. The Effect of Resistance Training in Healthy Adults on Body Fat Percentage, Fat Mass and Visceral Fat: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2022;52(2):287-300.
[30] YASUDA T, OGASAWARA R, SAKAMAKI M, et al. Relationship between limb and trunk muscle hypertrophy following high-intensity resistance training and blood flow-restricted low-intensity resistance training. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2011;31(5):347-351.
[31] SILLANPÄÄ E, LAAKSONEN DE, HÄKKINEN A, et al. Body composition, fitness, and metabolic health during strength and endurance training and their combination in middle-aged and older women. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2009;106(2):285-296.
[32] WILSON JM, MARIN PJ, RHEA MR, et al. Concurrent training: a meta-analysis examining interference of aerobic and resistance exercises. J Strength Cond Res. 2012;26(8):2293-2307.
[33] SCOTT BR, LOENNEKE JP, SLATTERY KM, et al. Blood flow restricted exercise for athletes: A review of available evidence. J Sci Med Sport. 2016;19(5):360-367.
[34] ANDERSEN LL, ANDERSEN JL, ZEBIS MK, et al. Early and late rate of force development: differential adaptive responses to resistance training? Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2010;20(1):e162-169.
[35] FERRARI R, FUCHS SC, KRUEL LF, et al. Effects of Different Concurrent Resistance and Aerobic Training Frequencies on Muscle Power and Muscle Quality in Trained Elderly Men: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Aging Dis. 2016;7(6):697-704.
[36] FAHS CA, ROSSOW LM, LOENNEKE JP, et al. Effect of different types of lower body resistance training on arterial compliance and calf blood flow. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2012;32(1):45-51.
[37] 刘严,齐丽彤,马为,等.桡动脉反射波增强指数与其他动脉硬化指标的关系[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2013,45(6):916-922.
[38] OTSUKI T, NAMATAME H, YOSHIKAWA T, et al. Combined aerobic and low-intensity resistance exercise training increases basal nitric oxide production and decreases arterial stiffness in healthy older adults. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2020;66(1):62-66.
[39] RAKOBOWCHUK M, MCGOWAN CL, DE GROOT PC, et al. Effect of whole body resistance training on arterial compliance in young men. Exp Physiol. 2005;90(4):645-651.
[40] LITWIN M, OBRYCKI Ł, NIEMIRSKA A, et al. Central systolic blood pressure and central pulse pressure predict left ventricular hypertrophy in hypertensive children. Pediatr Nephrol. 2019;34(4):703-712. |