| [1] Clark MA, Duhay FG, Thompson AK, et al. Clinical and economic outcomes after surgical aortic valve replacement in Medicare patients. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2012; 5: 117-126.[2] Maganti K, Rigolin VH, Sarano ME, et al. Valvular heart disease: diagnosis and management. Mayo Clin Proc. 2010;85(5): 483-500.[3] Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2016 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2016;133(4): e38-e360.[4] Hutcheson JD, Aikawa E, Merryman WD, et al. Potential drug targets for calcific aortic valve disease. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2014;11(4): 218-231.[5] Liu AC, Gotlieb AI. Characterization of cell motility in single heart valve interstitial cells in virto. Histol Histopathol. 2007;22: 873-882.[6] Taylor PM, Brand NJ, Thomas PS, et al. The cardiac valve interstitial cell. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2003;35: 113-118.[7] Xie C, Shen Y, Hu W, et al. Angiotensin II promotes an osteoblast-like phenotype in porcine aortic valve myofibroblasts. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2016;28(2): 181-187.[8] Dweck MR, Boon NA, Newby DE. Calcific aortic stenosis: a disease of the valve and the myocardium. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60(19): 1854-1863.[9] Liu AC, Joag VR, Gotlieb AI. The emerging role of valve interstitial cell phenotypes in regulating heart valve pathobiology. Am J Pathol. 2007;171(5): 1407-1418.[10] Rajamannan NM, Subramaniam M, Caira F, et al. Atorvastatin inhibits hypercholesterolemia-induced calcification in the aortic valves via the Lrp5 receptor pathway. Circulation. 2005;112(9 Suppl): I229-234.[11] 牛建立,成杞润,贾清仁,等. 心脏瓣膜间质细胞的表型转化及其与瓣膜病理形态发生的关系[J]. 中国危重病急救医学,2001, 13(3): 140-142.[12] Gao X, Zhang L, Gu G, et al. The effect of oxLDL on aortic valve calcification via the Wnt/ β-catenin signaling pathway: an important molecular mechanism. J Heart Valve Dis. 2015;24(2):190-196.[13] Parisi V, Leosco D, Ferro G, et al. The lipid theory in the pathogenesis of calcific aortic stenosis. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2015;25(6): 519-525.[14] 沈迎念,胡伟林,陈正平,等. 丹参酮IIA抑制主动脉瓣成肌纤维细胞向成骨细胞样表型转化的机制[J].中国中药杂志, 2015,40(18):3636-3643.[15] 关于发布《关于善待实验动物的指导性意见》的通知. 2006-09-30.[16] 沈迎念,胡伟林,张莉伟,等. 氧化型低密度脂蛋白对心脏瓣膜成肌纤维细胞的增殖及骨相关蛋白表达的影响[J].中国现代医学杂志,2015,14(25): 1-6.[17] Rajamannan NM, Evans FJ, Aikawa E, et al. Calcific aortic valve disease: not simply a degenerative process: A review and agenda for research from the National Heart and Lung and Blood Institute Aortic Stenosis Working Group. Executive summary: Calcific aortic valve disease-2011 update. Circulation. 2011; 124(16): 1783-1791.[18] Calloway TJ, Martin LJ, Zhang X, et al. Risk factors for aortic valve disease in bicuspid aortic valve: a family-based study. Am J Med Genet A. 2011; 155A(5): 1015-1020.[19] New SE, Aikawa E. Molecular imaging insights into early inflammatory stages of arterial and aortic valve calcification. Circ Res. 2011;108(11): 1381-1391.[20] Hjortnaes J, Butcher J, Figueiredo JL, et al. Arterial and aortic valve calcification inversely correlates with osteoporotic bone remodelling: a role for inflammation. Eur Heart J. 2010;31(16): 1975-1984.[21] Coté N, Mahmut A, Bosse Y, et al. Inflammation is associated with the remodeling of calcific aortic valve disease. Inflammation. 2013;36(3): 573-581.[22] Bertazzo S, Gentleman E, Cloyd KL, et al. Nano-analytical electron microscopy reveals fundamental insights into human cardiovascular tissue calcification. Nat Mater. 2013;12(6): 576-583.[23] 张米,刘晓红,张伯尧,等.人主动脉瓣间质细胞原代培养及体外钙化模型的建立[J].第二军医大学学报, 2013,34(5): 488-492.[24] Hjortnaes J, Camci-Unal G, Hutcheson JD, et al. Directing valvular interstitial cell myofibroblast-like differentiation in a hybrid hydrogel platform. Adv Healthc Mater. 2015;4(1): 121-130.[25] Syväranta S, Alanne-Kinnunen M, Oörni K, et al. Potential pathological roles for oxidized low-density lipoprotein and scavenger receptors SR-AI, CD36, and LOX-1 in aortic valve stenosis. Atherosclerosis. 2014; 235(2): 398-407.[26] Merryman WD, Lukoff HD, Long RA, et al. Synergistic effects of cyclic tension and transforming growth factor-beta1 on the aortic valve myofibroblast. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2007;16(5): 268-276.[27] Beazley KE, Deasey S, Lima F, et al. Transglutaminase 2-mediated activation of beta-catenin signaling has a critical role in warfarin-induced vascular calcification. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012;32(1): 123-130.[28] Kaden JJ, Sarikoç A, Hagl S, et al. Tumor necrosis factor alpha promotes an osteoblast like phenotype in human aortic valve myofibroblasts :a potential regulatory mechanism of valvular calcification. Source Int J Mol Med. 2005;16(5): 869-872.[29] Kaden JJ, Dempfle CE, Kiliç R, et al. Influence of receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B on human aortic valve myofibroblasts. Exp Mol Pathol. 2005; 78(1): 36-40.[30] Nadlonek NA, Lee JH, Weyant MJ, et al. ox-LDL induces PiT-1 expression in human aortic valve interstitial cells. J Surg Res. 2013; 184(1): 6-9.[31] Lee SH, Choi JH. Involvement of Immune Cell Network in Aortic Valve Stenosis: Communication between Valvular Interstitial Cells and Immune Cells. Immune Netw. 2016;16(1): 26-32.[32] Filip DA, Radu A, Simionescu M. Interstitial cells of the heart valves possess characteristics similar to smooth muscle cells. Circ Res. 1986; 59(3): 310-320. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
肌成纤维细胞:瓣膜间质细胞位于瓣膜内皮下,是心脏瓣膜最多的细胞类型,和瓣膜内皮细胞一起是构成心脏瓣膜内稳态最重要的细胞。成肌纤维细胞是一种能够表达平滑肌α-平滑肌肌动蛋白和Ⅰ型胶原纤维、并具有一定分化潜能的重要的瓣膜间质细胞,不仅在瓣膜的结构中起着支架作用,尤其在瓣膜的正常生理以及病理应答过程中发挥着重要的调控作用。
钙化性心脏瓣膜病:多指老年退行性心脏瓣膜病。随着年龄增长,心脏瓣膜结缔组织发生退行性变、纤维化、钙化等,而导致的瓣膜或支架的功能异常。目前,钙化性主动脉瓣疾病已成为主动脉瓣狭窄及瓣膜置换的首要病因,预计其发病率进一步提高,但其发病机制尚不明确。
文题释义:
肌成纤维细胞:瓣膜间质细胞位于瓣膜内皮下,是心脏瓣膜最多的细胞类型,和瓣膜内皮细胞一起是构成心脏瓣膜内稳态最重要的细胞。成肌纤维细胞是一种能够表达平滑肌α-平滑肌肌动蛋白和Ⅰ型胶原纤维、并具有一定分化潜能的重要的瓣膜间质细胞,不仅在瓣膜的结构中起着支架作用,尤其在瓣膜的正常生理以及病理应答过程中发挥着重要的调控作用。
钙化性心脏瓣膜病:多指老年退行性心脏瓣膜病。随着年龄增长,心脏瓣膜结缔组织发生退行性变、纤维化、钙化等,而导致的瓣膜或支架的功能异常。目前,钙化性主动脉瓣疾病已成为主动脉瓣狭窄及瓣膜置换的首要病因,预计其发病率进一步提高,但其发病机制尚不明确。.jpg) 文题释义:
肌成纤维细胞:瓣膜间质细胞位于瓣膜内皮下,是心脏瓣膜最多的细胞类型,和瓣膜内皮细胞一起是构成心脏瓣膜内稳态最重要的细胞。成肌纤维细胞是一种能够表达平滑肌α-平滑肌肌动蛋白和Ⅰ型胶原纤维、并具有一定分化潜能的重要的瓣膜间质细胞,不仅在瓣膜的结构中起着支架作用,尤其在瓣膜的正常生理以及病理应答过程中发挥着重要的调控作用。
钙化性心脏瓣膜病:多指老年退行性心脏瓣膜病。随着年龄增长,心脏瓣膜结缔组织发生退行性变、纤维化、钙化等,而导致的瓣膜或支架的功能异常。目前,钙化性主动脉瓣疾病已成为主动脉瓣狭窄及瓣膜置换的首要病因,预计其发病率进一步提高,但其发病机制尚不明确。
文题释义:
肌成纤维细胞:瓣膜间质细胞位于瓣膜内皮下,是心脏瓣膜最多的细胞类型,和瓣膜内皮细胞一起是构成心脏瓣膜内稳态最重要的细胞。成肌纤维细胞是一种能够表达平滑肌α-平滑肌肌动蛋白和Ⅰ型胶原纤维、并具有一定分化潜能的重要的瓣膜间质细胞,不仅在瓣膜的结构中起着支架作用,尤其在瓣膜的正常生理以及病理应答过程中发挥着重要的调控作用。
钙化性心脏瓣膜病:多指老年退行性心脏瓣膜病。随着年龄增长,心脏瓣膜结缔组织发生退行性变、纤维化、钙化等,而导致的瓣膜或支架的功能异常。目前,钙化性主动脉瓣疾病已成为主动脉瓣狭窄及瓣膜置换的首要病因,预计其发病率进一步提高,但其发病机制尚不明确。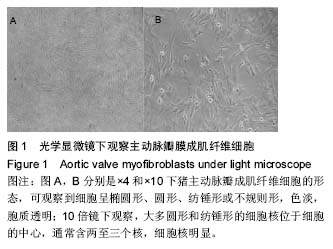
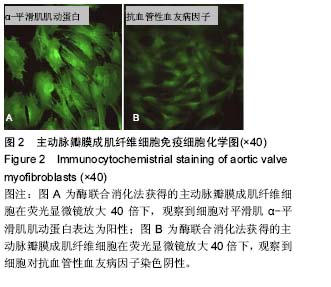

.jpg) 文题释义:
肌成纤维细胞:瓣膜间质细胞位于瓣膜内皮下,是心脏瓣膜最多的细胞类型,和瓣膜内皮细胞一起是构成心脏瓣膜内稳态最重要的细胞。成肌纤维细胞是一种能够表达平滑肌α-平滑肌肌动蛋白和Ⅰ型胶原纤维、并具有一定分化潜能的重要的瓣膜间质细胞,不仅在瓣膜的结构中起着支架作用,尤其在瓣膜的正常生理以及病理应答过程中发挥着重要的调控作用。
钙化性心脏瓣膜病:多指老年退行性心脏瓣膜病。随着年龄增长,心脏瓣膜结缔组织发生退行性变、纤维化、钙化等,而导致的瓣膜或支架的功能异常。目前,钙化性主动脉瓣疾病已成为主动脉瓣狭窄及瓣膜置换的首要病因,预计其发病率进一步提高,但其发病机制尚不明确。
文题释义:
肌成纤维细胞:瓣膜间质细胞位于瓣膜内皮下,是心脏瓣膜最多的细胞类型,和瓣膜内皮细胞一起是构成心脏瓣膜内稳态最重要的细胞。成肌纤维细胞是一种能够表达平滑肌α-平滑肌肌动蛋白和Ⅰ型胶原纤维、并具有一定分化潜能的重要的瓣膜间质细胞,不仅在瓣膜的结构中起着支架作用,尤其在瓣膜的正常生理以及病理应答过程中发挥着重要的调控作用。
钙化性心脏瓣膜病:多指老年退行性心脏瓣膜病。随着年龄增长,心脏瓣膜结缔组织发生退行性变、纤维化、钙化等,而导致的瓣膜或支架的功能异常。目前,钙化性主动脉瓣疾病已成为主动脉瓣狭窄及瓣膜置换的首要病因,预计其发病率进一步提高,但其发病机制尚不明确。