| [1] Ahn DK, Lee S, Moon SH, et al. Ossification of the ligamentum flavum. Asian Spine J. 2014;8(1):89-96.[2] Gao R, Yuan W, Yang L, et al. Clinical features and surgical outcomes of patients with thoracic myelopathy caused by multilevel ossification of the ligamentum flavum. Spine J. 2013;13(9):1032-1038.[3] Fong SY, Wong HK. Thoracic myelopathy secondary to ligamentum flavum ossification. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 2004;33(3):340-346.[4] Jia LS, Chen XS, Zhou SY, et al. En bloc resection of lamina and ossified ligamentum flavum in the treatment of thoracic ossification of the ligamentum flavum. Neurosurgery. 2010; 66(6):1181-1186.[5] Zaki SM. Study of the human ligamentum flavum in old age: a histological and morphometric study. Folia Morphol (Warsz). 2014;73(4):492-499.[6] Klosinski M, Skrzat J, Walocha J, et al. Contemporary views on the ossification of the ligamenta flava. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil. 2012;14(6):495-503.[7] Kim YH, Khuyagbaatar B, Kim K. Biomechanical effects of spinal cord compression due to ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament and ligamentum flavum: a finite element analysis. Med Eng Phys. 2013;35(9):1266-1271.[8] Ren L, Hu H, Sun X, et al. The roles of inflammatory cytokines in the pathogenesis of ossification of ligamentum flavum. Am J Transl Res. 2013;5(6):582-585.[9] Fan D, Chen Z, Chen Y, et al. Mechanistic roles of leptin in osteogenic stimulation in thoracic ligament flavum cells. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(41):29958-29966.[10] Ono K, Yonenobu K, Miyamoto S, et al. Pathology of ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament and ligamentum flavum. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999;(359):18-26.[11] Wiseman DB, Stokes JK, Toselli RM. Paraparesis in a black man brought on by ossification of the ligamentum flavum: case report and review of the literature. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2002;15(6):542-545.[12] Pascal-Moussellard H, Cabre P, Smadja D, et al. Symptomatic ossification of the ligamentum flavum: a clinical series from the French Antilles. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30(14):E400-E405.[13] Tokala DP, Lam KS, Prince HG. Ossification of the proximal thoracic ligamenta flava causing acute myelopathy in a Caucasian: case report and literature review. Spinal Cord. 2007;45(4):310-313.[14] Kim HN, Min WK, Jeong JH, et al. Combination of Runx2 and BMP2 increases conversion of human ligamentum flavum cells into osteoblastic cells. BMB Rep 2011;44(7):446-451.[15] Liu Y, Zhao Y, Chen Y, et al. RUNX2 polymorphisms associated with OPLL and OLF in the Han population. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2010;468(12):3333-3341.[16] 陈雄生,贾连顺,倪斌,等.重组人骨形态发生蛋白-2诱发黄韧带骨化的实验模型[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2002,12(1):31-34.[17] Kong Q, Ma X, Li F, et al. COL6A1 polymorphisms associated with ossification of the ligamentum flavum and ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2007;32(25):2834-2838.[18] Cai HX, Yayama T, Uchida K, et al. Cyclic tensile strain facilitates the ossification of ligamentum flavum through beta-catenin signaling pathway: in vitro analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(11):E639-E646.[19] Braddock R, Siman CM, Hamilton K, et al. Gamma-linoleic acid and ascorbate improves skeletal ossification in offspring of diabetic rats. Pediatr Res. 2002;51(5):647-652.[20] Wang Z, Li XD, Li MQ, et al. Changes in basic metabolic elements associated with the degeneration and ossification of ligamenta flava. J Spinal Cord Med. 2008;31(3):279-284.[21] Hunter GK. Role of osteopontin in modulation of hydroxyapatite formation. Calcif Tissue Int. 2013;93(4): 348-354.[22] Morinobu M, Ishijima M, Rittling SR, et al. Osteopontin expression in osteoblasts and osteocytes during bone formation under mechanical stress in the calvarial suture in vivo. J Bone Miner Res. 2003;18(9):1706-1715.[23] 张宇,吴少鹏,夏雄智,等.人黄韧带细胞体外原代培养方法的比较[J].广东医学,2011,(13):1668-1671.[24] 王哲,许汉鹏,罗卓荆,等.胸椎黄韧带骨化患者黄韧带细胞的体外培养及初步鉴定[J].中华骨科杂志,2007;27(9):705-710.[25] Hirota S, Asada H, Kohri K, et al. Possible role of osteopontin in deposition of calcium phosphate in human pilomatricomas. J Invest Dermatol. 1995;105(1):138-142.[26] Rangaswami H, Bulbule A, Kundu GC. Osteopontin: role in cell signaling and cancer progression. Trends Cell Biol. 2006; 16(2):79-87.[27] Franzen A, Heinegard D. Isolation and characterization of two sialoproteins present only in bone calcified matrix. Biochem J. 1985;232(3):715-724.[28] Sodek KL, Tupy JH, Sodek J, et al. Relationships between bone protein and mineral in developing porcine long bone and calvaria. Bone. 2000;26(2):189-198.[29] Chen Q, Shou P, Zhang L, et al. An osteopontin-integrin interaction plays a critical role in directing adipogenesis and osteogenesis by mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells. 2014; 32(2):327-337.[30] Hynes RO. Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell.1992;69(1):11-25.[31] Wu X, Mogford JE, Platts SH, et al. Modulation of calcium current in arteriolar smooth muscle by alphav beta3 and alpha5 beta1 integrin ligands. J Cell Biol. 1998;143(1): 241-252.[32] Lakemeier S, Schmid R, Foltz L, et al. Increased expression of CD44 in hypertrophied ligamentum flavum and relevance of splice variants CD44v5 and CD44v6. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2012;154(2):359-365. |
.jpg)
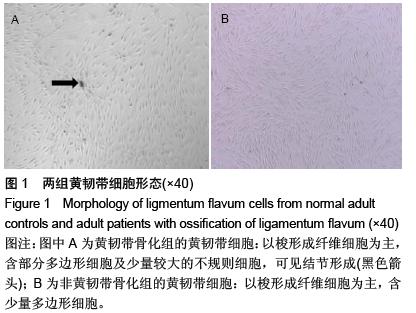
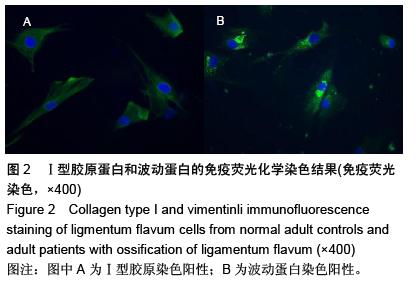
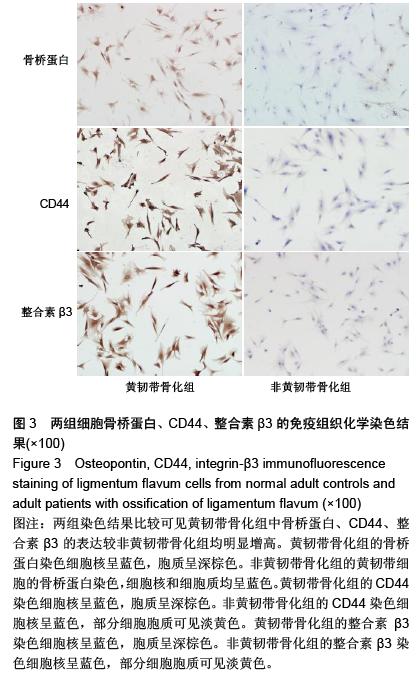
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)