| [1] Jiang SD, Jiang LS, Dai LY. Degenerative cervical spondylolisthesis: a systematic review. Int Orthop. 2011; 35(6):869-875.[2] Ng HW, Teo EC, Lee KK, et al. Finite element analysis of cervical spinal instability under physiologic loading. Spinal Disord Tech. 2003;16(1):55-65.[3] Kawakami M, Tamaki T, Ando M, et al. Preoperative instability does not influence the clinical outcome in patients with cervical spondilotic myelopathy treated with expansive laminoplasty. Spinal Disord Tech. 2002;15(4):277-283.[4] Onari K,Akiyama N, Kondo S, et al. Long- term follow up results of anterior interbody fusion applied for cervical myelopathy due to ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament.Spine. 2001;26(5):488-493.[5] 石志才,贾连顺,余科炜,等.脊髓性颈椎病早期诊断的前瞻性研究[J].中华外科杂志,1998,36(12):717-720.[6] 石志才,贾连顺,李家顺,等.动态霍夫曼征与颈椎病早期诊断[J].第二军医大学学报,2001,22(10):917-919.[7] 崔志明,贾连顺,倪斌.下颈椎不稳对颈椎后纵韧带骨化症早期发病的影响[J].中国临床康复,2002,6(16):2402-2403.[8] Ratliff J,Voorhies R. Increased MRI signal intensity in association with myelopathy and cervical instability:case report and review of the literature. Surq Neurol. 2000;53(1): 8-13.[9] 申勇,张英泽,吴华荣,等.退行性下颈椎不稳症的早期手术治疗[J].中华骨科杂志,2005,25(5):297-299.[10] Hilibrand AS, Matthew R. Adjacent segment degeneration and adjacent segment disease: the consequences of spinal fusion. Spine. 2004;4(6)190-194. [11] Wigfied CC, Skrzypiec D, Jackowski A, et al. Internal stress distribution in cervical discs: the infuence of an artificial cervical joint and simulated anterior interbody fusion. Spinal Disord Tech. 2003;16( 5):441-449.[12] Azmi H, Schlenk RP. Surgery for postarthrodesis adjacent-cervical segment degeneration. Neurosurg Focus. 2003;15(3):E6.[13] 贾连顺.颈椎病研究的现状进展和展望[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2001, 8(8):733-734. [14] Hilibrand AS, Robbins M. Adjacent segment degeneration and adjacent segment disease: the consequences of spinal fusion. Spine. 2004;4(6):190-194.[15] Spron MB, Robert AB. Peptide growth factors and their receptors. New York: Springer-Verlag. 1990:419-456.[16] Hoogendoorn R, Doulabi BZ, Huang CL, et al. Molecular changes in the degenerated goat intervertebral disc. Spine. 2008;33(16):1714-1721.[17] Hoogendoorn RJ, Wuisman PI, SmitTH, et al. Experimental intervertebral disc degeneration induced by chondroitinase ABC in the goat. Spine. 2007;32(17):1816-1825.[18] 魏威,廖胜辉,韩颖,等.非创伤性生理曲度变直与颈椎退变关系的生物力学研究[J].中华中医药学刊,2011,29(11):2474-2477.[19] Bellini CM, Galbusera F, Raimondi MT, et al. Biomechanics of the lumbar spine after dynamic stabilization. Spinal Disord Tech. 2007;20(6):423-429.[20] Sowa G, Vadala G, Studer R, et al. Characterization of intervertebral disc aging: longitud in alanalysis of a rabbit model by magnetic resonance imaging, histology, and gene expression. Spine. 2008;33(17):1821-1828.[21] Rousseau MA, Ulrich JA, Bass EC, et al. Stab incision for inducing intervertebral disc degeneration in the rat. Spine. 2007;32(1):17-24.[22] Kandel R, Roberts S, Urban JP. Tissue engineering and the intervertebral disc: the challenges. Eur Spine. 2008;17 Suppl 4:480-491.[23] Lurie JD, Berven SH, Gibson-Chambers J, et al. Patient preferences and expectations for care: determinants in patients with lumbar intervertebral disc herniation. Spine. 2008;33(24):2663-2668.[24] Dimari SJ, Howe AM, Haralson MA, et al. Effects of transforming growth factor-beta on collagen synthesis by fetal rat lung epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991; 4(5): 455-462.[25] Smith LJ, Nerurkar NL, Choi KS, et al. Degeneration and regeneration of the intervertebral disc: lessons from development. Dis Model Mech. 2011;4(1):31-41. [26] Yoon JY, Chang H, Park KB, et al. Effect of the number of involved spinal cord segments on gait function in patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Asian Spine. 2012;6(4): 233-240. [27] Kotani Y, Takahata M, Abumi K, et al. Cervical myelopathy resulting from combined ossification of the ligamentum flavum and posterior longitudinal ligament: report of two cases and literature review. Spine. 2013;13(1):e1-6.[28] Rosińczuk-Tonderys J, Za?uski R, Gdesz M, et al. Spine and spinal cord injuries-causes and complications. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2012;21(4):477-485.[29] Oshima Y, Seichi A, Takeshita K, et al. Natural course and prognostic factors in patients with mild cervical spondylotic myelopathy with increased signal intensity on T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012; 37(22):1909-1913.[30] Yagi M, Ninomiya K, Kihara M, et al. Long-term surgical outcome and risk factors in patients with cervical myelopathy and a change in signal intensity of intramedullary spinal cord on Magnetic Resonance imaging. J Neurosurg Spine. 2010; 12(1):59-65.[31] Song J, Mizuno J, Inoue T, et al. Clinical evaluation of traumatic central cord syndrome: emphasis on clinical significance of prevertebral hyperintensity, cord compression, and intramedullary high-signal intensity on magnetic resonance imaging. Surg Neurol. 2006;65(2):117-123. |
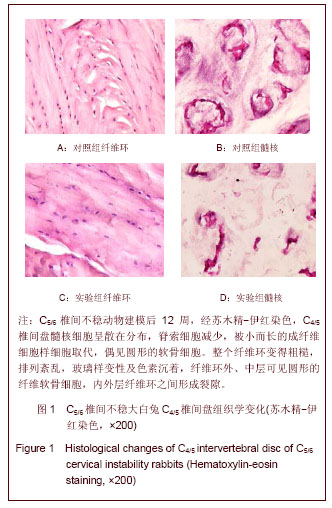
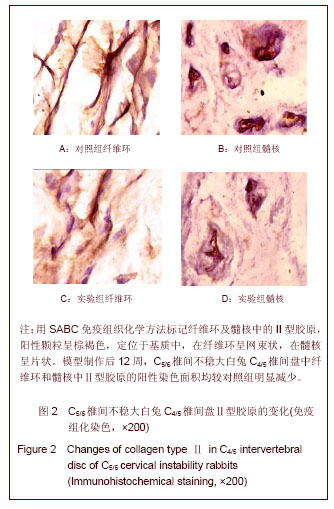
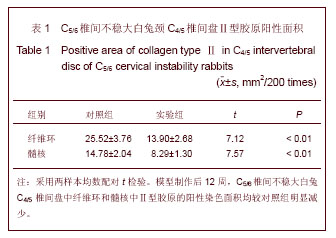
.jpg)