[1] SILVA-CORREIA J, CORREIA SI, OLIVEIRA JM, et al. Tissue engineering strategies applied in the regeneration of the human intervertebral disk. Biotechnol Adv. 2013;31(8):1514-1531.
[2] FRAPIN L, CLOUET J, CHEDEVILLE C, et al. Controlled release of biological factors for endogenous progenitor cell migration and intervertebral disc extracellular matrix remodelling. Biomaterials. 2020;253:120107.
[3] KUMAR H, HA DH, LEE EJ, et al. Safety and tolerability of intradiscal implantation of combined autologous adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells and hyaluronic acid in patients with chronic discogenic low back pain: 1-year follow-up of a phase I study. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):262.
[4] AOYAGI K, HE JH, NICOL AL, et al. A Subgroup of Chronic Low Back Pain Patients With Central Sensitization. Clin J Pain. 2019;35(11):869-879.
[5] HRABALEK L, WANEK T, ADAMUS M, et al. Surgery for Degenerative Spondylolisthesis of the Lumbar Spine Using Intra-Articular Fusion. A Prospective Study. Acta Chir Orthop Tr. 2014;81(5):323-327.
[6] BREDOW J, EYSEL P, OIKONOMIDIS S. Postoperative management of weight bearing and rehabilitation after lumbar spinal surgery. Orthopade. 2020;49(3):201-210.
[7] TSAHTSARLIS A, WOOD M. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumber interbody fusion and degenerative lumbar spine disease. Eur Spine J. 2012;21(11):2300-2305.
[8] LIU Y, LI Y, NAN LP, et al.Insights of stem cell-based endogenous repair of intervertebral disc degeneration. World J Stem Cells. 2020;12(4): 266-276.
[9] NEIDLINGER-WILKE C, GALBUSERA F, PRATSINIS H, et al. Mechanical loading of the intervertebral disc: from the macroscopic to the cellular level. Eur Spine J. 2014;23:S333-S343.
[10] Pham DT, Shapter JG, Costi JJ. Tensile behaviour of individual fibre bundles in the human lumbar anulus fibrosus. J Biomech. 2018;67:24-31.
[11] CHEN HT, HUANG AB, HE YL, et al. Wnt11 overexpression promote adipose-derived stem cells differentiating to the nucleus pulposus-like phenotype. Eur Rev Med Pharmaco. 2017;21(7):1462-1470.
[12] VEDICHERLA S, BUCKLEY CT. In vitro extracellular matrix accumulation of nasal and articular chondrocytes for intervertebral disc repair. Tissue Cell. 2017;49(4):503-513.
[13] SEE EYS, TOH SL, GOH JCH. Simulated intervertebral disc-like assembly using bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell sheets and silk scaffolds for annulus fibrosus regeneration. J Tissue Eng Regen M. 2012;6(7):528-535.
[14] RECUERDA M, PERIE D, GILBERT G, et al. Assessment of mechanical properties of isolated bovine intervertebral discs from multi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging. Bmc Musculoskel Dis. 2012;13:195.
[15] DE CICCO FL, CAMINO WILLHUBER GO. Nucleus Pulposus Herniation. StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL),2020.
[16] MOLLADAVOODI S, MCMORRAN J, GREGORY D. Mechanobiology of annulus fibrosus and nucleus pulposus cells in intervertebral discs. Cell Tissue Res. 2020;379(3):429-444.
[17] MOUW JK, OU GQ, WEANER VM. Extracellular matrix assembly: a multiscale deconstruction.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.2014;15(12):771-785.
[18] LANGLAIS T, DESPRAIRIES P, PIETTON R, et al. Microstructural characterization of annulus fibrosus by ultrasonography: a feasibility study with an in vivo and in vitro approach. Biomech Model Mechan. 2019;18(6):1979-1986.
[19] BALDIT A, AMBARD D, CHERBLANC F, et al. Annulus fibrosus microstructure: an explanation to local heterogeneities. Comput Method Biomec. 2014;17:38-39.
[20] CHU G, SHI C, WANG H, et al. Strategies for Annulus Fibrosus Regeneration: From Biological Therapies to Tissue Engineering. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2018;6:90.
[21] SLOAN SR JR, LINTZ M, HUSSAIN I, et al. Biologic Annulus Fibrosus Repair: A Review of Preclinical In Vivo Investigations. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2018;24(3):179-190.
[22] AMBARD D, CHERBLANC F. Mechanical Behavior of Annulus Fibrosus: A Microstructural Model of Fibers Reorientation. Ann Biomed Eng. 2009;37(11):2256-2265.
[23] TORRE OM, MROZ V, BARTELSTEIN MK, et al. Annulus fibrosus cell phenotypes in homeostasis and injury: implications for regenerative strategies. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2019;1442(1):61-78.
[24] HEDMAN TP, KOSTUIK JP, FERNIE GR, et al. Design of an intervertebral disc prosthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1991;16(6 Suppl):S256-260.
[25] HOU TS, TU KY, XU YK, et al. Lumbar intervertebral disc prosthesis. An experimental study. Chin Med J (Engl). 1991;104(5):381-386.
[26] LINK HD. History, design and biomechanics of the LINK SB Charite artificial disc. Eur Spine J. 2002;11 Suppl 2:S98-S105.
[27] ISLAM S, BHUIYAN MAR, ISLAM MN. Chitin and Chitosan: Structure, Properties and Applications in Biomedical Engineering. J Polym Environ. 2017;25(3):854-866.
[28] NEGM NA, HEFNI HHH, ABD-ELAAL AA, et al. Advancement on modification of chitosan biopolymer and its potential applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;152:681-702.
[29] ISLAM MM, SHAHRUZZAMAN M, BISWAS S, et al. Chitosan based bioactive materials in tissue engineering applications-A review. Bioact Mater. 2020;5(1):164-183.
[30] JI C, SHI J. Thermal-crosslinked porous chitosan scaffolds for soft tissue engineering applications. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2013;33(7): 3780-3785.
[31] ROUGHLEY P, HOEMANN C, DESROSIERS E, et al. The potential of chitosan-based gels containing intervertebral disc cells for nucleus pulposus supplementation. Biomaterials. 2006;27(3):388-396.
[32] RICHARDSON SM, HUGHES N, HUNT JA, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cell differentiation to NP-like cells in chitosan-glycerophosphate hydrogels. Biomaterials. 2008;29(1):85-93.
[33] SASSON A, PATCHORNIK S, ELIASY R, et al. Hyperelastic mechanical behavior of chitosan hydrogels for nucleus pulposus replacement-experimental testing and constitutive modeling. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2012;8:143-153.
[34] GHORBANI M, AI J, NOURANI MR, et al. Injectable natural polymer compound for tissue engineering of intervertebral disc: In vitro study. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;80:502-508.
[35] ANTUNES JC, PEREIRA CL, TEIXEIRA GQ, et al. Poly(gamma-glutamic acid) and poly(gamma-glutamic acid)-based nanocomplexes enhance type II collagen production in intervertebral disc. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2017;28(1):6.
[36] TEIXEIRA GQ, LEITE PEREIRA C, CASTRO F, et al. Anti-inflammatory Chitosan/Poly-gamma-glutamic acid nanoparticles control inflammation while remodeling extracellular matrix in degenerated intervertebral disc. Acta Biomater. 2016;42:168-179.
[37] DANG JM, SUN DD, SHIN-YA Y, et al. Temperature-responsive hydroxybutyl chitosan for the culture of mesenchymal stem cells and intervertebral disk cells. Biomaterials. 2006;27(3):406-418.
[38] LI Z, SHIM H, CHO MO, et al. Thermo-sensitive injectable glycol chitosan-based hydrogel for treatment of degenerative disc disease. Carbohydr Polym. 2018;184:342-353.
[39] GUO LL, ZHENG D, XU JC, et al. Effects of ionic crosslinking on physical and mechanical properties of alginate mulching films. Carbohyd Polym. 2016;136:259-265.
[40] HERNANDEZ-GONZALEZ AC, TELLEZ-JURADO L, RODRIGUEZ-LORENZO LM. Alginate hydrogels for bone tissue engineering, from injectables to bioprinting: A review. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;229:115514.
[41] ANSARI S, DINIZ IM, CHEN C, et al. Alginate/hyaluronic acid hydrogel delivery system characteristics regulate the differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells toward chondrogenic lineage. J Mater Sci Mater M. 2017;28(10):162.
[42] JEON O, BOUHADIR KH, MANSOUR JM, et al. Photocrosslinked alginate hydrogels with tunable biodegradation rates and mechanical properties. Biomaterials. 2009;30(14):2724-2734.
[43] LU MZ, LAN HL, WANG FF, et al. Cell encapsulation with alginate and alpha-phenoxycinnamylidene-acetylated poly(allylamine). Biotechnol Bioeng. 2000;70(5):479-483.
[44] KALAF EAG, PENDYALA M, BLEDSOE JG, et al. Characterization and restoration of degenerated IVD function with an injectable, in situ gelling alginate hydrogel: An in vitro and ex vivo study. J Mech Behav Biomed. 2017;72:229-240.
[45] YANG JC, YANG XL, WANG L, et al. Biomimetic nanofibers can construct effective tissue-engineered intervertebral discs for therapeutic implantation. Nanoscale. 2017;9(35):13095-13103.
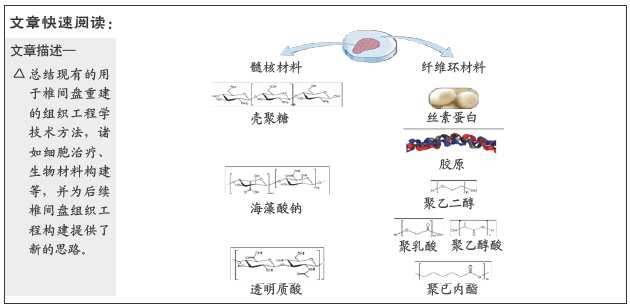
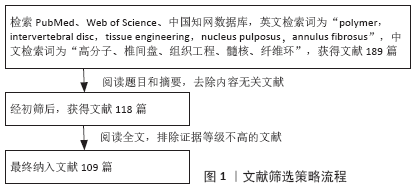
[46] 张子言,佟珅,颜华东,等.人椎间盘髓核组织工程研究进展[J].中国老年学杂志,2013,33(5):1214-1218.
[47] ZENG Y, FENG SY, LIU W, et al. Preconditioning of mesenchymal stromal cells toward nucleus pulposus-like cells by microcryogels-based 3D cell culture and syringe-based pressure loading system. J Biomed Mater Res B. 2017;105(3):507-520.
[48] NI YL, TANG ZR, CAO WX, et al. Tough and elastic hydrogel of hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate as potential cell scaffold materials. Int J Biol Macromol. 2015;74:367-375.
[49] CSOKA AB, FROST GI, STERN R. The six hyaluronidase-like genes in the human and mouse genomes. Matrix Biol. 2001;20(8):499-508.
[50] CHEN YC, SU WY, YANG SH, et al. In situ forming hydrogels composed of oxidized high molecular weight hyaluronic acid and gelatin for nucleus pulposus regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(2):5181-5193.
[51] TURLEY EA, NOBLE PW, BOURGUIGNON LYW. Signaling properties of hyaluronan receptors. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(7):4589-4592.
[52] SU WY, CHEN YC, LIN FH. Injectable oxidized hyaluronic acid/adipic acid dihydrazide hydrogel for nucleus pulposus regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2010;6(8):3044-3055.
[53] Kalson NS, Richardson S, Hoyland JA. Strategies for regeneration of the intervertebral disc. Regen Med. 2008;3(5):717-729.
[54] GLORIA A, BORZACCHIELLO A, CAUSA F, et al. Rheological Characterization of Hyaluronic Acid Derivatives as Injectable Materials Toward Nucleus Pulposus Regeneration. J Biomater Appl. 2012;26(6): 745-759.
[55] KAZEZIAN Z, LI Z, ALINI M, et al. Injectable hyaluronic acid down-regulates interferon signaling molecules, IGFBP3 and IFIT3 in the bovine intervertebral disc. Acta Biomater. 2017;52:118-129.
[56] LIU X, LIU J, WANG J, et al. Bioinspired, Microstructured Silk Fibroin Adhesives for Flexible Skin Sensors. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020; 12(5):5601-5609.
[57] CENGIZ IF, MAIA FR, DA SILVA MORAIS A, et al. Entrapped in cage (EiC) scaffolds of 3D-printed polycaprolactone and porous silk fibroin for meniscus tissue engineering. Biofabrication. 2020;12(2):025028.
[58] Lu Q, Hu X, Wang X, et al. Water-insoluble silk films with silk I structure. Acta Biomater. 2010;6(4):1380-1387.
[59] GOSLINE JM, GUERETTE PA, ORTLEPP CS, et al. The mechanical design of spider silks: from fibroin sequence to mechanical function. J Exp Biol. 1999;202(Pt 23):3295-3303.
[60] XU M, LI H, ZHAI D, et al. Hierarchically porous nagelschmidtite bioceramic–silk scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. J Mater Chem B. 2015;3(18):3799-3809.
[61] LIU H, XU GW, WANG YF, et al. Composite scaffolds of nano-hydroxyapatite and silk fibroin enhance mesenchymal stem cell-based bone regeneration via the interleukin 1 alpha autocrine/paracrine signaling loop. Biomaterials. 2015;49:103-112.
[62] SUNTIVICH R, DRACHUK I, CALABRESE R, et al. Inkjet printing of silk nest arrays for cell hosting. Biomacromolecules. 2014;15(4):1428-1435.
[63] DIAB T, PRITCHARD EM, UHRIG BA, et al. A silk hydrogel-based delivery system of bone morphogenetic protein for the treatment of large bone defects. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2012;11:123-131.
[64] WENK E, MURPHY AR, KAPLAN DL, et al. The use of sulfonated silk fibroin derivatives to control binding, delivery and potency of FGF-2 in tissue regeneration. Biomaterials. 2010;31(6):1403-1413.
|