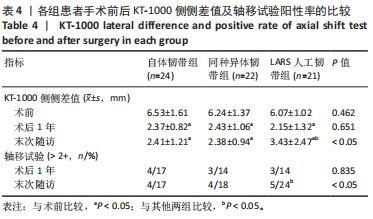
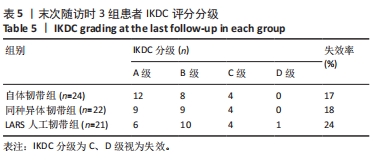
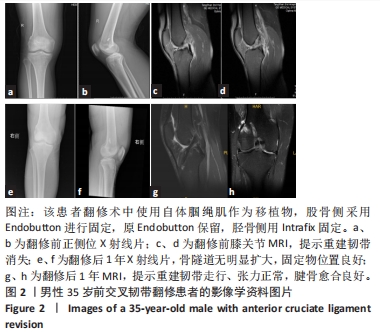
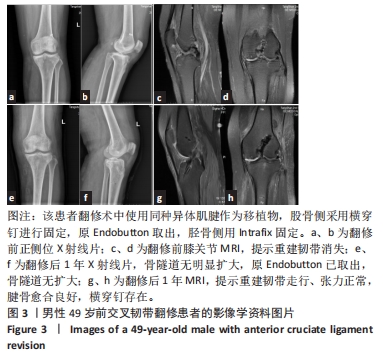
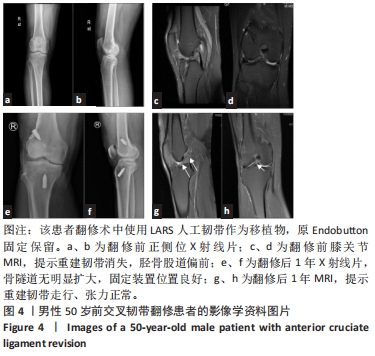
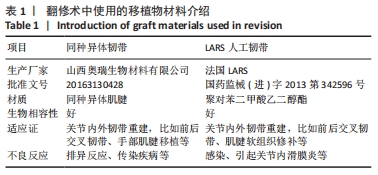
[1] WRIGHT RW, HUSTON LJ, HAAS AK, et al. Association Between Graft Choice and 6-Year Outcomes of Revision Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction in the MARS Cohort. Am J Sports Med. 2021;49(10):2589-2598.
[2] RAHARDJA R, ZHU M, LOVE H, et al. No difference in revision rates between anteromedial portal and transtibialdrilling of the femoral graft tunnel in primary anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: early results from the New Zealand ACL Registry. Knee. Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020;28:3631-3638.
[3] DING DY, ZHANG AL, ALLEN CR, et al. Subsequent Surgery After Revision Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: Rates and Risk Factors From a Multicenter Cohort. Am J Sports Med. 2017;45(9):2068-2076.
[4] KANAKAMEDALA AC, EDGAR CM, FANELLI GC, et al. Surgical Considerations in Revision Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction. Instr Course Lect. 2022;71: 475-487.
[5] MIAO S, LI S, WU Z, et al. The Clinical Efficacy and Risk Factors after Revision and Reconstruction of Anterior Cruciate Ligament. J Healthc Eng. 2021;2021:6606492.
[6] 蒋艳芳,王健,王永健,等.前交叉韧带翻修重建术后中长期临床疗效及影响因素[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2021,53(5):857-864.
[7] TULLOCH SJ, DEVITT BM, PORTER T, et al. Primary ACL reconstruction using the LARS device is associated with a high failure rate at minimum of 6-year follow-up. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27(11):3626-3632.
[8] JANSSEN RP, SCHEFFLER SU. Intra-articular remodelling of hamstring tendon grafts after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014;22(9):2102-2108.
[9] 李韬,朱彦霖,林唐棣,等.同种异体肌腱重建膝关节前交叉韧带的研究进展与临床应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(10):1605-1610.
[10] MARS Group. Meniscal and Articular Cartilage Predictors of Clinical Outcome After Revision Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction. Am J Sports Med. 2016;44(7):1671-1679.
[11] GROSSMAN MG, ELATTRACHE NS, SHIELDS CL, et al. Revision anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: three- to nine-year follow-up. Arthroscopy. 2005;21(4): 418-423.
[12] AHN JH, LEE YS, HA HC. Comparison of revision surgery with primary anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction and outcome of revision surgery between different graft materials. Am J Sports Med. 2008;36(10):1889-1895.
[13] 运行,魏钰,李众利,等.前交叉韧带翻修术中期疗效研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2021,35(1):58-63.
[14] 马勇,敖英芳,崔国庆,等.前交叉韧带重建后翻修的临床研究[J].中华外科杂志,2008,46(9):650-653.
[15] CRISTIANI R, ENGSTROM B, EDMAN G, et al. Revision anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction restores knee laxity but shows inferior functional knee outcome compared with primary reconstruction. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27(1):137-145.
[16] WRIGHT RW, JOHNSON L, BROPHY RH, et al. Revision Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Outcomes at a Minimum of 5-Year Follow-Up: A Systematic Review. J Knee Surg. 2019;32(3):218-221.
[17] WRIGHT RW, HUSTON LJ, HAAS AK, et al. Predictors of Patient-Reported Outcomes at 2 Years After Revision Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction. Am J Sports Med. 2019;47(10):2394-2401.
[18] LIEN-IVERSEN T, MORGAN DB, JENSEN C, et al. Does surgery reduce knee osteoarthritis, meniscal injury and subsequent complications compared with non-surgery after ACL rupture with at least 10 years follow-up? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med. 2020;54(10):592-598.
[19] GRASSI A, ZAFFAGNINI S, MARCHEGGIANI MG, et al. After revision anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction, who returns to sport? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med. 2015;49(20):1295-1304.
[20] KUECHLE DK, PEARSON SE, BEACH WR, et al. Allograft anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in patients over 40 years of age. Arthroscopy. 2002;18(8):845-853.
[21] YU SB, YANG RH, ZUO ZN, et al. Histological characteristics and ultrastructure of polyethylene terephthalate LARS ligament after the reconstruction of anterior cruciate ligament in rabbits. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014;7(9):2511-2518.
[22] JIA Z, XUE C, WANG W, et al. Clinical outcomes of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using LARS artificial graft with an at least 7-year follow-up. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(14):e6568.
[23] YU A, PRENTICE HA, BURFEIND WE, et al. Risk of Infection After Allograft Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: Are Nonprocessed Allografts More Likely to Get Infected? A Cohort Study of Over 10,000 Allografts. Am J Sports Med. 2018;46(4):846-851.
[24] GUO L, YANG L, DUAN XJ, et al. Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with bone-patellar tendon-bone graft: comparison of autograft, fresh-frozen allograft, and gamma-irradiated allograft. Arthroscopy. 2012;28(2):211-217.
[25] CRISTIANI R, ENGSTROM B, EDMAN G, et al. Revision anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction restores knee laxity but shows inferior functional knee outcome compared with primary reconstruction. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27(1):137-145.
[26] O’NEILL DB. Revision arthroscopically assisted anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with previously unharvested ipsilateral autografts. Am J Sports Med. 2004;32(8):1833-1841.
[27] YUMASHEV AV, BALTINA TV, BABASKIN DV. Outcomes after arthroscopic revision surgery for anterior cruciate ligament injuries. Acta Orthop. 2021;92(4):443-447.
[28] MARTIN RK, WASTVEDT S, PAREEK A, et al. Predicting anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction revision: a machine learning analysis utilizing the Norwegian Knee Ligament Register. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2022;104:145-153.
[29] WOLFSON TS, MANNINO B, OWENS BD, et al. Tunnel Management in Revision Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: Current Concepts. Am J Sports Med. 2023;51(2):545-556.
[30] AHN JH, SON DW, AHN JH, et al. Remnant Preservation of the Primary Vertical Graft in Revision Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction. Orthop J Sports Med. 2023;11(3):951749052.
[31] BELK JW, LITTLEFIELD CP, SMITH JH, et al. Autograft Demonstrates Superior Outcomes for Revision Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction When Compared With Allograft: A Systematic Review. Am J Sports Med. 2023:3635465231152232. doi: 10.1177/03635465231152232.
[32] HEFFNER M, CHANG RN, ROYSE KE, et al. Association Between Graft Type and Risk of Repeat Revision Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: A Cohort Study of 1747 Patients. Am J Sports Med. 2023;51(6):1434-1440.
[33] HELITO CP, SOBRADO MF, MOREIRA DSA, et al. The Addition of Either an Anterolateral Ligament Reconstruction or an Iliotibial Band Tenodesis Is Associated With a Lower Failure Rate After Revision Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: A Retrospective Comparative Trial. Arthroscopy. 2023;39(2):308-319.
[34] PAUDEL YR, SOMMERFELDT M, VOAKLANDER D. Incidence and risk factors for revision and contralateral anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: A population-based retrospective cohort study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023;102(20):e33669.
[35] LEON J, FLANIGAN DC, COLATRUGLIO M, et al. Larger Prior Tibial Tunnel Size Is Associated with Increased Failure Risk following Revision Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction. J Knee Surg. 2023;36(8):820-826.
[36] PENG Y, XU JC, FU DJ, et al. [Efficacy comparison between a new generation of artificial ligaments and bone-patellar tendon-bone autograft for anterior cruciate ligament revision]. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2023;103(11):822-828.
[37] SASAKI E, KIMURA Y, SASAKI S, et al. Influence of hamstring tendon and bone-patellar tendon-bone autografts on worsened patient reported outcome measurements in revision anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: Comparing outcomes between primary and revision reconstructions. Asia Pac J Sports Med Arthrosc Rehabil Technol. 2022;29:1-8.
[38] GLASBRENNER J, FISCHER M, RASCHKE MJ, et al. Primary stability of single-stage revision reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament in case of failure of dynamic intraligamentary stabilization depends on implant position during ACL repair. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2022;142(7):1589-1595.
[39] ROSSO F, ROSSI R, FALETTI R, et al. Transepicondylar distance measured on MRI can predict the length of the graft required for different anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction (ACLR) techniques useful for revision surgery. J Orthop Traumatol. 2022;23(1):50.
[40] HAFFAR A, ALI R, MEHTA N, et al. Prior Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Does Not Compromise the Functional Outcomes of Medial Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty Although Revision for Progressive Arthritis May Occur Earlier. J Arthroplasty. 2022;37(2):238-242.
|