中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (13): 1983-1988.doi: 10.12307/2024.161
• 脐带脐血干细胞 umbilical cord blood stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
微电场对人脐带间充质干细胞增殖和成骨分化的影响
刘 中1,李克威1,王 敏2,刘文惠2,张蕾蕾2,郭 松1,钱 晖2,付 强 1
- 1上海交通大学医学院附属第一人民医院骨科,上海市 200080;2江苏大学医学院,江苏省镇江市 212013
Effects of micro-electric field on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells
Liu Zhong1, Li Kewei1, Wang Min2, Liu Wenhui2, Zhang Leilei2, Guo Song1, Qian Hui2, Fu Qiang1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Shanghai General Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200080, China; 2School of Medicine, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212013, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
人脐带间充质干细胞:是从新生儿脐带中提取出来的干细胞,具有较强的增殖能力、分化能力、自我更新能力以及合成并分泌一系列营养因子和细胞因子的能力,具有供给丰富、收集过程无创,低免疫原性、易于体外扩增、无伦理限制等诸多优势,成为组织工程研究和再生医学的最佳来源干细胞之一。微电场:通过一种体外电刺激细胞装置,调节刺激参数,连接电源后可在细胞中形成一种微电场,对细胞进行均匀而稳定的电刺激。
背景:电刺激是一种可用于诱导细胞增殖、分化、凋亡等各种细胞活动的物理方法,诱导干细胞成骨分化将有利于骨的再生。
目的:观察微电场是否可以促进人脐带间充质干细胞的增殖与成骨分化。
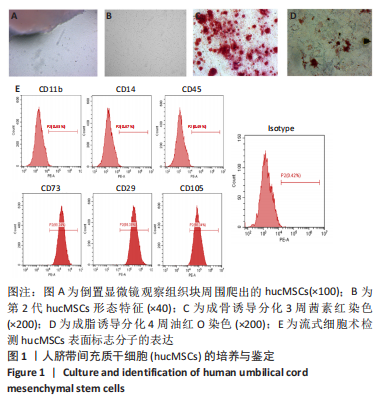
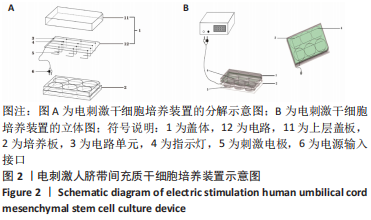
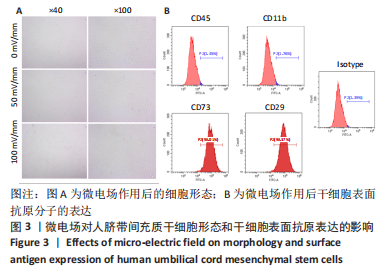
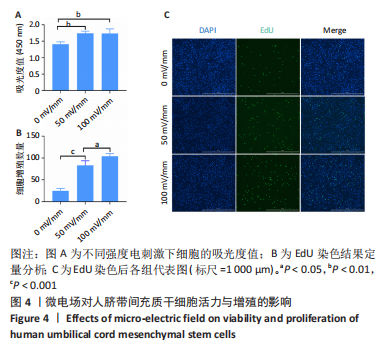
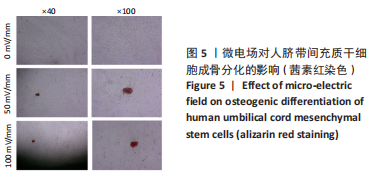
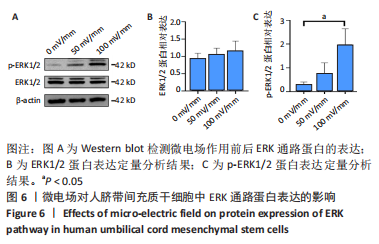
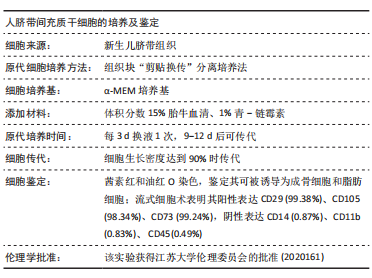
方法:从人新鲜脐带组织获取脐带间充质干细胞,待细胞培养传代至第3代接种于6孔板内,24 h后分别给予0,50,100 mV/mm微电场刺激,刺激频率为每天1 h,连续刺激3 d,然后用显微镜观察细胞生长情况与形态变化,CCK-8和EdU染色法检测细胞的增殖情况,茜素红染色检测细胞的成骨分化能力,Western blot检测ERK通路蛋白的表达水平。结果与结论:①50,100 mV/mm组人脐带间充质干细胞的吸光度值和增殖细胞数目显著高于未刺激组(P < 0.05);②微电场刺激前后人脐带间充质干细胞均能诱导分化为骨细胞,但50,100 mV/mm组的成骨分化速度比未刺激组快;③50,100 mV/mm组的p-ERK1/2蛋白表达高于未刺激组,且100 mV/mm组与未刺激组比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);④微电场促进人脐带间充质干细胞增殖的机制可能是通过促进ERK的磷酸化实现的。
https://orcid.org/0009-0005-2367-7465 (刘中);https://orcid.org/0009-0005-3840-1621 (付强)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: